Abstract
Purpose
We present the results of the visualisation of radial oxygen gradients in rats’ cortices and their potential use in neurocritical management.
Methods
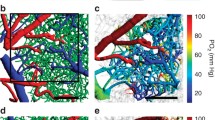
PO2 maps of the cortex of ten sedated, intubated and controlled ventilated Wistar rats were obtained with a camera (SensiMOD, PCO, Kelheim, Germany). Those pictures were analysed and edited by a custom-made software. A virtual matrix, designed to evaluate the cortical O2 partial pressure, was placed vertically to the artery under investigation, and afterwards multiple regions of interest were measured (width 10 pixels, length 15–50 pixels). The results showed a map of the cerebral oxygenation, which allowed us to calculate radial oxygen gradients over arterioles. Three groups were defined according to the level of the arterial pO2: PaO2 < 80, PaO2 80–120 and PaO2 > 120. Gradients were analysed from the middle of the vessel to its border (1), from the border into the parenchyma next to the vessel (2) and a combination of both (3).
Results
Gradient 1 showed significantly different cortical pO2 values between the three different groups. The mean pO2 values were 2.62, 5.29 and 5.82 mmHg/mm. Gradient 2 measured 0.56, 0.90 and 1.02 mmHg/mm respectively. Gradient 3 showed significant results between the groups with values of 3.18, 6.19 and 6.84 mmHg/mm.
Conclusion
Using these gradients, it is possible to describe and compare the distribution of oxygen to the brain parenchyma. With the presented technique, it is possible to detect pO2 changes in the oxygen supply of the brain cortex.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Babilas P, Liebsch G, Schacht V, Klimant I, Wolfbeis OS, Szeimies RM, Abels C (2005) In vivo phosphorescence imaging of pO2 using planar oxygen sensors. Microcirculation 12:477–487
Doppenberg EM, Zauner A, Bullock R, Ward JD, Fatouros PP, Young HF (1998) Correlations between brain tissue oxygen tension, carbon dioxide tension, pH, and cerebral blood flow—a better way of monitoring the severely injured brain? Surg Neurol 49:650–654
Erecinska M, Silver IA (2001) Tissue oxygen tension and brain sensitivity to hypoxia. Respir Physiol 128:263–276
Haitsma IK, Maas AI (2002) Advanced monitoring in the intensive care unit: brain tissue oxygen tension. Curr Opin Crit Care 8:115–120
Hartmann P, Trettnak W (1996) Effects of polymer matrices on calibration functions of luminescent oxygen sensors based on porphyrin ketone complexes. Anal Chem 68:2615–2620
Hlatky R, Valadka AB, Gopinath SP, Robertson CS (2008) Brain tissue oxygen tension response to induced hyperoxia reduced in hypoperfused brain. J Neurosurg 108:53–58
Holst G, Kohls O, Klimant I, Konig B, Kuhl M, Richter T (1998) A modular luminescence lifetime imaging system for mapping oxygen distribution in biological samples. Sens Actuators B 51:163–170
Jaeger M, Soehle M, Meixensberger J (2005) Brain tissue oxygen (PtiO2): a clinical comparison of two monitoring devices. Acta Neurochir Suppl 95:79–81
Jaeger M, Soehle M, Schuhmann MU, Winkler D, Meixensberger J (2005) Correlation of continuously monitored regional cerebral blood flow and brain tissue oxygen. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 147:51–56, discussion 56
Johnston AJ, Steiner LA, Chatfield DA, Coles JP, Hutchinson PJ, Al-Rawi PG, Menon DK, Gupta AK (2004) Effect of cerebral perfusion pressure augmentation with dopamine and norepinephrine on global and focal brain oxygenation after traumatic brain injury. Intensive Care Med 30:791–797
Johnston AJ, Steiner LA, Gupta AK, Menon DK (2003) Cerebral oxygen vasoreactivity and cerebral tissue oxygen reactivity. Br J Anaesth 90:774–786
Lang EW, Mulvey JM, Mudaliar Y, Dorsch NW (2007) Direct cerebral oxygenation monitoring—a systematic review of recent publications. Neurosurg Rev 30:99–106, discussion 106–107
Liebsch G, Klimant I, Frank B, Holst G, Wolfbeis OS (2000) Luminescence lifetime imaging of oxygen, pH, and carbon dioxide distribution using optical sensors. Appl Spectrosc 54:548–559
Liebsch G, Klimant I, Krause C, Wolfbeis OS (2001) Fluorescent imaging of pH with optical sensors using time domain dual lifetime referencing. Anal Chem 73:4354–4363
Liu KJ, Bacic G, Hoopes PJ, Jiang J, Du H, Ou LC, Dunn JF, Swartz HM (1995) Assessment of cerebral pO2 by EPR oximetry in rodents: effects of anesthesia, ischemia, and breathing gas. Brain Res 685:91–98
Meixensberger J, Vath A, Jaeger M, Kunze E, Dings J, Roosen K (2003) Monitoring of brain tissue oxygenation following severe subarachnoid hemorrhage. Neurol Res 25:445–450
Mulvey JM, Dorsch NW, Mudaliar Y, Lang EW (2004) Multimodality monitoring in severe traumatic brain injury: the role of brain tissue oxygenation monitoring. Neurocrit Care 1:391–402
Rose JC, Neill TA, Hemphill JC 3rd (2006) Continuous monitoring of the microcirculation in neurocritical care: an update on brain tissue oxygenation. Curr Opin Crit Care 12:97–102
Rosenthal G, Hemphill JC 3rd, Sorani M, Martin C, Morabito D, Obrist WD, Manley GT (2008) Brain tissue oxygen tension is more indicative of oxygen diffusion than oxygen delivery and metabolism in patients with traumatic brain injury. Crit Care Med 36:1917–1924
Scheufler KM, Rohrborn HJ, Zentner J (2002) Does tissue oxygen-tension reliably reflect cerebral oxygen delivery and consumption? Anesth Analg 95:1042–1048, table of contents
Tsai AG, Johnson PC, Intaglietta M (2003) Oxygen gradients in the microcirculation. Physiol Rev 83:933–963
Valadka AB, Gopinath SP, Contant CF, Uzura M, Robertson CS (1998) Relationship of brain tissue pO2 to outcome after severe head injury. Crit Care Med 26:1576–1581
van den Brink WA, van Santbrink H, Steyerberg EW, Avezaat CJ, Suazo JA, Hogesteeger C, Jansen WJ, Kloos LM, Vermeulen J, Maas AI (2000) Brain oxygen tension in severe head injury. Neurosurgery 46:868–876, discussion 876–868
van Santbrink H, van den Brink WA, Steyerberg EW, Carmona Suazo JA, Avezaat CJ, Maas AI (2003) Brain tissue oxygen response in severe traumatic brain injury. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 145:429–438, discussion 438
Vovenko E (1999) Distribution of oxygen tension on the surface of arterioles, capillaries and venules of brain cortex and in tissue in normoxia: an experimental study on rats. Pflugers Arch 437:617–623
Warnat J, Liebsch G, Stoerr EM, Brawanski A, Woertgen C (2008) Simultaneous imaging of cortical partial oxygen pressure and anatomic structures using a transparent optical sensor foil. J Neurosurg Anesthesiol 20:116–123
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Galler, M., Moritz, S., Liebsch, G. et al. Radial oxygen gradients over rat cortex arterioles. Acta Neurochir 152, 2175–2182 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0777-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-010-0777-4