Abstract
Background
In patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis, long-term effects of carotid artery stenting (CAS) on blood pressure (BP) changes have not been documented well. We evaluated the effects of CAS on BP and found out its predisposing factors in patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis.
Methods
Between January 2003 and June 2012, a total of 107 patients were recruited, and all subjects met the following inclusion criteria: (1) patients underwent CAS with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis > 50 %; (2) patients had clinical and radiographic data for at least 1 year of follow-up after CAS; and (3) patients had BP measurements at four different time points: pretreatment, post-treatment, 1-month follow-up, and 1-year follow-up. We evaluated the significance of the BP changes between the pretreatment BP and follow-up BPs, and determined its predisposing factors.
Results
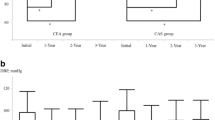
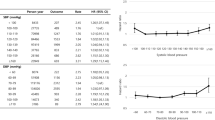
Compared to the mean systolic/diastolic BP value (141.0/87.4 mmHg) at the pretreatment BP, the follow-up BPs were significantly decreased after CAS (120.5/74.5, 126.2/76.9, and 129.2/79.0 mmHg at the post-treatment, the 1-month follow-up, and the 1-year follow-up, respectively [p < 0.01]). The location of the stenosis (odds ratio = 1.856, 95 % confidence interval, 1.388 to 5.589; p = 0.003) and hypertension (odds ratio = 1.627, 95 % confidence interval, 1.101 to 3.757; p = 0.014) were independent predisposing factors for BP-lowering effects of CAS on multivariate analysis.
Conclusions
For patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis, CAS might have a BP-lowering effect at the 1-year follow-up, especially in patients with hypertension or the stenosis at body lesions.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dangas G (2003) Hypotension after carotid revascularization. Stroke 34:2581–2582
Chung J, Kim BM, Paik HK, Hyun D-K, Park H (2012) Effects of carotid artery stenosis treatment on blood pressure. J Neurosurg 117:755–760
Furie KL, Kasner SE, Adams RJ, Albers GW, Bush RL, Fagan SC, Halperin JL, Johnston SC, Katzan I, Kernan WN, Mitchell PH, Ovbiagele B, Palesch YY, Sacco RL, Schwamm LH, Wassertheil-Smoller S, Turan TN, Wentworth D (2011) Guidelines for the prevention of stroke in patients with stroke or transient ischemic attack: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 42:227–276
Lewington S, Clarke R, Qizilbash N, Peto R, Collins R (2002) Prospective Studies Collaboration. Age-specific relevance of usual blood pressure to vascular mortality: a meta-analysis of individual data for one million adults in 61 prospective studies. Lancet 360:1903–1913
Nandalur KR, Baskurt E, Hagspiel KD, Finch M, Phillips CD, Bollampally SR, Kramer CM (2006) Carotid artery calcification on CT may independently predict stroke risk. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:547–552
Park ST, Kim JK, Yoon KH, Park SO, Park SW, Kim JS, Kim SJ, Suh DC (2010) Atherosclerotic carotid stenoses of apical versus body lesions in high-risk carotid stenting patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 31:1106–1112
Suh DC, Kim JL, Kim EH, Kim JK, Shin JH, Hyun DH, Lee HY, Lee DH, Kim JS (2012) Carotid baroreceptor reaction after stenting in 2 locations of carotid bulb lesions of different embryologic origin. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 33:977–981
Altinbas A, Algra A, Brown MM, Featherstone RL, Kappelle LJ, de Borst GJ, Mali WP, van der Worp HB (2011) Effects of carotid endarterectomy or stenting on blood pressure in the International Carotid Stenting Study (ICSS). Stroke 42:3491–3496
Lawes CM, Bennett DA, Feigin VL, Rodgers A (2004) Blood pressure and stroke: an overview of published reviews. Stroke 35:776–785
Turnbull F (2003) Effects of different blood-pressure-lowering regimens on major cardiovascular events: results of prospectively-designed overviews of randomised trials. Lancet 362:1527–1535
Yusuf S, Sleight P, Pogue J, Bosch J, Davies R, Dagenais G (2000) Effects of an angiotensin-converting-enzyme inhibitor, ramipril, on cardiovascular events in high-risk patients. N Engl J Med 342:145–153
Begshaw RJ, Barrer SJ (1987) Effects of angioplasty upon carotid sinus mechanical properties and blood pressure control in the dog. Neurosurgery 21:324–330
Nonaka T, Oka S, Miyata K, Mikami T, Koyanagi I, Houkin K, Yoshifuji K, Imaizumi T (2005) Prediction of prolonged postprocedural hypotension after carotid artery stenting. Neurosurgery 57:472–277
Doux JD, Yun AJ (2006) The link between carotid artery disease and ischemic stroke may be partially attributable to autonomic dysfunction and failure of cerebrovascular autoregulation triggered by Darwinian maladaptation of the carotid baroreceptors and chemoreceptors. Med Hypotheses 66:176–181
Qureshi AI, Luft AR, Sharma M, Janardhan V, Lopes DK, Khan J, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN (1999) Frequency and determinants of postprocedural hemodynamic instability after carotid angioplasty and stenting. Stroke 30:2086–2093
Kameda Y (2009) Hoxa3 and signaling molecules involved in aortic arch patterning and remodeling. Cell Tissue Res 336:165–178
Calhoun DA, Jones D, Textor S, Goff DC, Murphy TP, Toto RD, White A, Cushman WC, White W, Sica D, Ferdinand K, Giles TD, Falkner B, Carey RM (2008) Resistant hypertension: diagnosis, evaluation, and treatment: a scientific statement from the American Heart Association Professional Education Committee of the Council for High Blood Pressure Research. Circulation 117:e510–526
Zanchetti A (1997) The role of ambulatory blood pressure monitoring in clinical practice. Am J Hypertens 10:1069–1080
Stergiou GS, Zourbaki AS, Skeva II, Mountokalakis TD (1998) White coat effect detected using self-monitoring of blood pressure at home: comparison with ambulatory blood pressure. Am J Hypertens 11:820–827
Omvik P, Gerhardsen G (2003) The Norwegian office-, home-, and ambulatory blood pressure study (NOHA). Blood Press 12:211–219
Verberk WJ, Kroon AA, Kessels AG, de Leeuw PW (2005) Home blood pressure measurement: a systematic review. J Am Coll Cardiol 46:743–751
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chung, J., Kim, Y.B., Hong, CK. et al. Blood pressure-lowering effect of carotid artery stenting in patients with symptomatic carotid artery stenosis. Acta Neurochir 156, 69–75 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1928-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-013-1928-1