Abstract
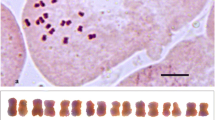
The present study is part of our research project on cytomorphology of gamopetalous flora of Kashmir Himalaya, a zone with rich biodiversity. Out of 134 species of Gamopetalae meiotically investigated, chromosome numbers for 30 accessions belonging to 17 species and six families are new or varied reports. Euphrasia paucifolia (n = 22), Lactuca decipiens (n = 8), Saussurea albescens (n = 17), Saussurea roylei (n = 16), Saussurea taraxacifolia (n = 16) and Veronica deltigera (n = 8) are first cytological reports for these species. Anaphalis nepalensis (n = 28), Codonopsis rotundifolia (n = 16) and Hieracium vulgatum (n = 27) are new euploid chromosome reports for these species suggesting potential speciation through chromosomal evolution. Besides, Androsace mucronifolia (n = 10), A. sempervivoides (n = 10), Cicerbita lessertiana (n = 8), Dracocephalum nutans (n = 5), Erigeron patentisquama (n = 9), Galium pauciflorum (n = 11), Onopordum acanthium (n = 17) and Xanthium spinosum (n = 8) are the first chromosome reports to Indian accessions of the species. Out of the 17 species, 9 species (52.9 %) viz. A. nepalensis, C. lessertiana, C. rotundifolia, D. nutans, E. patentisquama, Euphrasia paucifolia, L. decipiens, O. acanthium and V. deltigera show abnormal meiosis/microsporogenesis of one or other type, thereby leading to pollen anomalies.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beadle GW (1932) A gene in zea mays for failure of cytokinesis during meiosis. Cytologia 3:142–155
Bellucci M, Roscini C, Mariani A (2003) Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of Medicago sativa L. J Hered 94:512–516
Budantzev AL (1986) Chromosome numbers and some problems in the systematics of the genus Dracocephalum (Lamiaceae). Bot Zhur 71:1211–1217
Comai L (2005) The advantages and disadvantages of being polyploid. Nat Rev Genet 6(11):836–846
Dar GH, Bhagat RC, Khan MA (2002) Biodiversity of the Kashmir Himalaya. Anmol Publications, New Delhi. ISBN 81-261-1117-8
Darlington CD, Wylie AP (1955) Chromosome altas of flowering plants. George Allen and Unwin Ltd., London
Dmitrieva SA (1987) Kariologicheskaja kharakteristika nekotorykh predstaviteley sem. slozhnocvetnykh (Asteraceae Dumort.) flory Belorussii. Botanika (Minsk) 28:23–33
Druskovic B, Lovka M (1995) [Reports] In: Stace CA (ed) IOPB chromosome data 9. International Organanization of Plant Biosystematists Newsletter, vol 24, pp 15–19
Favarger C (1958) Contribution à l’étude cytologique des genres Androsace et Gregoria. Veröff. Geobot. Inst. Rübel Zürich 39:59–80
Fedorov ANA (1974) Chromosome number of flowering plants. Academy of Science of the USSR Komarov Botancial Institute, Leningard. Otto Koeltz Science Publishers, West Germay
Ghanima AM, Talaat AA (2003) Cytomixis and its possible evolutionary role in a Kuwaiti population of Diplotaxis harra (Brassicaceae). Bot J Linn Soc 143:169–175
Goldblatt P (1981, 1984, 1985, 1988) Index to Plant Chromosome Numbers, 1975–1978, 1979–1981, 1982–1983, 1984–1985: Monographs in Systematic Botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, USA, vols 5, 8, 13, 23
Goldblatt P, Johnson DE (1990, 1991, 1994, 1996, 1998, 2000, 2003) Index to Plant Chromosome Numbers, 1986–1987, 1988–1989, 1990–1991, 1992–1993, 1994–1995, 1996–1997, 1998–2000, 2001–2003: Monographs in Systematic Botany from the Missouri Botanical Garden, USA, vols 30, 40, 51, 58, 69, 81, 94, 106
Gottschalk W (1970) Chromosome and nucleus migration during microsporogenesis of Pisum sativum. Nucleus 13:1–9
Hill LM (1989) IOPB chromosome data 1. Int. Organ. Pl. Biosyst. Newslett (Zurich) 13:17–19
Holmgren PK, Holmgren NH (1998) Index Herbariorum: a global directory of public herbaria and associated staff. New York Botanical Garden’s Virtual Herbarium [online]. http://sweetgum.nybg.org/ih/. Accessed 22 Feb 2012
Jee V, Dhar U, Kachroo P (1989) Cytogeography of some endemic taxa of Kashmir Himalaya. Proc Indian Natl Sci Acad 55B:177–184
Jeelani SM, Rani S, Kumar S, Kumari S, Gupta RC (2011) Meiotic studies in some members of Caryophyllaceae Juss. from the Western Himalayas. Acta Biol Cracov Ser Bot 53(1):86–95
Jeelani SM, Kumari S, Gupta RC (2012) Meiotic studies in some selected angiosperms from the Kashmir Himalayas. J Syst Evol 50(3):244–257
Khatoon S, Ali SI (1993) Chromosome atlas of the angiosperms of Pakistan. Department of Botany, BCC &T Press, University of Karachi, Karachi
Khoshoo TN, Sobti SN (1958) Cytology of Indian species of Artemisia. Nature 181:853–854
Kim JS, Oginuma K, Tobe H (2009) Syncyte formation in the microsporangium of Chrysanthemum (Asteraceae): a pathway to infraspecific polyploidy. J Plant Res 122(4):439–444
Koul AK, Gohil RN (1973) Cytotaxonomical conspectus of the flora of Kashmir (I). Chromosome numbers of some common plants. Phyton 15:57–66
Krasnikov AA (1991) Chromosome numbers in some species of vascular plants from Novosibirsk region. Bot Zhur (Moscow & Leningrad) 76:476–479
Krasnikov AA, Zhirova OS, Lomonosova MN, Smirnov SV (2003) Chromosome numbers of Asteraceae from the southern Siberia and Kazakhstan. Bot Zhur (Moscow & Leningrad) 88(9):151–153
Kumar V, Subramaniam B (1986) Chromosome atlas of flowering plants of the Indian subcontinent: vol. I: Dicotyledons, Botanical Survey of India
Levan A (1941) Syncyte formation in the pollen mother cells of haploid Phleum pratense. Hereditas 27:243–253
Löve A, Löve D (1982) IOPB chromosome number reports LXXVI. Taxon 31:583–587
Löve A, Löve D (1986) IOPB chromosome number reports XCIII. Taxon 35:897–903
Lövkvist B, Hultgård UM (1999) Chromosome numbers in south Swedish vascular plants. Opera Botanica 137:1–42
Malik RA, Gupta RC, Kumari S (2011a) Exploration of cytomorphological diversity in Scrophulariaceae Juss. from Kashmir Himalaya. Chromosome Bot 6:85–90
Malik RA, Gupta RC, Kumari S (2011b) IAPT/IOPB chromosome data XII. Taxon 60(6):47–49
Malik RA, Gupta RC, Kumari S (2012) Cytogenetic diversity of Elsholtzia ciliata Benth. (Lamiaceae) from Kashmir Himalaya. Acta Biol Cracov Bot 54(1):1–8
Mehra PN, Remanandan P (1975) Cytological investigations on Indian Compositae, IV. Tribes Senecioneae, Eupatorieae, Vernonieae, and Inuleae. Nucleus 18:6–19
Mendes–Bonato AB, Pagliarini MS, Valle CB, Penteado MIO (2001) A severe case of chromosome stickiness in pollen mother cells of Brachiaria brizantha (Hochst.) Stapf (Gramineae). Cytologia 66:287–291
Moore RJ (1970, 1971, 1972, 1973, 1974, 1977) Index to Plant Chromosome Numbers 1967–1971, 1968, 1969, 1970, 1972, 1973–1974. Regnum Vegetable, vols 68, 77, 84, 90, 91, 96
Narain P (1976) Cytomixis in pollen mother cells of Hemerocallis Linn. Curr Sci India 48:996–998
Ornduff R (1968) Index to plant chromosome numbers (1966, 1967) Regnum Vegetable, vols 55, 59
Pagliarini MS, Risso-Pascotto C, Souza-Kaneshima AM, Valle CB (2008) Analysis of meiotic behavior in selecting potential genitors among diploid and artificially induced tetraploid accessions of Brachiaria ruziziensis (Poaceae). Euphytica 164:187
Rieseberg LH, Willis JH (2007) Plant speciation. Science 317(5840):910–914
Rudkya EG (1990) Chromosome numbers of vascular plants from the various regions of the USSR. Bot Zhur (Moscow & Leningrad) 75:1783–1786
Singhal VK, Kumar P (2008) Impact of cytomixis on meiosis, pollen viability and pollen size in wild populations of Himalayan poppy (Meconopsis aculeata Royle). J Bioscience 33:371–380
Stebbins GL, Jenkins JA, Walters M (1953) Chromosomes and phylogeny in the Compositae, tribe Cichorieae. Univ Calif Publ Bot 26:401–430
Tripathy R, Kumar G (2010) Genetic loss through heavy metal induced chromosomal stickiness in Grass pea. Caryologia 63(3):223–228
Zhukova PG (1967) Karyology of some plants cultivated in the Arctic–Alpine Botanical Garden. In: Avrorin, N.A. (ed.) Plantarum in Zonam Polarem Transportatio II. Leningrad, pp 139–149
Acknowledgments
Authors acknowledge University Grants Commission, New Delhi for providing financial assistance under SAP, ASIST (U.G.C) and FIST (DST) programs. We thank Head Department of Botany, Punjabi University for providing necessary lab facilities during the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Malik, R.A., Gupta, R.C. Meiotic studies in some selected members of Gamopetalae from Kashmir Himalaya. Plant Syst Evol 299, 1549–1560 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0818-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00606-013-0818-6