Abstract
Background
Juvenile pilocytic astrocytomas represent the largest group of pediatric brain tumors. The ideal management for these tumors is early, total surgical resection. To detect and track treatment response, a screening tool is needed to identify patients for surgical evaluation and assess the quality of treatment. The identification of aberrant miRNA profiles in the sera of juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma patients could provide such a screening tool.
Methods
The authors reviewed the serum profiles of 84 oncologically relevant miRNAs in pediatric juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma patients via qPCR screening.
Results
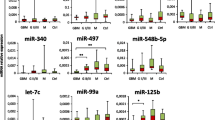
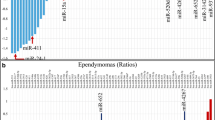
miR-21, miR-15b, miR-23a, and miR-146b were significantly elevated in the sera of JPA patients as compared to non-oncologic controls, oncologic controls, and post-JPA resection samples (p < 0.001, 0.022, 0.034, 0.044). miR-21 had the highest AUC on ROC analysis (AUC > 0.99, sensitivity 75%, specificity 100%). All four miRNAs also correlated well with tumor mural nodule size, though they only poorly correlated with total tumor size, including cystic components (Spearman’s R2: miR-21 91.7 vs 6.9%, miR-15b 86.3 vs 23.1%, miR-23a 85.8 vs 23.0%, miR-146b 59.8 vs 11.9%).
Conclusion
In this small pilot study, pediatric juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma patients had significant elevations in serum miR-21, miR-15b, miR-23a, and miR-146b levels that do not appear to be driven by hydrocephalus or local distortion of the intracranial contents. These alterations correlate with solid tumor component volume and reverse with complete tumor resection, suggesting that this serum miRNA profile may delineate biomarkers for screening and tracking juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma patients. Additional studies, with a larger cohort, are needed to verify these results.






Similar content being viewed by others

References
Areeb Z, Stylli SS, Koldej R, Ritchie DS, Siegal T, Morokoff AP, Kaye AH, Luwor RB (2015) MicroRNA as potential biomarkers in glioblastoma. J Neuro-Oncol 125:237–248. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-015-1912-0
Au Yeung CL, Co NN, Tsuruga T, Yeung TL, Kwan SY, Leung CS, Li Y, Lu ES, Kwan K, Wong KK, Schmandt R, Lu KH, Mok SC (2016) Exosomal transfer of stroma-derived miR21 confers paclitaxel resistance in ovarian cancer cells through targeting APAF1. Nat Commun 7:11150. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11150
Bjur KA, Payne ET, Nemergut ME, Hu D, Flick RP (2017) Anesthetic-related neurotoxicity and neuroimaging in children: a call for conversation. J Child Neurol 32:594–602. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073817691696
Cao Y, Green K, Quattlebaum S, Milam B, Lu L, Gao D, He H, Li N, Gao L, Hall F, Whinery M, Handley E, Ma Y, Xu T, Jin F, Xiao J, Wei M, Smith D, Bornstein S, Gross N, Pyeon D, Song J, Lu SL (2018) Methylated genomic loci encoding microRNA as a biomarker panel in tissue and saliva for head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Clin Epigenetics 10:43. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13148-018-0470-7
Correa-Gallego C, Maddalo D, Doussot A, Kemeny N, Kingham TP, Allen PJ, D'Angelica MI, DeMatteo RP, Betel D, Klimstra D, Jarnagin WR, Ventura A (2016) Circulating plasma levels of MicroRNA-21 and MicroRNA-221 are potential diagnostic markers for primary intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. PLoS One 11:e0163699. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0163699
Dong L, Li Y, Han C, Wang X, She L, Zhang H (2014) miRNA microarray reveals specific expression in the peripheral blood of glioblastoma patients. Int J Oncol 45:746–756. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijo.2014.2459
Feng S, Qian X, Li H, Zhang X (2017) Combinations of elevated tissue miRNA-17-92 cluster expression and serum prostate-specific antigen as potential diagnostic biomarkers for prostate cancer. Oncol Lett 14:6943–6949. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2017.7026
Gai C, Camussi F, Broccoletti R, Gambino A, Cabras M, Molinaro L, Carossa S, Camussi G, Arduino PG (2018) Salivary extracellular vesicle-associated miRNAs as potential biomarkers in oral squamous cell carcinoma. BMC Cancer 18:439. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12885-018-4364-z
Goto G, Hori Y, Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Sakamoto A (2014) Changes in the gene expression levels of microRNAs in the rat hippocampus by sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Mol Med Rep 9:1715–1722. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2014.2038
Grunder E, D'Ambrosio R, Fiaschetti G, Abela L, Arcaro A, Zuzak T, Ohgaki H, Lv SQ, Shalaby T, Grotzer M (2011) MicroRNA-21 suppression impedes medulloblastoma cell migration. Eur J Cancer 47:2479–2490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2011.06.041
Han Z, Zhou X, Li S, Qin Y, Chen Y, Liu H (2017) Inhibition of miR-23a increases the sensitivity of lung cancer stem cells to erlotinib through PTEN/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncol Rep 38:3064–3070. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2017.5938
Hermansen SK, Dahlrot RH, Nielsen BS, Hansen S, Kristensen BW (2013) MiR-21 expression in the tumor cell compartment holds unfavorable prognostic value in gliomas. J Neuro-Oncol 111:71–81. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11060-012-0992-3
Hermansen SK, Nielsen BS, Aaberg-Jessen C, Kristensen BW (2016) miR-21 is linked to glioma angiogenesis: a co-localization study. J Histochem Cytochem 64:138–148. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155415623515
Hsiao YC, Chu LJ, Chen YT, Chi LM, Chien KY, Chiang WF, Chang YT, Chen SF, Wang WS, Chuang YN, Lin SY, Chien CY, Chang KP, Chang YS, Yu JS (2018) Variability assessment of 90 salivary proteins in intraday and interday samples from healthy donors by multiple reaction monitoring-mass spectrometry. Proteomics Clin Appl 12. https://doi.org/10.1002/prca.201700039
Hu X, Chen D, Cui Y, Li Z, Huang J (2013) Targeting microRNA-23a to inhibit glioma cell invasion via HOXD10. Sci Rep 3:3423. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep03423
Ilhan-Mutlu A, Wagner L, Wöhrer A, Furtner J, Widhalm G, Marosi C, Preusser M (2012) Plasma MicroRNA-21 concentration may be a useful biomarker in glioblastoma patients. Cancer Investig 30:615–621. https://doi.org/10.3109/07357907.2012.708071
Ishikawa M, Tanaka S, Arai M, Genda Y, Sakamoto A (2012) Differences in microRNA changes of healthy rat liver between sevoflurane and propofol anesthesia. Anesthesiology 117:1245–1252. https://doi.org/10.1097/ALN.0b013e3182746676
Ivo D'Urso P, Fernando D'Urso O, Damiano Gianfreda C, Mezzolla V, Storelli C, Marsigliante S (2015) miR-15b and miR-21 as circulating biomarkers for diagnosis of glioma. Curr Genomics 16:304–311. https://doi.org/10.2174/1389202916666150707155610
Jiang S, Wang R, Yan H, Jin L, Dou X, Chen D (2016) MicroRNA-21 modulates radiation resistance through upregulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α-promoted glycolysis in non-small cell lung cancer cells. Mol Med Rep 13:4101–4107. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5010
Kan X, Sun Y, Lu J, Li M, Wang Y, Li Q, Liu Y, Liu M, Tian L (2016) Co-inhibition of miRNA-21 and miRNA-221 induces apoptosis by enhancing the p53-mediated expression of pro-apoptotic miRNAs in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Mol Med Rep 13:4315–4320. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5048
Kaur J, Jacobs R, Huang Y, Salvo N, Politis C (2018) Salivary biomarkers for oral cancer and pre-cancer screening: a review. Clin Oral Investig 22:633–640. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00784-018-2337-x
Lee JC, Zhao JT, Clifton-Bligh RJ, Gill A, Gundara JS, Ip JC, Glover A, Sywak MS, Delbridge LW, Robinson BG, Sidhu SB (2013) MicroRNA-222 and microRNA-146b are tissue and circulating biomarkers of recurrent papillary thyroid cancer. Cancer 119:4358–4365. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.28254
Lee TJ, Yoo JY, Shu D, Li H, Zhang J, Yu JG, Jaime-Ramirez AC, Acunzo M, Romano G, Cui R, Sun HL, Luo Z, Old M, Kaur B, Guo P, Croce CM (2017) RNA nanoparticle-based targeted therapy for glioblastoma through inhibition of oncogenic miR-21. Mol Ther https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2016.11.016
Li J, Li M, Gao F, Ge X (2017) Serum microRNA-15a level acts as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Biomark 18:11–17. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-160667
Li J, Zhai XW, Wang HS, Qian XW, Miao H, Zhu XH (2016) Circulating MicroRNA-21, MicroRNA-23a, and MicroRNA-125b as biomarkers for diagnosis and prognosis of Burkitt lymphoma in children. Med Sci Monit 22:4992–5002
Li M, Guan X, Sun Y, Mi J, Shu X, Liu F, Li C (2014) miR-92a family and their target genes in tumorigenesis and metastasis. Exp Cell Res 323:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2013.12.025
Li Y, Wang Y, Yu L, Sun C, Cheng D, Yu S, Wang Q, Yan Y, Kang C, Jin S, An T, Shi C, Xu J, Wei C, Liu J, Sun J, Wen Y, Zhao S, Kong Y (2013) miR-146b-5p inhibits glioma migration and invasion by targeting MMP16. Cancer Lett 339:260–269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.canlet.2013.06.018
Liu AM, Yao TJ, Wang W, Wong KF, Lee NP, Fan ST, Poon RT, Gao C, Luk JM (2012) Circulating miR-15b and miR-130b in serum as potential markers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2:e000825. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2012-000825
Lu Y, Jian MY, Ouyang YB, Han RQ (2015) Changes in rat brain microRNA expression profiles following sevoflurane and Propofol anesthesia. Chin Med J 128:1510–1515. https://doi.org/10.4103/0366-6999.157676
Luo G, Luo W, Sun X, Lin J, Wang M, Zhang Y (2017) MicroRNA-21 promotes migration and invasion of glioma cells via activation of Sox2 and β-catenin signaling. Mol Med Rep 15:187–193. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2016.5971
Mima K, Nishihara R, Nowak JA, Kim SA, Song M, Inamura K, Sukawa Y, Masuda A, Yang J, Dou R, Nosho K, Baba H, Giovannucci EL, Bowden M, Loda M, Giannakis M, Bass AJ, Dranoff G, Freeman GJ, Chan AT, Fuchs CS, Qian ZR, Ogino S (2016) MicroRNA MIR21 and T cells in colorectal cancer. Cancer Immunol Res 4:33–40. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-15-0084
Mima K, Nishihara R, Yang J, Dou R, Masugi Y, Shi Y, da Silva A, Cao Y, Song M, Nowak J, Gu M, Li W, Morikawa T, Zhang X, Wu K, Baba H, Giovannucci EL, Meyerhardt JA, Chan AT, Fuchs CS, Qian ZR, Ogino S (2016) MicroRNA MIR21 (miR-21) and PTGS2 expression in colorectal cancer and patient survival. Clin Cancer Res 22:3841–3848. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-2173
Mohamad M, Wahab NA, Yunus R, Murad NA, Zainuddin ZM, Sundaram M, Mokhtar NM (2016) Roles of microRNA21 and microRNA29a in regulating cell adhesion related genes in bone metastasis secondary to prostate cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev 17:3437–3445
Niu H, Wang K, Zhang A, Yang S, Song Z, Wang W, Qian C, Li X, Zhu Y, Wang Y (2012) miR-92a is a critical regulator of the apoptosis pathway in glioblastoma with inverse expression of BCL2L11. Oncol Rep 28:1771–1777. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2012.1970
Nolen BM, Orlichenko LS, Marrangoni A, Velikokhatnaya L, Prosser D, Grizzle WE, Ho K, Jenkins FJ, Bovbjerg DH, Lokshin AE (2013) An extensive targeted proteomic analysis of disease-related protein biomarkers in urine from healthy donors. PLoS One 8:e63368. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0063368
Nonaka T, Wong DTW (2018) Liquid biopsy in head and neck cancer: promises and challenges. J Dent Res:22034518762071. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518762071
Ogata-Kawata H, Izumiya M, Kurioka D, Honma Y, Yamada Y, Furuta K, Gunji T, Ohta H, Okamoto H, Sonoda H, Watanabe M, Nakagama H, Yokota J, Kohno T, Tsuchiya N (2014) Circulating exosomal microRNAs as biomarkers of colon cancer. PLoS One 9:e92921. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092921
Olivieri F, Spazzafumo L, Bonafè M, Recchioni R, Prattichizzo F, Marcheselli F, Micolucci L, Mensà E, Giuliani A, Santini G, Gobbi M, Lazzarini R, Boemi M, Testa R, Antonicelli R, Procopio AD, Bonfigli AR (2015) MiR-21-5p and miR-126a-3p levels in plasma and circulating angiogenic cells: relationship with type 2 diabetes complications. Oncotarget 6:35372–35382. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.6164
Pellatt DF, Stevens JR, Wolff RK, Mullany LE, Herrick JS, Samowitz W, Slattery ML (2016) Expression profiles of miRNA subsets distinguish human colorectal carcinoma and normal colonic mucosa. Clin Transl Gastroenterol 7:e152. https://doi.org/10.1038/ctg.2016.11
Piepoli A, Tavano F, Copetti M, Mazza T, Palumbo O, Panza A, di Mola FF, Pazienza V, Mazzoccoli G, Biscaglia G, Gentile A, Mastrodonato N, Carella M, Pellegrini F, di Sebastiano P, Andriulli A (2012) Mirna expression profiles identify drivers in colorectal and pancreatic cancers. PLoS One 7:e33663. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0033663
Prabowo AS, van Scheppingen J, Iyer AM, Anink JJ, Spliet WG, van Rijen PC, Schouten-van Meeteren AY, Aronica E (2015) Differential expression and clinical significance of three inflammation-related microRNAs in gangliogliomas. J Neuroinflammation 12:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12974-015-0315-7
Pricola Fehnel K, Duggins-Warf M, Zurakowski D, McKee-Proctor M, Majumder R, Raber M, Han X, Smith ER (2016) Using urinary bFGF and TIMP3 levels to predict the presence of juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma and establish a distinct biomarker signature. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:396–407. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.12.PEDS15448
Qaddoumi I, Sultan I, Gajjar A (2009) Outcome and prognostic features in pediatric gliomas: a review of 6212 cases from the surveillance, epidemiology, and end results database. Cancer 115:5761–5770. https://doi.org/10.1002/cncr.24663
Qu WQ, Liu L, Yu Z (2015) Clinical value of microRNA-23a upregulation in non-small cell lung cancer. Int J Clin Exp Med 8:13598–13603
Quan J, Jin L, Pan X, He T, Lai Y, Chen P, Lin C, Yang S, Zeng H (2017) Oncogenic miR-23a-5p is associated with cellular function in RCC. Mol Med Rep 16:2309–2317. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6829
Rapado-González Ó, Majem B, Muinelo-Romay L, Álvarez-Castro A, Santamaría A, Gil-Moreno A, López-López R, Suárez-Cunqueiro MM (2018) Human salivary microRNAs in Cancer. J Cancer 9:638–649. https://doi.org/10.7150/jca.21180
Regazzo G, Terrenato I, Spagnuolo M, Carosi M, Cognetti G, Cicchillitti L, Sperati F, Villani V, Carapella C, Piaggio G, Pelosi A, Rizzo MG (2016) A restricted signature of serum miRNAs distinguishes glioblastoma from lower grade gliomas. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 35:124. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0393-0
Rui M, Qu Y, Gao T, Ge Y, Feng C, Xu X (2017) Simultaneous delivery of anti-miR21 with doxorubicin prodrug by mimetic lipoprotein nanoparticles for synergistic effect against drug resistance in cancer cells. Int J Nanomedicine 12:217–237. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJN.S122171
Sierzega M, Kaczor M, Kolodziejczyk P, Kulig J, Sanak M, Richter P (2017) Evaluation of serum microRNA biomarkers for gastric cancer based on blood and tissue pools profiling: the importance of miR-21 and miR-331. Br J Cancer 117:266–273. https://doi.org/10.1038/bjc.2017.190
Sun G, Shi L, Yan S, Wan Z, Jiang N, Fu L, Li M, Guo J (2014) MiR-15b targets cyclin D1 to regulate proliferation and apoptosis in glioma cells. Biomed Res Int 2014:687826. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/687826
Sun M, Song J, Zhou Z, Zhu R, Jin H, Ji Y, Lu Q, Ju H (2016) comparison of serum MicroRNA21 and tumor markers in diagnosis of early non-small cell lung cancer. Dis Markers 2016:3823121. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/3823121
Sun Y, Huo C, Qiao Z, Shang Z, Uzzaman A, Liu S, Jiang X, Fan LY, Ji L, Guan X, Cao CX, Xiao H (2018) Comparative proteomic analysis of exosomes and microvesicles in human saliva for lung cancer. J Proteome Res 17:1101–1107. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.7b00770
Tang H, Liu Q, Liu X, Ye F, Xie X, Wu M (2015) Plasma miR-185 as a predictive biomarker for prognosis of malignant glioma. J Cancer Res Ther 11:630–634. https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-1482.146121
Umezu T, Ohyashiki K, Kuroda M, Ohyashiki JH (2013) Leukemia cell to endothelial cell communication via exosomal miRNAs. Oncogene 32:2747–2755. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2012.295
van Scheppingen J, Iyer AM, Prabowo AS, Mühlebner A, Anink JJ, Scholl T, Feucht M, Jansen FE, Spliet WG, Krsek P, Zamecnik J, Buccoliero AM, Giordano F, Genitori L, Kotulska K, Jozwiak S, Jaworski J, Liszewska E, van Vliet EA, Aronica E (2016) Expression of microRNAs miR21, miR146a, and miR155 in tuberous sclerosis complex cortical tubers and their regulation in human astrocytes and SEGA-derived cell cultures. Glia 64:1066–1082. https://doi.org/10.1002/glia.22983
Wang JH, Zhou WW, Cheng ST, Liu BX, Liu FR, Song JQ (2015) Downregulation of sprouty homolog 2 by microRNA-21 inhibits proliferation, metastasis and invasion, however promotes the apoptosis of multiple myeloma cells. Mol Med Rep 12:1810–1816. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2015.3567
Wang W, Li W, Ding M, Yuan H, Yang J, Meng W, Jin E, Wang X, Ma S (2016) Identification of miRNAs as non-invasive biomarkers for early diagnosis of lung cancers. Tumour Biol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5442-y
Wen Y, Han J, Chen J, Dong J, Xia Y, Liu J, Jiang Y, Dai J, Lu J, Jin G, Wei Q, Shen H, Sun B, Hu Z (2015) Plasma miRNAs as early biomarkers for detecting hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Cancer 137:1679–1690. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.29544
Wu Q, Lu Z, Li H, Lu J, Guo L, Ge Q (2011) Next-generation sequencing of microRNAs for breast cancer detection. J Biomed Biotechnol 2011:597145. https://doi.org/10.1155/2011/597145
Wu YR, Qi HJ, Deng DF, Luo YY, Yang SL (2016) MicroRNA-21 promotes cell proliferation, migration, and resistance to apoptosis through PTEN/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in esophageal cancer. Tumour Biol 37:12061–12070. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-016-5074-2
Xing W, Zeng C (2017) A novel serum microRNA-based identification and classification biomarker of human glioma. Tumour Biol 39:1010428317705339. https://doi.org/10.1177/1010428317705339
Yang C, Wang C, Chen X, Chen S, Zhang Y, Zhi F, Wang J, Li L, Zhou X, Li N, Pan H, Zhang J, Zen K, Zhang CY, Zhang C (2013) Identification of seven serum microRNAs from a genome-wide serum microRNA expression profile as potential noninvasive biomarkers for malignant astrocytomas. Int J Cancer 132:116–127. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.27657
Yang W, Yu H, Shen Y, Liu Y, Yang Z, Sun T (2016) MiR-146b-5p overexpression attenuates stemness and radioresistance of glioma stem cells by targeting HuR/lincRNA-p21/β-catenin pathway. Oncotarget 7:41505–41526. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.9214
Ye X, Wei W, Zhang Z, He C, Yang R, Zhang J, Wu Z, Huang Q, Jiang Q (2017) Identification of microRNAs associated with glioma diagnosis and prognosis. Oncotarget 8:26394–26403. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14445
Yong FL, Wang CW, Roslani AC, Law CW (2014) The involvement of miR-23a/APAF1 regulation axis in colorectal cancer. Int J Mol Sci 15:11713–11729. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150711713
Yue X, Lan F, Hu M, Pan Q, Wang Q, Wang J (2016) Downregulation of serum microRNA-205 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for human glioma. J Neurosurg 124:122–128. https://doi.org/10.3171/2015.1.JNS141577
Zhang W, Ni M, Su Y, Wang H, Zhu S, Zhao A, Li G (2016) MicroRNAs in serum exosomes as potential biomarkers in clear-cell renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol Focus https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2016.09.007
Zheng P, Chen L, Yuan X, Luo Q, Liu Y, Xie G, Ma Y, Shen L (2017) Exosomal transfer of tumor-associated macrophage-derived miR-21 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36:53. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-017-0528-y
Zhi F, Shao N, Wang R, Deng D, Xue L, Wang Q, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Xia X, Wang S, Lan Q, Yang Y (2015) Identification of 9 serum microRNAs as potential noninvasive biomarkers of human astrocytoma. Neuro-Oncology 17:383–391. https://doi.org/10.1093/neuonc/nou169
Acknowledgments
The authors would also like to thank Paul Kanev, MD, Jon Martin, MD, and Petronella Stoltz, APRN of the Connecticut Children’s Medical Center Division of Neurosurgery for their participation in screening and accruing patients. We would also like to thank Todd Jensen, MS for his technical assistance with specimen processing.
Funding
The Connecticut Brain Tumor Alliance and the Somberg Family provided financial support in the form of generous gifts in support of pediatric brain cancer research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the Connecticut Children’s Medical Center Institutional Review Board and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Comments
In this study, the authors screen a small number of patients with juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma for a range of miRNAs in their serum using a commercially available qPCR screening tool. Out of a total of 84 oncologically relevant miRNAs, they identify four that are present in the serum at a statistically higher level in patients than in controls with no disease or in patients with ependymoma. They demonstrate that the serum levels fall after resection of the tumour; in one tumour where resection was incomplete, residual miR-21 was present in the serum after surgery. The authors also demonstrate that the volume of the nodule is proportional to the level of these miRNAs in the serum. They suggest that these miRNAs would be useful to screen for pilocytic astrocytomas, to track patients on treatment, and to help distinguish these tumours from other lesions on imaging.This is an important study and builds on recent work seeking to define the role of circulating tumor markers such as cell-free DNA and RNA. Although the patient population studied is small, it forms the basis for more definitive investigation based on larger numbers of patients and controls.
This is an important study and builds on recent work seeking to define the role of circulating tumor markers such as cell-free DNA and RNA. Although the patient population studied is small, it forms the basis for more definitive investigation based on larger numbers of patients and controls.
Kristian Aquilina
London, UK
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Brain Tumours
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bookland, M., Tang-Schomer, M., Gillan, E. et al. Circulating serum oncologic miRNA in pediatric juvenile pilocytic astrocytoma patients predicts mural nodule volume. Acta Neurochir 160, 1571–1581 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3589-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3589-6