Abstract
Background
We aimed to investigate the effects of oxiracetam on cognitive impairment in the early phase of traumatic brain injury (TBI), for which no specific treatment is currently available.
Methods
The in vitro study used a cell injury controller to damage SH-SY5Y cells and evaluate the effect of oxiracetam at a dosage of 100 nM. The in vivo study used a stereotaxic impactor to induce a TBI model in C57BL/6 J mice and analyzed immunohistochemical changes and cognitive function after an intraperitoneal injection of oxiracetam (30 mg/kg/day) for 5 days. The number of mice used in this study was 60. They were divided into three groups (sham, TBI, and TBI with oxiracetam treatment) (20 mice in each group).
Results
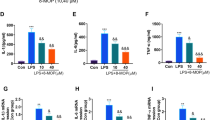
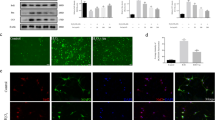
The in vitro study showed that oxiracetam treatment resulted in increased superoxide dismutase (SOD)1 and SOD2 mRNA expression. The mRNA and protein expression of COX-2, NLRP3, caspase-1, and interleukin (IL)-1 β were decreased after oxiracetam treatment, along with decreases in intracellular reactive oxygen species production and apoptotic effects. TBI mice treated with oxiracetam exhibited the loss of fewer cortical damaged lesions, less brain edema, and fewer Fluoro-Jade B (FJB)-positive and terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end-labeling (TUNEL)-positive cells compared to those without oxiracetam treatment. The mRNA and protein expression of COX-2, NLRP3, caspase-1, and IL-1β were decreased significantly after oxiracetam treatment. These inflammation-related markers, which colocalized with Iba-1-positive or GFAP-positive cells after TBI, were also decreased after oxiracetam treatment. TBI mice treated with oxiracetam had a smaller decrease in preference and more latency time than those not treated with oxiracetam, suggesting the amelioration of impaired cognitive impairment.
Conclusions
Oxiracetam may be helpful in restoring cognitive impairment by ameliorating neuroinflammation in the early phase of TBI.




Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Data is available upon possible request.
References
Bae YH, Joo H, Bae J, Hyeon SJ, Her S, Ko E, Choi HG, Ryu H, Hur E, Bu Y, Lee BD (2018) Brain injury induces HIF-1alpha-dependent transcriptional activation of LRRK2 that exacerbates brain damage. Cell Death Dis 9:1125
Baratz R, Tweedie D, Wang JY, Rubovitch V, Luo W, Hoffer BJ, Greig NH, Pick CG (2015) Transiently lowering tumor necrosis factor-alpha synthesis ameliorates neuronal cell loss and cognitive impairments induced by minimal traumatic brain injury in mice. J Neuroinflammation 12:45
Copani A, Genazzani AA, Aleppo G, Casabona G, Canonico PL, Scapagnini U, Nicoletti F (1992) Nootropic drugs positively modulate alpha-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid-sensitive glutamate receptors in neuronal cultures. J Neurochem 58:1199–1204
Ding Y, Fu X, Wang Q, Liu H, Wang H, Wu D (2021) The Complex Interplay between Autophagy and NLRP3 Inflammasome in Renal Diseases. Int J Mol Sci 22
Einarsen CE, van der Naalt J, Jacobs B, Follestad T, Moen KG, Vik A, Haberg AK, Skandsen T (2018) Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury: Clinical Characteristics and a Prognostic Model of 12-Month Outcome. World Neurosurg 114:e1199–e1210
Fordyce DE, Clark VJ, Paylor R, Wehner JM (1995) Enhancement of hippocampally-mediated learning and protein kinase C activity by oxiracetam in learning-impaired DBA/2 mice. Brain Res 672:170–176
Fu C, Zhang X, Zeng Z, Tian Y, Jin X, Wang F, Xu Z, Chen B, Zheng H, Liu X (2020) Neuroprotective Effects of Qingnao Dripping Pills Against Cerebral Ischemia via Inhibiting NLRP3 Inflammasome Signaling Pathway: In Vivo and In Vitro. Front Pharmacol 11:65
Gonzalez-Reyes RE, Nava-Mesa MO, Vargas-Sanchez K, Ariza-Salamanca D, Mora-Munoz L (2017) Involvement of Astrocytes in Alzheimer’s Disease from a Neuroinflammatory and Oxidative Stress Perspective. Front Mol Neurosci 10:427
Harrison JL, Rowe RK, O’Hara BF, Adelson PD, Lifshitz J (2014) Acute over-the-counter pharmacological intervention does not adversely affect behavioral outcome following diffuse traumatic brain injury in the mouse. Exp Brain Res 232:2709–2719
Heneka MT, Kummer MP, Stutz A, Delekate A, Schwartz S, Vieira-Saecker A, Griep A, Axt D, Remus A, Tzeng T, Gelpi E, Halle A, Korte M, Latz E, Golenbock DT (2013) NLRP3 is activated in Alzheimer’s disease and contributes to pathology in APP/PS1 mice. Nature 493:674–678
Jassam YN, Izzy S, Whalen M, McGavern DB, El Khoury J (2017) Neuroimmunology of Traumatic Brain Injury: Time for a Paradigm Shift. Neuron 95:1246–1265
Jeon JP, Kim S, Kim TY, Han SW, Lim SH, Youn DH, Kim BJ, Hong EP, Park CH, Kim J, Ahn JH, Rhim JK, Park JJ, Kim HC, Kang SH (2021) Association Between Copeptin and Six-Month Neurologic Outcomes in Patients With Moderate Traumatic Brain Injury. Front Neurol 12:749110
Kalra S, Malik R, Singh G, Bhatia S, Al-Harrasi A, Mohan S, Albratty M, Albarrati A, TaMBUWALA MM (2022) Pathogenesis and management of traumatic brain injury (TBI): role of neuroinflammation and anti-inflammatory drugs. Inflammopharmacology 30:1153–1166
Kim CK, Kim T, Choi IY, Soh M, Kim D, Kim YJ, Jang H, Yang H, Kim JY, Park H, Park SP, Park S, Yu T, Yoon B, Lee S, Hyeon T (2012) Ceria nanoparticles that can protect against ischemic stroke. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 51:11039–11043
Kuo MF, Grosch J, Fregni F, Paulus W, Nitsche MA (2007) Focusing effect of acetylcholine on neuroplasticity in the human motor cortex. J Neurosci 27:14442–14447
Kuribara H, Tadokoro S (1988) Facilitating effect of oxiracetam and piracetam on acquisition of discrete two-way shuttle avoidance in normal mice. Jpn J Pharmacol 48:494–498
Li JW, Yang DJ, Chen XY, Liang HQ (2013) Protective effect of oxiracetam on traumatic brain injury in rats. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 29:298–300
Li W, Liu H, Jiang H, Wang C, Guo Y, Sun Y, Zhao X, Xiong X, Zhang X, Zhang K, Nie Z, Pu X (2017) (S)-Oxiracetam is the Active Ingredient in Oxiracetam that Alleviates the Cognitive Impairment Induced by Chronic Cerebral Hypoperfusion in Rats. Sci Rep 7:10052
Li XX, Liu SH, Zhuang SJ, Guo SF, Pang SL (2020) Effects of oxiracetam combined with ginkgo biloba extract in the treatment of acute intracerebral hemorrhage: A clinical study. Brain Behav 10:e01661
Malik M, Tlustos P (2022) Nootropics as Cognitive Enhancers: Types, Dosage and Side Effects of Smart Drugs. Nutrients 14
Mochizuki D, Sugiyama S, Shinoda Y (1992) Biochemical studies of oxiracetam (CT-848) on cholinergic neurons. Nihon Yakurigaku Zasshi 99:27–35
Nakata M, Nakagomi T, Maeda M, Nakano-Doi A, Momota Y, Matsuyama T (2017) Induction of Perivascular Neural Stem Cells and Possible Contribution to Neurogenesis Following Transient Brain Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Transl Stroke Res 8:131–143
O’Brien WT, Pham L, Symons GF, Monif M, Shultz SR, McDonald SJ (2020) The NLRP3 inflammasome in traumatic brain injury: potential as a biomarker and therapeutic target. J Neuroinflammation 17:104
Park JS, Kam TI, Lee S, Park H, Oh Y, Kwon SH, Song JJ, Kim D, Kim H, Na DH, Lee KC, Park EJ, Pomper MG, Pletnikova O, Troncoso J, Ko HS, Dawson VL, Dawson TM, Lee S (2021) Blocking microglial activation of reactive astrocytes is neuroprotective in models of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol Commun 9:78
Patil SS, Sunyer B, Hoger H, Lubec G (2009) Evaluation of spatial memory of C57BL/6J and CD1 mice in the Barnes maze, the Multiple T-maze and in the Morris water maze. Behav Brain Res 198:58–68
Salvador E, Burek M, Forster CY (2018) An In Vitro Model of Traumatic Brain Injury. Methods Mol Biol 1717:219–227
Schimmel SJ, Acosta S, Lozano D (2017) Neuroinflammation in traumatic brain injury: A chronic response to an acute injury. Brain Circ 3:135–142
Skotak M, Wang F, Chandra N (2012) An in vitro injury model for SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: effect of strain and strain rate. J Neurosci Methods 205:159–168
Song L, Pei L, Yao S, Wu Y, Shang Y (2017) NLRP3 Inflammasome in Neurological Diseases, from Functions to Therapies. Front Cell Neurosci 11:63
Taverni JP, Seliger G, Lichtman SW (1998) Donepezil medicated memory improvement in traumatic brain injury during post acute rehabilitation. Brain Inj 12:77–80
Tsai YC, Liu CJ, Huang HC, Lin JH, Chen PY, Su YK, Chen CT, Chiu HY (2021) A Meta-analysis of Dynamic Prevalence of Cognitive Deficits in the Acute, Subacute, and Chronic Phases After Traumatic Brain Injury. J Neurosci Nurs 53:63–68
Tsolaki M, Pantazi T, Kazis A (2001) Efficacy of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors versus nootropics in Alzheimer’s disease: a retrospective, longitudinal study. J Int Med Res 29:28–36
Wang C, Li F, Guan Y, Zhu L, Fei Y, Zhang J, Pan Y (2014) Bone marrow stromal cells combined with oxiracetam influences the expression of B-cell lymphoma 2 in rats with ischemic stroke. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 23:2591–2597
Wang J, Sun R, Li Z, Pan Y (2019) Combined bone marrow stromal cells and oxiracetam treatments ameliorates acute cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury through TRPC6. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 51:767–777
Wortzel HS, Arciniegas DB (2012) Treatment of post-traumatic cognitive impairments. Curr Treat Options Neurol 14:493–508
Youn DH, Tran NM, Kim BJ, Kim Y, Jeon JP, Yoo H (2021) Shape effect of cerium oxide nanoparticles on mild traumatic brain injury. Sci Rep 11:15571
Youn DH, Jung H, Tran NM, Jeon JP, Yoo H (2022) The Therapeutic Role of Nanoparticle Shape in Traumatic Brain Injury : An in vitro Comparative Study. J Korean Neurosurg Soc 65:196–203
Yu TS, Kim A, Kernie SG (2015) Donepezil rescues spatial learning and memory deficits following traumatic brain injury independent of its effects on neurogenesis. PLoS ONE 10:e0118793
Zavadenko NN, Guzilova LS (2009) Sequelae of closed craniocerebral trauma and the efficacy of piracetam in its treatment in adolescents. Neurosci Behav Physiol 39:323–328
Zhang H, Jia L, Jia J (2020) Oxiracetam Offers Neuroprotection by Reducing Amyloid beta-Induced Microglial Activation and Inflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front Neurol 11:623
Zheng RZ, Lee KY, Qi ZX, Wang Z, Xu ZY, Wu XH, Mao Y (2022) Neuroinflammation Following Traumatic Brain Injury: Take It Seriously or Not. Front Immunol 13:855701
Funding
This study is supported by research grants from the Samjin Pharmaceuticals (grant no. 6S190101937S000100), the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) grant funded by the Korea government (MSIT) (No.2022R1A5A8019303), and Hallym University Research Fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval
All experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of the participating university (approval no. Hallym2020-51).
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Youn, D.H., Han, S.W., Kim, JT. et al. Oxiracetam alleviates anti-inflammatory activity and ameliorates cognitive impairment in the early phase of traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir 165, 2201–2210 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05674-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-023-05674-8