Abstract.
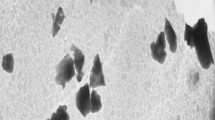
A study of the surface electronic configuration and surface morphology of excimer laser irradiated organo-platinum films [cis-dichlorobis(triphenylphosphine)platinum(II)] is presented. The films were deposited by thermal evaporation to a thickness of approximately 1 µm. The organo-platinum films were irradiated in air with 248 nm UV light in order to produce metallic deposits. The irradiation source used was a krypton fluoride excimer laser with a pulse length of approximately 20 ns. After irradiation, the surface morphology of the films was studied by atomic force microscopy, which yielded information concerning the effect of exposure dose on the surface roughness. The composition of the deposits was investigated using X-ray photoelectron and Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy. The effect of annealing the deposits has also been studied. XPS analysis of the annealed samples has provided evidence for the formation of platinum silicide (PtSi).
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Davidson, M., Fan, Y., Berry, G. et al. Analysis of Laser Irradiated Organo-Platinum Films. Mikrochim Acta 139, 43–48 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040200037
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s006040200037