Summary.
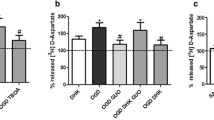
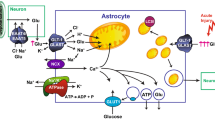
Cysteine uptake is the rate-limiting process in glutathione synthesis. Previously we have shown that the inhibitors of excitatory amino acid transporters (EAATs) significantly enhance glutamate toxicity via depletion of intracellular glutathione. In this study we show evidence that the neuronal glutamate transporter EAAT3 is directly enrolled in cysteine uptake in cultured neurons. Neuronal cysteine uptake was dependent on the extracellular sodium, and was suppressed by EAAT inhibitors. Cysteine uptake was suppressed by extracellular glutamate and aspartate, substrates of EAATs, and not by substrates of cysteine transporters. Intracellular glutathione levels were reduced by EAAT inhibitors, and not by inhibitors of cysteine transporters. Knock down of EAAT3 expression using antisense oligonucleotide significantly reduced cysteine uptake, intracellular glutathione level, and neuronal viability against oxidative stress. These facts indicate that EAAT3 functions as a cysteine transporter, and this function seems to be unique and distinct from cysteine transporters that have been reported.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Himi, T., Ikeda, M., Yasuhara, T. et al. Role of neuronal glutamate transporter in the cysteine uptake and intracellular glutathione levels in cultured cortical neurons. J Neural Transm 110, 1337–1348 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0049-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00702-003-0049-z