Abstract
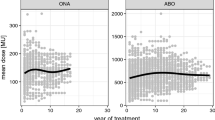
In earlier studies, we have demonstrated the efficacy of albumin-supplemented botulinum toxin type A (ASBTA) in principle. Here, we present long-term data from 106 patients who received ASTBA over 5–10 years for the treatment of cervical dystonia, blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. Vials of Dysport® were diluted in 0.1% albumin solution to a concentration of 25 units/ml. Overall patients and indications, the mean latency to response was 7.1 ± 2.2 days, the mean duration of response was 12.3 ± 3.1 weeks and the mean global clinical improvement (scale 0–3) was 2.6 ± 0.2. Only one patient had neutralizing antibodies against BoNT-A. Side effects were less frequent than known for conventional BoNT-A and generally mild. These findings were confirmed by analysis of data of 71 patients who have been reconverted from ASBTA to conventional dilutions of Dysport® or Botox®. We conclude that long-term treatment with ASBTA is effective, safe and help to reduce costs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoki K (1999) Preclinical update on Botox (botulinum toxin type A)-purified neurotoxin complex relative to other botulinum neurotoxin preparations. Eur J Neurol 6(Suppl 4):S3–S10
Bhidayasiri R, Cardoso F, Truong DD (2006) Botulinum toxin in blepharospasm and oromandibular dystonia: comparing different botulinum toxin preparations. Eur J Neurol 13(Suppl 1):21–29
Bigalke H, Wohlfarth K, Irmer A, Dengler R (2001) Botulinum A toxin: Dysport improvement of biological availability. Exp Neurol 168(1):162–170
Costa J, Espirito-Santo C, Borges A, Ferreira JJ, Coelho M, Moore P, Sampaio C (2005a) Botulinum toxin type A therapy for blepharospasm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD004900
Costa J, Espirito-Santo C, Borges A, Ferreira JJ, Coelho M, Moore P, Sampaio C (2005b) Botulinum toxin type A therapy for hemifacial spasm. Cochrane Database Syst Rev (1):CD004899
D’Costa DF, Abbott RJ (1991) Low dose botulinum toxin in spasmodic torticollis. J R Soc Med 84(11):650–651
Elston JS (1992) The management of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm. J Neurol 239(1):5–8
Giess R, Naumann M, Werner E, Riemann R, Beck M, Puls I, Reiners C, Toyka KV (2000) Injections of botulinum toxin A into the salivary glands improve sialorrhoea in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 69(1):121–123
Goschel H, Wohlfarth K, Frevert J, Dengler R, Bigalke H (1997) Botulinum A toxin therapy: neutralizing and non-neutralizing antibodies—therapeutic consequences. Exp Neurol 147(1):96–102
Greene P, Fahn S, Diamond B (1994) Development of resistance to botulinum toxin type A in patients with torticollis. Mov Disord 9(2):213–217
Haussermann P, Marczoch S, Klinger C, Landgrebe M, Conrad B, Ceballos-Baumann A (2004) Long-term follow-up of cervical dystonia patients treated with botulinum toxin A. Mov Disord 19(3):303–308
Heckmann M, Plewig G (2005) Low-dose efficacy of botulinum toxin A for axillary hyperhidrosis: a randomized, side-by-side, open-label study. Arch Dermatol 141(10):1255–1259
Jankovic J (2004) Treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin. Mov Disord 19(Suppl 8):S109–S115
Jankovic J, Schwartz K (1995) Response and immunoresistance to botulinum toxin injections. Neurology 45(9):1743–1746
Jankovic J, Vuong KD, Ahsan J (2003) Comparison of efficacy and immunogenicity of original versus current botulinum toxin in cervical dystonia. Neurology 60(7):1186–1188
Jitpimolmard S, Tiamkao S, Laopaiboon M (1998) Long term results of botulinum toxin type A (Dysport) in the treatment of hemifacial spasm: a report of 175 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(6):751–757
Jost WH (2006) Other indications of botulinum toxin therapy. Eur J Neurol 13(Suppl 1):65–69
Kessler KR, Skutta M, Benecke R (1999) Long-term treatment of cervical dystonia with botulinum toxin A: efficacy, safety, and antibody frequency. German Dystonia Study Group. J Neurol 246(4):265–274
Laubis-Herrmann U, Fries K, Topka H (2002) Low-dose botulinum toxin-a treatment of cervical dystonia—a double-blind, randomized pilot study. Eur Neurol 47(4):214–221
Marchetti A, Magar R, Findley L, Larsen JP, Pirtosek Z, Ruzicka E, Jech R, Slawek J, Ahmed F (2005) Retrospective evaluation of the dose of Dysport and BOTOX in the management of cervical dystonia and blepharospasm: the REAL DOSE study. Mov Disord 20(8):937–944
Mejia NI, Vuong KD, Jankovic J (2005) Long-term botulinum toxin efficacy, safety, and immunogenicity. Mov Disord 20(5):592–597
Moore AP, Blumhardt LD (1991) A double blind trial of botulinum toxin “A” in torticollis, with one year follow-up. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 54(9):813–816
Naumann M (2001) Evidence-based medicine: botulinum toxin in focal hyperhidrosis. J Neurol 248(Suppl 1):31–33
Poewe W, Deuschl G, Nebe A, Feifel E, Wissel J, Benecke R, Kessler KR, Ceballos-Baumann AO, Ohly A, Oertel W, Kunig G (1998) What is the optimal dose of botulinum toxin A in the treatment of cervical dystonia? Results of a double blind, placebo controlled, dose ranging study using Dysport. German Dystonia Study Group. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 64(1):13–17
Rollnik JD, Matzke M, Wohlfarth K, Dengler R, Bigalke H (2000) Low-dose treatment of cervical dystonia, blepharospasm and facial hemispasm with albumin-diluted botulinum toxin type A under EMG guidance. An open label study. Eur Neurol 43(1):9–12
Suputtitada A, Suwanwela NC (2005) The lowest effective dose of botulinum A toxin in adult patients with upper limb spasticity. Disabil Rehabil 27(4):176–184
Suputtitada A, Phanthumchinda K, Locharernkul C, Suwanwela NC (2004) Hemifacial spasm: results of treatment with low dose botulinum toxin injection. J Med Assoc Thai 87(10):1205–1211
Truong D, Duane DD, Jankovic J, Singer C, Seeberger LC, Comella CL, Lew MF, Rodnitzky RL, Danisi FO, Sutton JP, Charles PD, Hauser RA, Sheean GL (2005) Efficacy and safety of botulinum type A toxin (Dysport) in cervical dystonia: results of the first US randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Mov Disord 20(7):783–791
Van den Bergh P, Francart J, Mourin S, Kollmann P, Laterre EC (1995) Five-year experience in the treatment of focal movement disorders with low-dose Dysport botulinum toxin. Muscle Nerve 18(7):720–729
Viriyavejakul A, Vachalathiti R, Poungvarin N (1998) Botulinum treatment for post-stroke spasticity: low dose regime. J Med Assoc Thai 81(6):413–422
Wohlfarth K, Goschel H, Frevert J, Dengler R, Bigalke H (1997) Botulinum A toxins: units versus units. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 355(3):335–340
Yu YL, Fong KY, Chang CM (1992) Treatment of idiopathic hemifacial spasm with botulinum toxin. Acta Neurol Scand 85(1):55–57
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadi, B., Kollewe, K., Wegener, M. et al. Experience with long-term treatment with albumin-supplemented botulinum toxin type A. J Neural Transm 116, 437–441 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0200-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-009-0200-6