Abstract
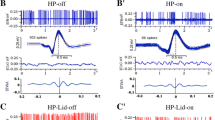
Electrical stimulation of the rat pedunculopontine nucleus (PPTg) (<25 Hz) synchronized firing of subthalamic neurons (STN) with each stimulus, and a continuous irregular activity often preceded recovery of burst discharges in control as well as in 6-hydroxydopamine lesioned animals. Firing was blocked both by increasing frequency of stimulation (>50 Hz) and current intensity (>500 µA). The data suggest that clinically relevant frequencies for PPTg deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease modulate burst discharges in STN neurons.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aravamuthan BR, Muthusamy KA, Stein JF, Aziz TZ, Johansen-Berg H (2007) Topography of cortical and subcortical connections of the human pedunculopontine and subthalamic nuclei. Neuroimage 37:694–705
Bergman H, Wichmann T, Karmon B, DeLong MR (1994) The primate subthalamic nucleus. II. Neuronal activity in the MPTP model of parkinsonism. J Neurophysiol 72:507–520
Bevan MD, Magill PJ, Hallworth NE, Bolam JP, Wilson CJ (2002) Regulation of the timing and pattern of action potential generation in rat subthalamic neurons in vitro by GABA-A IPSPs. J Neurophysiol 87:1348–1362
Breit S, Bouali-Benazzouz R, Popa RC, Gasser T, Benabid AL, Benazzouz A (2007) Effects of 6-hydroxydopamine-induced severe or partial lesion of the nigrostriatal pathway on the neuronal activity of pallido-subthalamic network in the rat. Exp Neurol 205:36–47
Delwaide PJ, Pepin JL, De PV, de Noordhout AM (2000) Projections from basal ganglia to tegmentum: a subcortical route for explaining the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease signs? J Neurol 247(Suppl 2):II75–II81
Dowsey-Limousin P, Fraix V, Benabid AL, Pollak P (2001) Deep brain stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Funct Neurol 16:67–71
Florio T, Scarnati E, Confalone G, Minchella D, Galati S, Stanzione P, Stefani A, Mazzone P (2007) High-frequency stimulation of the subthalamic nucleus modulates the activity of pedunculopontine neurons through direct activation of excitatory fibres as well as through indirect activation of inhibitory pallidal fibres in the rat. Eur J Neurosci 25:1174–1186
Galati S, Scarnati E, Mazzone P, Stanzione P, Stefani A (2008) Deep brain stimulation promotes excitation and inhibition in subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. NeuroReport 19:661–666
Garcia-Rill E, Skinner RD, Miyazato H, Homma Y (2001) Pedunculopontine stimulation induces prolonged activation of pontine reticular neurons. Neuroscience 104:455–465
Garcia L, Audin J, D’Alessandro G, Bioulac B, Hammond C (2003) Dual effect of high-frequency stimulation on subthalamic neuron activity. J Neurosci 23:8743–8751
Hassani OK, Mouroux M, Feger J (1996) Increased subthalamic neuronal activity after nigral dopaminergic lesion independent of disinhibition via the globus pallidus. Neuroscience 72:105–115
Hirsch EC, Graybiel AM, Duyckaerts C, Javoy-Agid F (1987) Neuronal loss in the pedunculopontine tegmental nucleus in Parkinson disease and in progressive supranuclear palsy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5976–5980
Hammond C, Rouzaire-Dubois B, Feger J, Jackson A, Crossman AR (1983) Anatomical and electrophysiological studies on the reciprocal projections between the subthalamic nucleus and nucleus tegmenti pedunculopontine in the rat. Neuroscience 9:41–52
Jellinger K (1988) The pedunculopontine nucleus in Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 51:540–543
Jenkinson N, Nandi D, Miall RC, Stein JF, Aziz TZ (2004) Pedunculopontine nucleus stimulation improves akinesia in a Parkinsonian monkey. Neuroreport 15:2621–2624
Kaneoke Y, Vitek JL (1996) Burst and oscillation as disparate neuronal properties. J Neurosci Methods 68:211–223
Kreiss DS, Mastropietro CW, Rawji SS, Walters JR (1997) The response of subthalamic nucleus neurons to dopamine receptor stimulation in a rodent model of Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 17:6807–6819
Lee HJ, Rye DB, Hallanger AE, Levey AI, Wainer BH (1988) Cholinergic vs. noncholinergic efferents from the mesopontine tegmentum to the extrapyramidal motor system nuclei. J Comp Neurol 275:469–492
Magnin M, Morel A, Jeanmonod D (2000) Single-unit analysis of the pallidum, thalamus and subthalamic nucleus in parkinsonian patients. Neuroscience 96:549–564
Mazzone P, Lozano A, Stanzione P, Galati S, Scarnati E, Peppe A, Stefani A (2005) Implantation of human pedunculopontine nucleus: a safe and clinically relevant target in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 16:1877–1881
Mazzone P, Sposato S, Di Lazzaro V, Scarnati E (2008) Stereotaxic surgery of the nucleus tegmenti pedunculopontinus. Brit J Neurosurg (in press)
Mena-Segovia J, Sims HM, Magill PJ, Bolam JP (2008) Cholinergic brainstem neurons modulate cortical gamma activity during slow oscillations. J Physiol 586:2947–2960
Mesulam MM, Geula C, Bothwell MA, Hersh LB (1989) Human reticular formation: cholinergic neurons of the pedunculopontine and laterodorsal tegmental nuclei and some cytochemical comparisons to forebrain cholinergic neurons. J Comp Neurol 283:611–633
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz M, Rodriguez M, Lanciego JL, Arieda J, Gonzalo N, Olanow CW (2000) Pathophysiology of the basal ganglia in Parkinson’s disease. Trends Neurosci 23:S8–S19
Olszewski J, Baxter D (1982) Cytoarchitecture of the human brain stem. Karger, Basel (Switzerland)
Paxinos G, Watson G (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic Press, San Diego
Plaha P, Gill SS (2005) Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the pedunculopontine nucleus for Parkinson’s disease. Neuroreport 16:1883–1887
Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Rodriguez M, Guridi J, Mewes K, Chockkman V, Vitek J, DeLong MR, Obeso JA (2001) The subthalamic nucleus in Parkinson’s disease: somatotopic organization and physiological characteristics. Brain 124:1777–1790
Ryan LJ, Sanders DJ, Clark KB (1992) Auto- and cross-correlation analysis of subthalamic nucleus neuronal activity in neostriatal- and globus pallidal-lesioned rats. Brain Res 583:253–261
Stefani A, Lozano AM, Peppe A, Stanzione P, Galati S, Tropepi D, Pierantozzi M, Brusa L, Scarnati E, Mazzone P (2007) Bilateral deep brain stimulation of the pedunculopontine and subthalamic nuclei in severe Parkinson’s disease. Brain 130:1596–1607
Zweig RM, Jankel WR, Hedreen JC, Mayeux R, Price DL (1989) The pedunculopontine nucleus in Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol 26:41–46
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from Medtronic Italia, University of L’Aquila (RIA) and overhead from European Community Biomed 2 program to ES. The Authors wish to thank Dr. Salvatore Galati for constructing some density histograms, and Prof. Alessandro Stefani for his comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Capozzo, A., Florio, T., Confalone, G. et al. Low frequency stimulation of the pedunculopontine nucleus modulates electrical activity of subthalamic neurons in the rat. J Neural Transm 116, 51–56 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-008-0155-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-008-0155-z