Abstract
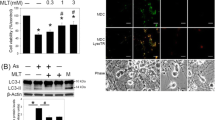
Trimethyltin (TMT) is a triorganotin compound which determines neurodegeneration of specific brain areas particularly damaging the limbic system. Earlier ultrastructural studies indicated the formation of autophagic vacuoles in neurons after TMT intoxication. However, no evaluation has been attempted to determine the role of the autophagic pathway in TMT neurotoxicity. To assess the contribution of autophagy to TMT-induced neuronal cell death, we checked the vulnerability of neuronal cultures to TMT after activation or inhibition of autophagy. Our results show that autophagy inhibitors (3-methyladenine and l-asparagine) greatly enhanced TMT neurotoxicity. Conversely, known activators of autophagy, such as lithium and rapamycin, displayed neuroprotection against this toxic compound. Due to its diverse targets, the action of lithium was complex. When lithium was administered according to a chronic treatment protocol (6 days pretreatment) it was able to rescue both hippocampal and cortical neurons from TMT (or from glutamate toxicity used as reference). This effect was accompanied by an increased phosphorylation of glycogen synthase kinase 3 which is a known target for lithium neuroprotection. If the pre-incubation time was reduced to 2 h (acute treatment protocol), lithium was still able to counteract TMT toxicity in hippocampal but not in cortical neurons. The neuroprotective effect of lithium acutely administered against TMT in hippocampal neurons can be completely reverted by an excess of inositol and is possibly related to the inactivation of inositol monophosphatase, a key regulator of autophagy. These data indicate that TMT neurotoxicity can be dramatically modified, at least in vitro, by lithium addition which seems to act through different mechanisms if acutely or chronically administered.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Besser R, Krämer G, Thümler R, Bohl J, Gutmann L, Hopf HC (1987) Acute trimethyltin limbic-cerebellar syndrome. Neurology 37:945–950
Biederbick A, Kern HF, Elsässer HP (1995) Monodansylcadaverine (MDC) is a specific in vivo marker for autophagic vacuoles. Eur J Cell Biol 66:3–14
Billingsley ML, Yun J, Reese BE, Davidson CE, Buck-Koehntop BA, Veglia G (2006) Functional and structural properties of stannin: roles in cellular growth, selective toxicity, and mitochondrial responses to injury. J Cell Biochem 98:243–250
Bouldin TW, Goines ND, Bagnell RC, Krigman MR (1981) Pathogenesis of trimethyltin neuronal toxicity. Ultrastructural and cytochemical observations. Am J Pathol 104:237–249
Brown AW, Aldridge WN, Street BW, Verschoyle RD (1979) The behavioral and neuropathologic sequelae of intoxication by trimethyltin compounds in the rat. Am J Pathol 97:59–82
Bursch W (2001) The autophagosomal-lysosomal compartment in programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 8:569–581
Bushnell PJ, Angell KE (1992) Effects of trimethyltin on repeated acquisition (learning) in the radial-arm maze. Neurotoxicology 13:429–441
Calderò J, Brunet N, Tarabal O, Piedrafita L, Hereu M, Ayala V, Esquerda JE (2010) Lithuum prevents excitotoxic cell death of motoneuronsin organotypic slice cultures of spinal cord. Neuroscience 165:1353–1369
Cao D, Jiang G, Zhou Q, Yang R (2009) Organotin pollution in China: an overview of the current state and potential health risk. J Environ Manage 90:S16–S24
Chalecka-Franaszek E, Chuang EM (1999) Lithium activates the serine/threonine kinase Akt-1 and suppresses glutamate-induced inhibition of Akt-1 activity in neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:8745–8750
Chang LW, Dyer RS (1983) Trimethyltin induced pathology in sensory neurons. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 5:673–696
Chang LW, Dyer RS (1985) Septotemporal gradients of trimethyltin-induced hippocampal lesions. Neurobehav Toxicol Teratol 7:43–49
Chang LW, Wenger GR, McMillan DE (1984) Neuropathology of trimethyltin intoxication. IV. Changes in the spinal cord. Environ Res 34:123–134
Chiu CT, Chuang DM (2010) Molecular actions and therapeutic potential of lithium in preclinical and clinical studies of CNS disorders. Pharmacol Ther 128:281–304
Eskelinen EL (2005) Maturation of autophagic vacuoles in mammalian cells. Autophagy 1:1–10
Fent K (1996) Ecotoxicology of organotin compounds. Crit Rev Toxicol 26:1–117
Fimia GM, Piacentini M (2010) Regulation of autophagy in mammals and its interplay with apoptosis. Cell Mol Life Sci 67:1581–1588
Goslin K, Banker G (1990) Rapid changes in the distribution of GAP-43 correlate with the expression of neuronal polarity during normal development and under experimental conditions. J Cell Biol 110:1319–1331
Hansen MB, Nielsen SE, Berg K (1989) Re-examination and further development of a precise and rapid dye method for measuring cell growth/cell kill. J Immunol Methods 119:203–210
Høyvik H, Gordon PB, Berg TO, Strømhaug PE, Seglen PO (1991) Inhibition of autophagic-lysosomal delivery and autophagic lactolysis by asparagine. J Cell Biol 113:1305–1312
Hwang CH (2009) The sequential magnetic resonance images of tri-methyl tin leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Sci 30:153–158
Ishikawa K, Kubo T, Shibanoki S, Matsumoto A, Hata H, Asai S (1997) Hippocampal degeneration inducing impairment of learning in rats: model of dementia? Behav Brain Res 83:39–44
Jope RS (2003) Lithium and GSK-3: one inhibitor, two inhibitory actions, multiple outcomes. Trends Pharmacol Sci 24:441–443
Kawada K, Yoneyama M, Nagashima R, Ogita K (2008) In vivo acute treatment with trimethyltin chloride causes neuronal degeneration in the murine olfactory bulb and anterior olfactory nucleus by different cascades in each region. J Neurosci Res 86:1635–1646
Leng Y, Liang MH, Ren M, Marinova Z, Leeds P, Chuang DM (2008) Synergistic neuroprotective effects of lithium and valproic acid or other histone deacetylase inhibitors in neurons: roles of glycogen synthase kinase-3 inhibition. J Neurosci 28:2576–2588
Misiti F, Orsini F, Clementi ME, Lattanzi W, Giardina B, Michetti F (2007) Mitochondrial oxygen consumption inhibition importance for TMT-dependent cell death in undifferentiated PC12 cells. Neurochem Int 52:1092–1099
Mizushima N (2004) Methods for monitoring autophagy. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 36:2491–2502
Mundy WR, Freudenrich TM (2006) Apoptosis of cerebellar granule cells induced by organotin compounds found in drinking water: involvement of MAP kinases. Neurotoxicology 27:71–81
Nishimura T, Imai H, Minabe Y, Sawa A, Kato N (2006) Beneficial effects of FK506 for experimental temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Res 56:386–390
Parthasarathy LK, Seelan RS, Wilson MA, Vadnal RE, Parthasarathy RN (2003) Regional changes in rat brain inositol monophosphatase 1 (IMPase 1) activity with chronic lithium treatment. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 27:55–60
Pasquali L, Busceti CL, Fulceri F, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2010) Intracellular pathways underlying the effects of lithium. Behav Pharmacol 21:473–492
Pendergrass W, Wolf N, Poot M (2004) Efficacy of MitoTracker Green and CMXrosamine to measure changes in mitochondrial membrane potentials in living cells and tissues. Cytometry A 61:162–169
Phiel CJ, Klein PS (2001) Molecular targets of lithium action. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 41:789–813
Philbert MA, Billingsley ML, Reuhl KR (2000) Mechanisms of injury in the central nervous system. Toxicol Pathol 28:43–53
Piver WT (1973) Organotin compounds: industrial applications and biological investigation. Environ Health Perspect 4:61–79
Rubinsztein DC, DiFiglia M, Heintz N, Nixon RA, Qin ZH, Ravikumar B, Stefanis L, Tolkovsky A (2005) Autophagy and its possible roles in nervous system diseases, damage and repair. Autophagy 1:11–22
Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ (2007) Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:304–312
Sarkar S, Rubinsztein DC (2006) Inositol and IP3 levels regulate autophagy: biology and therapeutic speculations. Autophagy 2:132–134
Sarkar S, Floto RA, Berger Z, Imarisio S, Cordenier A, Pasco M, Cook LJ, Rubinsztein DC (2005) Lithium induces autophagy by inhibiting inositol monophosphatase. J Cell Biol 170:1101–1111
Sarkar S, Krishna G, Imarisio S, Saiki S, O’Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2008) A rational mechanism for combination treatment of Huntington’s disease using lithium and rapamycin. Hum Mol Genet 17:170–178
Shawky S, Emons H (1998) Distribution pattern of organotin compounds at different trophic levels of aquatic ecosystems. Chemosphere 36:523–535
Stroikin Y, Dalen H, Lööf S, Terman A (2004) Inhibition of autophagy with 3-methyladenine results in impaired turnover of lysosomes and accumulation of lipofuscin-like material. Eur J Cell Biol 83:583–590
Thompson TA, Lewis JM, Dejneka NS, Severs WB, Polavarapu R, Billingsley ML (1996) Induction of apoptosis by organotin compounds in vitro: neuronal protection with antisense oligonucleotides directed against stannin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 276:1201–1216
Trabucco A, Di Pietro P, Nori SL, Fulceri F, Fumagalli L, Paparelli A, Fornai F (2009) Methylated tin toxicity a reappraisal using rodents models. Arch Ital Biol 147:141–153
Tsujimoto Y, Shimizu S (2005) Another way to die: autophagic programmed cell death. Cell Death Differ 12:1528–1534
Yoo CI, Kim Y, Jeong KS, Sim CS, Choy N, Kim J, Eum JB, Nakajima Y, Endo Y, Kim YJ (2007) A case of acute organotin poisoning. J Occup Health 49:305–310
Zoncu R, Efeyan A, Sabatini DM (2011) mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 12:21–35
Acknowledgments
These studies were supported by grants awarded by PRIN 2008, Università Sapienza (Ricerche Universitarie 2010) to LF.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fabrizi, C., Somma, F., Pompili, E. et al. Role of autophagy inhibitors and inducers in modulating the toxicity of trimethyltin in neuronal cell cultures. J Neural Transm 119, 1295–1305 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0785-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-012-0785-z