Abstract
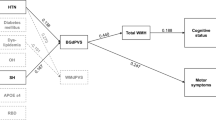
Cognitive dysfunction constitutes a major non-motor manifestation of Parkinson disease (PD), but the mechanisms remain incompletely understood. Neurocirculatory abnormalities such as supine hypertension (SH) and orthostatic hypotension (OH), white matter hyperintensities upon magnetic resonance imaging, and dementia are inter-related in PD, even in patients with early, levodopa-untreated disease. These abnormalities might in turn be associated with carotid atherosclerosis which, by a variety of interacting means could contribute to repeated episodes of cerebral hypo- and hyper-perfusion. We investigated inter-correlations among neurocirculatory and carotid sonographic measurements [intimal-medial thickness (IMT) and wall:lumen ratios (WLR)] in 65 patients with levodopa-untreated, de novo PD who underwent tilt table testing and 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring. Increased mean IMT and WLR were associated with OH and supine and overnight blood pressures. Across individuals the orthostatic fall in systolic pressure was correlated with both IMT and WLR. Since arteriosclerosis would be expected to splint carotid sinus baroreceptors, complex positive interactions among carotid wall thickening, SH, and OH may result in myriad episodes of cerebral hypo- and hyper-perfusion, contributing to microvascular injury and consequently to the cognitive dysfunction attending PD.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biaggioni I, Robertson RM (2002) Hypertension in orthostatic hypotension and autonomic dysfunction. Cardiol Clin 20:291–301
Birkenhäger AM, van den Meiracker AH (2007) Causes and consequences of a non-dipping blood pressure profile. Neth J Med 65:127–131
Bohr DF, Dominiczak AF, Webb RC (1991) Pathophysiology of the vasculature in hypertension. Hypertension 18:III69–III75
Cuspidi C, Sala C, Valerio C, Negri F, Mancia G (2012) Nocturnal hypertension and organ damage in dippers and nondippers. Am J Hypertens 25:869–875
Ejaz AA, Sekhon IS, Munjal S (2006) Characteristic findings on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in a series of patients with Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Intern Med 17:417–420
Ejaz AA, Kazory A, Heinig ME (2007) 24-hour blood pressure monitoring in the evaluation of supine hypertension and orthostatic hypotension. J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 9:952–955
Fedorowski A, Ostling G, Persson M, Struck J, Engström G, Nilsson PM, Hedblad B, Melander O (2012) Orthostatic blood pressure response, carotid intima-media thickness, and plasma fibrinogen in older nondiabetic adults. J Hypertens 30:522–529
Folkow B (1990) “Structural factor” in primary and secondary hypertension. Hypertension 16:89–101
Freeman R, Wieling W, Axelrod FB, Benditt DG, Benarroch E, Biaggioni I, Cheshire WP, Chelimsky T, Cortelli P, Gibbons CH, Goldstein DS, Hainsworth R, Hilz MJ, Jacob G, Kaufmann H, Jordan J, Lipsitz LA, Levine BD, Low PA, Mathias C, Raj SR, Robertson D, Sandroni P, Schatz I, Schondorff R, Stewart JM, van Dijk JG (2011) Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, neurally mediated syncope and the postural tachycardia syndrome. Clin Auton Res 21:69–72
Gibb WR, Lees AJ (1988) The relevance of the Lewy body to the pathogenesis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:745–752
Goldstein DS (2006) Orthostatic hypotension as an early finding in Parkinson disease. Clin Auton Res 16:46–64
Goldstein DS, Eldadah BA, Holmes C, Pechnik S, Moak J, Saleem A, Sharabi Y (2005) Neurocirculatory abnormalities in Parkinson disease with orthostatic hypotension: independence from levodopa treatment. Hypertension 46:1333–1339
Howard G, Sharrett AR, Heiss G, Evans GW, Chambless LE, Riley WA, Burke GL (1993) Carotid artery intimal-medial thickness distribution in general populations as evaluated by B-mode ultrasound. ARIC Investigators. Stroke 24:1297–1304
Jain S, Goldstein DS (2012) Cardiovascular dysautonomia in Parkinson disease: from pathophysiology to pathogenesis. Neurobiol Dis 46:572–580
Kaufmann H (1996) Consensus statement on the definition of orthostatic hypotension, pure autonomic failure and multiple system atrophy. Clin Auton Res 6:125–126
Kim JS, Oh YS, Lee KS, Kim YI, Yang DW, Goldstein DS (2012) Association of cognitive dysfunction with neurocirculatory abnormalities in early Parkinson disease. Neurology 79:1323–1331
Lagi A, Spini S (2010) Clinostatic hypertension and orthostatic hypotension. Clin Cardiol 33:E10–E15
Lohmeier TE, Iliescu R (2011) Chronic lowering of blood pressure by carotid baroreflex activation: mechanisms and potential for hypertension therapy. Hypertension 57:880–886
Lohmeier TE, Iliescu R, Dwyer TM, Irwin ED, Cates AW, Rossing MA (2010) Sustained suppression of sympathetic activity and arterial pressure during chronic activation of the carotid baroreflex. Am J Physiol 299:H402–H409
Mancia G, De Backer G, Dominiczak A, Cifkova R, Fagard R, Germano G, Grassi G, Heagerty AM, Kjeldsen SE, Laurent S, Narkiewicz K, Ruilope L, Rynkiewicz A, Schmieder RE, Struijker Boudier HA, Zanchetti A, Vahanian A, Camm J, De Caterina R, Dean V, Dickstein K, Filippatos G, Funck-Brentano C, Hellemans I, Kristensen SD, McGregor K, Sechtem U, Silber S, Tendera M, Widimsky P, Zamorano JL, Kjeldsen SE, Erdine S, Narkiewicz K, Kiowski W, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Cifkova R, Dominiczak A, Fagard R, Heagerty AM, Laurent S, Lindholm LH, Mancia G, Manolis A, Nilsson PM, Redon J, Schmieder RE, Struijker-Boudier HA, Viigimaa M, Filippatos G, Adamopoulos S, Agabiti-Rosei E, Ambrosioni E, Bertomeu V, Clement D, Erdine S, Farsang C, Gaita D, Kiowski W, Lip G, Mallion JM, Manolis AJ, Nilsson PM, O’Brien E, Ponikowski P, Redon J, Ruschitzka F, Tamargo J, van Zwieten P, Viigimaa M, Waeber B, Williams B, Zamorano JL, The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension, The task force for the management of arterial hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (2007) 2007 Guidelines for the management of arterial hypertension: The Task Force for the Management of Arterial Hypertension of the European Society of Hypertension (ESH) and of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur Heart J 28:1462–1536
Mattace-Raso FU, van der Cammen TJ, Knetsch AM, van den Meiracker AH, Schalekamp MA, Hofman A, Witteman JC (2006) Arterial stiffness as the candidate underlying mechanism for postural blood pressure changes and orthostatic hypotension in older adults: the Rotterdam Study. J Hypertens 24:339–344
Mazza A, Ravenni R, Antonini A, Casiglia E, Rubello D, Pauletto P (2013) Arterial hypertension, a tricky side of Parkinson’s disease: physiopathology and therapeutic features. Neurol Sci 34:621–627
Mlekusch W, Schillinger M, Sabeti S, Nachtmann T, Lang W, Ahmadi R, Mina E (2003) Hypotension and bradycardia after elective carotid artery stenting: frequency and risk factors. J Endovasc Ther 10:851–859
Nakaso K, Yasui K, Kowa H, Kusumi M, Ueda K, Yoshimoto Y, Takeshima T, Sasaki K, Nakashima K (2003) Hypertrophy of IMC of carotid artery in Parkinson’s disease is associated with l-DOPA, homocysteine, and MTHFR genotype. J Neurol Sci 207:19–23
Oh YS, Kim JS, Yang DW, Koo JS, Kim YI, Jung HO, Lee KS (2013) Nighttime blood pressure and white matter hyperintensities in patients with Parkinson disease. Chronobiol Int 30:811–817
Oka H, Yoshioka M, Onouchi K, Morita M, Mochio S, Suzuki M, Hirai T, Ito Y, Inoue K (2007) Characteristics of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. Brain 130:2425–2432
Olsen MH, Wachtell K, Hermann KL, Frandsen E, Dige-Petersen H, Rokkedal J, Devereux RB, Ibsen H (2002) Is cardiovascular remodeling in patients with essential hypertension related to more than high blood pressure? A life substudy. Losartan intervention for endpoint-reduction in hypertension. Am Heart J 144:530–537
Pathak A, Senard JM (2006) Blood pressure disorders during Parkinson’s disease: epidemiology, pathophysiology and management. Expert Rev Neurother 6:1173–1180
Pursiainen V, Haapaniemi TH, Korpelainen JT, Huikuri HV, Sotaniemi KA, Myllylä VV (2002) Circadian heart rate variability in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol 249:1535–1540
Schmidt C, Berg D, Herting B, Prieur S, Junghanns S, Schweitzer K, Globas C, Schöls L, Reichmann H, Ziemssen T (2009) Loss of nocturnal blood pressure fall in various extrapyramidal syndromes. Mov Disord 24:2136–2142
Senard JM, Rai S, Lapeyre-Mestre M, Brefel C, Rascol O, Rascol A, Montastruc JL (1997) Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 63:584–589
Sharabi Y, Goldstein DS (2011) Mechanisms of orthostatic hypotension and supine hypertension in Parkinson disease. J Neurol Sci 310:123–128
Sommer S, Aral-Becher B, Jost W (2011) Nondipping in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2011:897586
Suter OC, Sunthorn T, Kraftsik R, Straubel J, Darekar P, Khalili K, Miklossy J (2002) Cerebral hypoperfusion generates cortical watershed microinfarcts in Alzheimer disease. Stroke 33:1986–1992
Vasunta RL, Kesäniemi YA, Ylitalo A, Ukkola O (2012) Nondipping pattern and carotid atherosclerosis in a middle-aged population: OPERA Study. Am J Hypertens 25:60–66
Velseboer DC, de Haan RJ, Wieling W, Goldstein DS, de Bie RM (2011) Prevalence of orthostatic hypotension in Parkinson’s disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 17:724–729
Yano Y, Kario K (2012) Nocturnal blood pressure and cardiovascular disease: a review of recent advances. Hypertens Res 35:695–701
Acknowledgements
Dr. Goldstein is supported by the Division of Intramural Research of the NINDS.
This research was supported by Seoul St. Mary’s Hospital Clinical Medicine Research Program years of 2013 through the Catholic University of Korea.
Conflict of interest
The Authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JS., Oh, YS., Lee, KS. et al. Carotid artery thickening and neurocirculatory abnormalities in de novo Parkinson disease. J Neural Transm 121, 1259–1268 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1203-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-014-1203-5