Abstract
Background
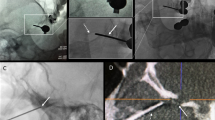
Radiofrequency rhizotomy of the Gasserian ganglion for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia via percutaneous cannulation of the foramen ovale is facilitated by various localization modalities. In our preliminary study, we described the feasibility of computed tomography (CT) using an integrated neuronavigation system to cannulate the foramen ovale.
Methods
Analysis was performed on 42 consecutive patients who underwent cannulation of the foramen ovale for radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy guided by CT using an integrated neuronavigation system. The reproducibility and safety of the neuronavigation-guided procedure were evaluated.
Results
Overall, the average dimension of the foramen ovale was 7.1 (1.5) × 4.7 (1.1) mm, and it was successfully cannulated by neuronavigation guidance in 31 (73.8%) patients with a mean cannulation time of 3.1 (0.7) min and an overall procedure time of 68.2 (16.4) min. The remaining 11 (26.2%) patients required subsequent CT guidance for successful puncture of the foramen ovale.
Conclusions
These data demonstrate that neuronavigation-guided cannulation of the foramen ovale can be executed both quickly and safely on an outpatient basis. Additionally, the use of CT with integrated neuronavigation technology provides superior visual-spatial information compared to conventional fluoroscopy, the process of CT scanning, object planning, and neuronavigation-guided intervention can be completed in the same locale, and its application is easy to master and has the potential to enhance procedure tolerability of awake patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agazzi S, Chang S, Drucker MD, Youssef AS, Van Loveren HR (2009) Sudden blindness as a complication of percutaneous trigeminal procedures: mechanism analysis and prevention. J Neurosurg 110:638–641
Arrese I, Lobato RD, Alén JF, Lagares A, Miranda P (2005) Acute subdural and intratemporal hematoma as a complication of percutaneous compression of the Gasserian ganglion for trigeminal neuralgia. Neurocirugia (Astur) 16:177–182
Bale RJ, Laimer I, Martin A, Schlager A, Mayr C, Rieger M, Czermak BV, Kovacs P, Widmann G (2006) Frameless stereotactic cannulation of the foramen ovale for ablative treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Neurosurgery 59:394–401
Brown JA (1997) Direct carotid cavernous fistula after trigeminal balloon microcompression gangliolysis: case report. Neurosurgery 40:886
Daszkiewicz P, Zwoliński P, Roszkowski M (2009) Neuronavigation-guided implantation of foramen ovale electrodes in a child. J Neurosurg Pediatr 4:47–49
Egan RA, Pless M, Shults WT (2001) Monocular blindness as a complication of trigeminal radiofrequency rhizotomy. Am J Ophthalmol 131:237–240
Grunert P, Glaser M, Kockro R, Boor S, Oertel J (2010) An alternative projection for fluoroscopic-guided needle insertion in the foramen ovale: technical note. Acta Neurochir 152:1785–1792
Gusmão S, Magaldi M, Arantes A (2003) Trigeminal radiofrequency rhizotomy for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia: results and technical modification. Arq Neuropsiquiatr 61:434–440
Gusmão S, Olivera M, Tazinaffo U, Honey CR (2003) Percutaneous trigeminal nerve radiofrequency rhizotomy guided by computerized tomography fluoroscopy: technical note. J Neurosurg 99:785–786
Hakanson S (1981) Trigeminal neuralgia treated by the injection of glycerol into the trigeminal cistern. Neurosurgery 9:638–646
Harrigan MR, Chandler WF (1998) Abducens nerve palsy after radiofrequency rhizolysis for trigeminal neuralgia: case report. Neurosurgery 43:623–625
Haertel F (1912) Die Leitungsanästhesie und Injektionsbehandlung des Ganglion Gasseri und der Trigeminusstaemme. Arch Klin Chir 100:193–292, Ger
Ivanov M, Brodbelt A, Ianovici N, Ciurea AV, Poeata I, Gramada FM (2010) Neuronavigation in the percutaneous treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Technical note. Rom Neurosurg 27:166–170
James EA, Kibbler CC, Gillespie SH (1995) Meningitis due to oral streptococci following percutaneous glycerol rhizotomy of the trigeminal ganglion. J Infect 31:55–57
Kanpolat Y, Savas A, Bekar A, Berk C (2001) Percutaneous controlled radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for the treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia: 25-year experience with 1,600 patients. Neurosurgery 48:524–532
Kaplan M, Erol FS, Ozveren MF, Topsakal C, Sam B, Tekdemir I (2007) Review of complications due to foramen ovale puncture. J Clin Neurosci 14:563–568
Koizuka S, Saito S, Kubo K, Tomioka A, Takazawa T, Sakurazawa S, Goto F (2006) Percutaneous radio-frequency mandibular nerve rhizotomy guided by CT fluoroscopy. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 27:1647–1648
Koizuka S, Saito S, Sekimoto K, Tobe M, Obata H, Koyama Y (2009) Percutaneous radio-frequency thermocoagulation of the Gasserian ganglion guided by high-speed real-time CT fluoroscopy. Neuroradiology 51:563–566
Koizuka S, Saito S, Tobe M, Sekimoto K, Obata H, Koyama Y (2010) Technical communication: percutaneous radiofrequency mandibular nerve rhizotomy guided by high-speed real-time computed tomography fluoroscopy. Anesth Analg 111:763–767
Kuether TA, O'Neill OR, Nesbit GM, Barnwell SL (1996) Direct carotid cavernous fistula after trigeminal balloon microcompression gangliolysis: case report. Neurosurgery 39:853–855
Langford P, Holt ME, Danks RA (2005) Cavernous sinus fistula following percutaneous balloon compression of the trigeminal ganglion. Case report. J Neurosurg 103:176–178
Liu M, Wu CY, Liu YG, Wang HW, Meng FG (2005) Three-dimensional computed tomography-guided radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy for treatment of idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia. Chin Med Sci J 20:206–209
Mandat T, Brozyna B, Krzymanski G, Podgorski JK (2009) An image-guided, noninvasive method of cannulation of the foramen ovale for awake, percutaneous radiofrequency rhizotomy. J Neurosurg 111:1223–1225
Moraci A, Buonaiuto C, Punzo A, Parlato C, Amalfi R (1992) Trigeminal neuralgia treated by percutaneous thermocoagulation. Comparative analysis of percutaneous thermocoagulation and other surgical procedures. Neurochirurgia (Stuttg) 35:48–53
Pagni CA, Fariselli L, Zeme S (2008) Trigeminal neuralgia. Non-invasive techniques versus microvascular decompression. It is really available any further improvement? Acta Neurochir Suppl 101:27–33
Patil AA (2010) Stereotactic approach to the trigeminal ganglion using a stereotactic frame and intraoperative computed tomography scans: technical note. Stereotact Funct Neurosurg 88:277–280
Rath GP, Dash HH, Bithal PK, Goyal V (2009) Intracranial hemorrhage after percutaneous radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy. Pain Pract 9:82–84
Savas A, Sayin M (2010) Subarachnoid bleeding into the superior cerebellopontine cistern after radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy: case report. Acta Neurochir 152:561–562
Taha J (2004) Trigeminal neuralgia: percutaneous procedures. Semin Neurosurg 15:115–134
Tatli M, Satici O, Kanpolat Y, Sindou M (2008) Various surgical modalities for trigeminal neuralgia: literature study of respective long-term outcomes. Acta Neurochir 150:243–255
Torroba L, Moreno S, Lorenzana L, Buzon L (1987) Purulent meningitis after percutaneous radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 50:1081–1082
Ugur HC, Savas A, Elhan A, Kanpolat Y (2004) Unanticipated complication of percutaneous radiofrequency trigeminal rhizotomy: rhinorrhea: report of three cases and a cadaver study. Neurosurgery 54:1522–1524
Xu SJ, Zhang WH, Chen T, Wu CY, Zhou MD (2006) Neuronavigator-guided percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation in the treatment of intractable trigeminal neuralgia. Chin Med J (Engl) 119:1528–1535
Yang Y, Shao Y, Wang H, Liu Y, Zhu S, Wu C (2007) Neuronavigation-assisted percutaneous radiofrequency thermocoagulation therapy in trigeminal neuralgia. Clin J Pain 23:159–164
Acknowledgments
We thank Yi-Chen Lee for help in performing this operative technique.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This work has not been presented nor is it under evaluation for publication elsewhere.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lin, M.HC., Lee, MH., Wang, TC. et al. Foramen ovale cannulation guided by intra-operative computed tomography with integrated neuronavigation for the treatment of trigeminal neuralgia. Acta Neurochir 153, 1593–1599 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1009-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-011-1009-2