Abstract
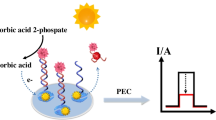
A competitive-type photoelectrochemical (PEC) aptasensor coupled with a novel Au@Cd:SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposite was designed for the detection of 17β-estradiol (E2) in microfluidic devices. The designed Au@Cd:SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposites exhibit high photoelectrochemical activity owing to the good matching of cascade band-edge and the efficient separation of photo-generated e−/h+ pairs derived from the Cd-doped defects in the energy level. The Au@Cd:SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposites were loaded into carbon paste electrodes (CPEs) to immobilize complementary DNA (cDNA) and estradiol aptamer probe DNA (E2-Apt), forming a double-strand DNA structure on the CPE surface. As the target E2 interacts with the double-strand DNA, E2-Apt is sensitively released from the CPE, subsequently increasing the photocurrent intensity due to the reduced steric hindrance of the electrode surface. The competitive-type sensing mechanism, combined with high PEC activity of the Au@Cd:SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposites, contributed to the rapid and sensitive detection of E2 in a “signal on” manner. Under the optimized conditions, the PEC aptasensor exhibited a linear range from 1.0 × 10−13 mol L−1 to 3.2 × 10−6 mol L−1 and a detection limit of 1.2 × 10−14 mol L−1 (S/N = 3). Moreover, the integration of microfluidic device with smartphone controlled portable electrochemical workstation enables the on-site detection of E2. The small sample volume (10 µL) and short analysis time (40 min) demonstrated the great potential of this strategy for E2 detection in rat serum and river water. With these advantages, the PEC aptasensor can be utilized for point-of-care testing (POCT) in both clinical and environmental applications.
Graphical abstract









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analysed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
References
Fuentes N, Nicoleau M, Cabello N, Montes D, Zomorodi N, Chroneos ZC, Silveyra P (2019) 17beta-Estradiol affects lung function and inflammation following ozone exposure in a sex-specific manner. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 317(5):L702–L716. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajplung.00176.2019
Nezami A, Nosrati R, Golichenari B, Rezaee R, Chatzidakis GI, Tsatsakis AM, Karimi G (2017) Nanomaterial-based aptasensors and bioaffinity sensors for quantitative detection of 17β-estradiol. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 94:95–105. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.07.003
Pezzolato M, Maurella C, Varello K, Meloni D, Bellino C, Borlatto L, Di Corcia D, Capra P, Caramelli M, Bozzetta E (2011) High sensitivity of a histological method in the detection of low-dosage illicit treatment with 17β-estradiol in male calves. Food Control 22(10):1668–1673. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.03.027
Russell N, Grossmann M (2019) Mechanisms in endocrinology: Estradiol as a male hormone. Eur J Endocrinol 181(1):R23–R43. https://doi.org/10.1530/eje-18-1000
Godfray HCJ, Stephens AEA, Jepson PD, Jobling S, Johnson AC, Matthiessen P, Sumpter JP, Tyler CR, McLean AR (2019) A restatement of the natural science evidence base on the effects of endocrine disrupting chemicals on wildlife. Proc Biol Sci 286(1897):2416–2427. https://doi.org/10.1098/rspb.2018.2416
Gaikwad NW (2013) Ultra performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for profiling of steroid metabolome in human tissue. Anal Chem 85(10):4951–4960. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac400016e
Azzouz A, Ballesteros E (2015) Multiresidue method for the determination of pharmacologically active substances in egg and honey using a continuous solid-phase extraction system and gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 178:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.01.044
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Choo J, Chen L (2021) Molecular imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater 33(30):e2100543. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543
Arabi M, Chen L (2022) Technical challenges of Molecular-Imprinting-based optical sensors for environmental pollutants. Langmuir 38(19):5963–5967. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.2c00935
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Wang Y, Mei R, Fu L, Li J, Wang X, Chen L (2022) Chiral molecular imprinting-based SERS detection strategy for absolute enantiomeric discrimination. Nat Commun 13(1):5757. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-33448-w
Ge L, Liu Q, Hao N, Kun W (2019) Recent developments of photoelectrochemical biosensors for food analysis. J Mater Chem B 7(46):7283–7300. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9tb01644a
Aydin EB, Sezginturk MK (2017) Indium tin oxide (ITO): a promising material in biosensing technology. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 97:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.09.021
Hu Y, Wang K, Zhang Q, Li F, Wu T, Niu L (2012) Decorated graphene sheets for label-free DNA impedance biosensing. Biomaterials 33(4):1097–1106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2011.10.045
Yazhini K, Suja SK, Kalaivani GJ, Bagyalaksmi J, Pavalamalar S (2018) Non-enzymatic sensing of kidney dysfunction biomarker using pectin - MWCNT nanocomposite. Appl Surf Sci 449:736–744. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.01.197
Alves GM, da Silva JL, Stradiotto NR (2021) A novel citrus pectin-modified carbon paste electrochemical sensor used for copper determination in biofuel. Measurement 169:380–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2020.108356
Zhu J-H, Gou H, Zhao T, Mei L-P, Wang A-J, Feng J-J (2022) Ultrasensitive photoelectrochemical aptasensor for detecting telomerase activity based on Ag2S/Ag decorated ZnIn2S4/C3N4 3D/2D Z-scheme heterostructures and amplified by Au/Cu2+-boron-nitride nanozyme. Biosens Bioelectron 203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114048
Cheng F, Liang J, Tao Z, Chen J (2011) Functional materials for rechargeable batteries. Adv Mater 23(15):1695–1715. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201003587
Hu L, Chen F, Hu P, Zou L, Hu X (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of SnO2/ZnS nanocomposite as a photocatalyst for degradation of rhodamine B under simulated and natural sunlight. J Mol Catal A: Chem 411:203–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2015.10.003
Zhang Z, Wang L, Xiao J, Xiao F, Wang S (2015) One-pot synthesis of three-dimensional graphene/carbon nanotube/SnO2 hybrid architectures with enhanced lithium storage properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(32):17963–17968. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b04673
Deng L, Zhu Z, Liu L, Liu H (2017) Synthesis of Ag2O and Ag co-modified flower-like SnS2 composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity under solar light irradiation. Solid State Sci 63:76–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2016.11.016
Zhang YC, Yao L, Zhang G, Dionysiou DD, Li J, Du X (2014) One-step hydrothermal synthesis of high-performance visible-light-driven SnS2/SnO2 nanoheterojunction photocatalyst for the reduction of aqueous cr(VI). Appl Catal B 144:730–738. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apcatb.2013.08.006
Fan C, Plaxco KW, Heeger AJ (2003) Electrochemical interrogation of conformational changes as a reagentless method for the sequence-specific detection of DNA. 100(16):9134–9137. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1633515100
Herne TM, Tarlov MJ (1997) Characterization of DNA Probes immobilized on gold surfaces. J Am Chem Soc 119(38):8916–8920. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja9719586
Cox JC, Ellington AD (2001) Automated selection of anti-protein aptamers. Bioorg Med Chem 9(10):2525–2531. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0968-0896(01)00028-1
Kim YS, Jung HS, Matsuura T, Lee HY, Kawai T, Gu MB (2007) Electrochemical detection of 17 beta-estradiol using DNA aptamer immobilized gold electrode chip. Biosens Bioelectron 22(11):2525–2531. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2006.10.004
Eisold A, Labudde D (2018) Detailed analysis of 17beta-estradiol-aptamer interactions: a molecular dynamics simulation study. Molecules 23(7):747–769. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules23071690
Alsager OA, Kumar S, Zhu B, Travas-Sejdic J, McNatty KP, Hodgkiss JM (2015) Ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of 17beta-estradiol: the effect of shortening DNA aptamer sequences. Anal Chem 87(8):4201–4209. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.5b00335
Green MA, Ho-Baillie A, Snaith HJ (2014) The emergence of perovskite solar cells. Nat Photonics 8(7):506–514. https://doi.org/10.1038/nphoton.2014.134
Maestre D, Hernández E, Cremades A, Amati M, Piqueras J (2012) Synthesis and characterization of small dimensional structures of Er-Doped SnO2 and erbium–tin–oxide. Cryst Growth Des 12(5):2478–2484. https://doi.org/10.1021/cg300106k
Mo F, Wu J, Chen M, Meng H, Han Q, Fu Y (2019) Enzyme-free on-off-on photoelectrochemical biosensor based on cascaded quadratic amplification strategy for miRNA 141 detection. Sens Actuators B: Chem 289:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.044
Feng R, Tian K, Zhang Y, Liu W, Fang J, Khan MS, Wei Q, Wu R (2020) Recognition of M2 type tumor-associated macrophages with ultrasensitive and biocompatible photoelectrochemical cytosensor based on ce doped SnO(2)/SnS(2) nano heterostructure. Biosens Bioelectron 165:112367–112375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112367
Liu X, Liu P, Tang Y, Yang L, Li L, Qi Z, Li D, Wong DKY (2018) A photoelectrochemical aptasensor based on a 3D flower-like TiO2-MoS2-gold nanoparticle heterostructure for detection of kanamycin. Biosens Bioelectron 112:193–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.04.041
Li Z, Ng KH, Xu S, Zhang Y, Lei Y, Huang J, Lai Y (2022) Facile preparation of tremella-like TiO(2)/Cd:ZnIn(2)S(4) photoanode with enhanced photo-electro-chemical (PEC) performance for energy and environmental applications. Chemosphere 307:135758–135767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2022.135758
Huang H, Xiao K, Dong F, Wang J, Du X, Zhang Y (2016) Sulfur-doping synchronously ameliorating band energy structure and charge separation achieving decent visible-light photocatalysis of Bi2O2CO3. RSC Adv 6(97):94361–94364. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra04888a
Hasegawa H, Savory N, Abe K, Ikebukuro K (2016) Methods for improving aptamer binding Affinity. Molecules 21(4):421. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules21040421
Liu W, Li H, Yu S, Zhang J, Zheng W, Niu L, Li G (2018) Poly(3,6-diamino-9-ethylcarbazole) based molecularly imprinted polymer sensor for ultra-sensitive and selective detection of 17-β-estradiol in biological fluids. Biosens Bioelectron 104:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.01.002
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81503037), Basic research projects of Liaoning Provincial Department of Education (No. LJKMZ20221355), Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province (2021-MS-211), and Career Development Support Plan for Young and Middle-aged Teachers in Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (No. ZQN202301). Also, the authors would like to thank Shiyanjia Lab (www.shiyanjia.com/) for the support of relevant analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yonglun Zhang: conceptualization, methodology, writing—original draft, writing—review and editing. Shihua Zhang: formal analysis, investigation, validation. Zijing Xu: formal analysis, investigation. Jiaxing Zhang: writing—review and editing. Zhuangzhuang Qu: resources. Weilu Liu: conceptualization, writing—review and editing, project administration, supervision
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
Animal experiments were conducted according to the guidelines formulated by the Ethics Committee of Shenyang Pharmaceutical University (SYPU-IACUC-2024-0311-028).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Zhang, S., Xu, Z. et al. A competitive-type photoelectrochemical aptasensor for 17 beta-estradiol detection in microfluidic devices based on a novel Au@Cd:SnO2/SnS2 nanocomposite. Microchim Acta 191, 383 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06478-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06478-y