Abstract
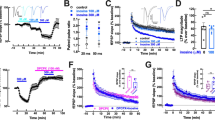
Endo- as well as exogenous adenosine exhibits anticonvulsant action. Participation of individual types of adenosine receptors was studied in present experiments in immature rats. Cortical epileptic afterdischarges were used as a model in rat pups 12, 18 and 25 days old. CCPA, an agonist of A1 adenosine receptors, decreased markedly duration of afterdischarges whereas DPCPX, an antagonist of A1 receptors, exhibited strong proconvulsant action. Action of either drug was best expressed in 12-day-old rats and it decreased with age. Drugs influencing A2A adenosine receptors (agonist CGS21680 and antagonist ZM241385) did not exhibit systematic effects in our model. Motor phenomena accompanying cortical stimulation or epileptic afterdischarge were never influenced by any of the four drugs studied. A1 adenosine receptors are important in the model of cortical seizures, especially in the youngest group studied.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdul-Ghani AS, Attwell PJ, Bradford HF (1997) The protective effect of 2-chloroadenosine against the development of amygdala kindling and on amygdala-kindled seizures. Eur J Pharmacol 326:7–14
Adami M, Bertorelli R, Ferri N, Foddi MC, Ongini E (1995) Effect of repeated administration of selective adenosine A1 and A2A receptor agonists on pentylenetetrazole-induced convulsions in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 294:383–389
Albertson TE, Stark LG, Joy RM, Bowyer JF (1983) Aminophylline and kindled seizures. Exp Neurol 81:703–713
Bernášková K, Mareš P (2000) Proconvulsant effect of aminophylline on cortical epileptic afterdischarges varies during ontogeny. Epilepsy Res 39:183–190
Boison D (2005) Adenosine and epilepsy: from therapeutic rationale to new therapeutic strategies. Neuroscientist 11:25–36
Boison D (2013a) Role of adenosine in status epilepticus: a potential new target? Epilepsia 54(Suppl 6):20–22. doi:10.1111/epi.12268
Boison D (2013b) Adenosine and seizure termination: endogenous mechanisms. Epilepsy Curr 13(1):35–37. doi:10.5698/1535-7511-13.1.35
Browning RA, Nelson BK (1985) Variation in threshold and pattern of electroshock-induced seizures in rats depending on site of stimulation. Life Sci 37:2205–2211
Chu N-S (1981) Caffeine- and aminophylline-induced seizures. Epilepsia 22:85–94
De Sarro G, De Sarro A, Di Paola ED, Bertorelli R (1999) Effects of adenosine receptor agonists and antagonists on audiogenic seizure-sensible DBA/2 mice. Eur J Pharmacol 371:137–145
Dragunow M (1988) Purinergic mechanisms in epilepsy. Progr Neurobiol 31:85–108
Dunwiddie TV, Masino SA (2001) The role and regulation of adenosine in the central nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:31–55
Dunwiddie TV, Worth T (1982) Sedative and anticonvulsant effects of adenosine analogs in mouse and rat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 220:70–76
During MJ, Spencer DD (1992) Adenosine: a potential mediator of seizure arrest and postictal refractoriness. Ann Neurol 32:618–624
Francis A, Fochtmann L (1994) Caffeine augmentation of electroconvulsive seizures. Psychopharmacology 115:320–324
Fredholm BB, Chen J-F, Cunha RA, Svennigsson P, Vaugeois J-M (2005) Adenosine and brain function. Int Rev Neurobiol 63:191–270
Fukuda M, Suzuki Y, Hino H, Morimoto T, Ishii E (2010) Activation of central adenosine A(2A) receptors lowers the seizure threshold of hyperthermia-induced seizure in childhood rats. Seizure 20:156–159
Geiger JD, Labella FS, Nagy JI (1984) Ontogenesis of adenosine receptors in the central nervous system of the rat. Dev Brain Res 13:97–104
Handforth A, Treiman DM (1994) Effect of an adenosine antagonist and an adenosine agonist on status entry and severity in a model of limbic status epilepticus. Epilepsy Res 18:29–42
Hauser WA, Hesdorffer DH (1990) Epilepsy: frequency, causes and consequences. Demos Press, New York
Hung PL, Lai MC, Yang SN, Wang CL, Liou CW, Wu CL, Wang TJ, Huang LT (2002) Aminophylline exacerbates status epilepticus-induced neuronal damages in immature rats: a morphological, motor and behavioral study. Epilepsy Res 49:218–225
Jacobson KA (2009) Introduction to adenosine receptors as therapeutic targets. Handb Exp Pharmacol 193:1–24
Johansson B, Georgiev V, Fredholm BB (1997) Distribution and postnatal ontogeny of adenosine A2A receptors in rat brain: comparison with dopamine receptors. Neuroscience 80:1187–1207
Kagan D, Dlouhá K, Roubalová L, Svoboda P (2012) Ontogenetic development of GABAB-receptor signaling cascade in plasma membranes isolated from rat brain cortex; the number of GABAB-receptors is high already shortly after the birth. Physiol Res 61:629–635
Khan GM, Smolders I, Ebinger G, Michotte Y (2000) Anticonvulsant effect and neurotransmitter modulation of focal and systemic 2-chloroadenosine against the development of pilocarpine-induced seizures. Neuropharmacology 39:2418–2432
Kršek P, Haugvicová R, Mareš P (1998) Age-dependent phenytoin effects on cortical stimulation in rats. Physiol Res 47:143–149
Kubová H, Mareš P, Vorlíček J (1993) Stable anticonvulsant action of benzodiazepines during development in rats. J Pharm Pharmacol 45:807–810
Kubová H, Lanštiaková M, Mocková M, Mareš P, Vorlíček J (1996) Pharmacology of cortical epileptic afterdischarges in rats. Epilepsia 37:336–341
Kulkarni C, David J, Joseph T (1997) Influence of adenosine, dipyridamole, adenosine antagonists and antiepileptic drugs on EEG after discharge following cortical stimulation. Ind J Exp Biol 35:342–347
Li T, Ren G, Lusardi T, Wilz A, Lan JQ, Iwasato T, Itohara S, Simon RP, Boison D (2008) Adenosine kinase is a target for the prediction and prevention of epileptogenesis in mice. J Clin Investig 118:571–582
Lojková-Janečková D, Ng J, Mareš P (2009) Antagonists of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors and cortical afterdischarges in immature rats. Epilepsia 50:2123–2129
Malhotra J, Gupta YK (1997) Effect of adenosine receptor modulation on pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures in rats. Brit J Pharmacol 120:282–288
Marangos PJ, Patel J, Stivers J (1982) Ontogeny of adenosine binding sites in rat forebrain and cerebellum. J Neurochem 39:267–270
Mareš P (2010) Anticonvulsant action of 2-chloroadenosine against pentetrazol-induced seizures in immature rats is due to activation of A1 adenosine receptors. J Neural Transm 117:1269–1277
Mareš P (2013) Proconvulsant action of two GABAB receptor antagonists is age-dependent. Physiol Res 62(Suppl. 1):S109–S114
Mareš P, Kubová H (2006) Electrical stimulation-induced models of seizures. In: Pitkanen A, Schwartzkroin PA, Moshé SL (eds) Models of seizures and epilepsy, Elsevier, Amsterdam, p 153–159
Mareš P, Kubová H, Czuczwar SJ (1994) Aminophylline exhibits convulsant action in rats during ontogenesis. Brain Dev 16:296–300
Mareš P, Haugvicová R, Kubová H (2002) Unequal development of thresholds for various phenomena induced by cortical stimulation in rats. Epilepsy Res 49:35–43
Mareš P, Tichá K, Mikulecká A (2013) Anticonvulsant and behavioral effects of GABAB receptor positive modulator CGP7930 in immature rats. Epilepsy Behav 28:113–120
Morgan PF, Durcan MJ (1990) Caffeine-induced seizures: apparent proconvulsant action of N-ethyl carboxamidoadenosine (NECA). Life Sci 47:1–8
Morgan PF, Montgomery P, Marangos PJ (1987) Ontogenetic profile of the adenosine uptake sites in rat forebrain. J Neurochem 49:852–855
Nehlig A, Daval JL, Debry G (1992) Caffeine and the central nervous system: mechanisms of action, biochemical, metabolic and psychostimulant effects. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 17:139–170
Pagonopoulou O, Efthimiadou A, Asimakopoulos B, Nikolettos NK (2006) Modulatory role of adenosine and its receptors in epilepsy: possible therapeutic approaches. Neurosci Res 56:14–20
Polášek R, Kubová H, Šlamberová R, Mareš P, Vorlíček J (1996) Suppression of cortical epileptic afterdischarges in developing rats by anticonvulsants increasing GABAergic inhibition. Epilepsy Res 25:177–184
Pometlová M, Kubová H, Mareš P (2010) Effects of 2-chloroadenosine on cortical epileptic afterdischarges in immature rats. Pharmacol Rep 62:62–67
Pourgholami MH, Mirnajafi-Zadeh J, Behzadi J (1997) Effect of intraperitoneal and intrahippocampal (CA1) 2-chloroadenosine in amygdaloid kindled rats. Brain Res 751:259–264
Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM, de Mendonça A (2002) Adenosine receptors in the nervous system: pathophysiological implications. Prog Neurobiol 68:377–392
Sanchez RM, Jensen FE (2001) Maturational aspects of epilepsy mechanisms and consequences for the immature brain. Epilepsia 42:577–585
Scheibel ME, Davies TL, Scheibel AB (1976) Ontogenetic development of somatosensory thalamus. I. Morphogenesis. Exp Neurol 51:392–406
Szybala C, Prichard EM, Lusardi TA, Li T, Wilz A, Kaplan DL, Boison D (2009) Antiepileptic effects of silk-based adenosine release in kindled rats. Exp Neurol 219:126–135
Tchekalarova J, Kubová H, Mareš P (2010) Postnatal period of caffeine treatment and time of testing modulate the effect of acute caffeine on cortical epileptic afterdischarges in rats. Brain Res 1356:121–129
Trommer BL, Pasternak JF, Suyeoka GM (1989) Proconvulsant effects of aminophylline during amygdala kindling in developing rats. Dev Brain Res 46:169–172
Turski WA, Cavalheiro EA, Ikonomidou C, Mello LE, Bortolotto ZA, Turski L (1985) Effects of aminophylline and 2-chloroadenosine on seizures produced by pilocarpine in rats: morphological and electroencephalographic correlates. Brain Res 361:309–323
Ukena D, Schudt C, Sybrecht GW (1993) Adenosine receptor-blocking xanthines as inhibitors of phosphodiesterase isozymes. Biochem Pharmacol 45:847–851
Velíšek L, Mareš P (1992) Differential effects of naloxone on postictal depression. Epilepsy Res 12:37–43
Wardas J, Konieczny I, Pietraszek M (2003) Influence of CGS 21680, a selective adenosine A(2A) agonist, on phencyclidine-induced sensorimotor gating deficit and motor behaviour in rats. Psychopharmacology 168:299–306
Wu Y-N, Chen J-JJ, Zhang L-G, Hyland BI (2009) Regulation of hind-limb tone by adenosine A2A receptor in rats. Neuroscience 159:1408–1413
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mareš, P. A1 not A2A adenosine receptors play a role in cortical epileptic afterdischarges in immature rats. J Neural Transm 121, 1329–1336 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1234-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1234-y