Abstract
Surface fouling poses a significant challenge that restricts the analytical performance of electrochemical sensors in both in vitro and in vivo applications. Biofouling resistance is paramount to guarantee the reliable operation of electrochemical sensors in complex biofluids (e.g., blood, serum, and urine). Seeking efficient strategies for surface fouling and establishing highly sensitive sensing platforms for applications in complex media have received increasing attention in the past. In this review, we provide a comprehensive overview of recent research efforts focused on antifouling electrochemical sensors. Initially, we present a detailed illustration of the concept about biofouling along with an exploration of four key antifouling mechanisms. Subsequently, we delve into the commonly employed antifouling strategies in the fabrication of electrochemical sensors. These encompass physical surface topography (micro/nanostructure coatings and filtration membranes) and chemical surface modifications (PEG and its derivatives, zwitterionic polymers, peptides, proteins, and various other antifouling materials). The progress in antifouling electrochemical sensors is proposed concerning the antifouling mechanisms as well as sensing capability assessments (e.g., sensitivity, stability, and practical application ability). Finally, we summarize the evolving trends in the field and highlight some key remaining limitations.
Graphical abstract



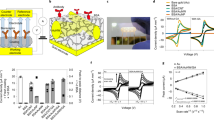
Reproduced with permission from reference [53]. Copyright 2022 Wiley. (B) SEM images depicting electrodes undergoing a progressive series of roughening pulse cycles. (C) Quantification of glucose concentration through direct glucose oxidation employing planar, MSE, and R-MSE. (D) Quantifying glucose concentration through direct glucose oxidation utilizing R-MSEs in 1 × PBS buffer, 1 × PBS buffer/BSA 40 mg·mL−1 and 1 × PBS buffer/BSA 40 mg·mL−1/50 μM AA. Reproduced with permission from reference [54]. Copyright 2023 Wiley

Reproduced with permission from reference [62]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (C) Schematic showing the antifouling PTA − PANI nanoporous membrane-coated CFE and the structure of the PTA − PANI nanoporous membrane. Reproduced with permission from reference [63]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. (D) Illustration of antifouling SNM-coated CFME for continuous monitoring of O2 in rat brain. Reproduced with permission from reference [64]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society. (E) Illustration of antifouling property of membrane-coated CF electrodes in vivo monitoring of pH. Reproduced with permission from reference [65]. Copyright 2019 American Chemical Society

Reproduced with permission from reference [80]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. (B) Synthesis scheme and chemical structures of the PEGMA-based multifunctional polymers. Reproduced with permission from reference [81]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (C) Schematic illustration of the construction of the bifunctional SAM of PEG-thiol-modified electrodes for electrochemical sensing for NS1 and IgG in diluted serum. Reproduced with permission from reference [83]. Copyright 2018 Elsevier. (D) Schematic illustration of the preparation of PMS-M2+/AuNPs/PEG/CS and the label-free electrochemical biosensor for simultaneous detection of CgA and CgB. Reproduced with permission from reference [84]. Copyright 2021 Elsevier. (E) Illustration of the fabrication of Fe3O4@Au@PEG@CS NPs and low-fouling biosensor for the detection of mycoplasma ovipneumonia. Reproduced with permission from reference [85]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier

Reproduced with permission from reference [93]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (B) Illustration of the mechanisms of monolayer degradation and multiday stability approaches for electrochemical aptamer sensors. Reproduced with permission from reference [98]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society. (C) Illustration of the PSN-based biosensor for CA125 sensing in undiluted human serum. Reproduced with permission from reference [99]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (D) Illustration of the fabrication process of the PDA-PSBMA-based sensing platform. Reproduced with permission from reference [100]. Copyright 2020 Elsevier. (E) Electrochemical sensing platform for sensitive recognition of neurotransmitters based on zwitterion/dopamine Copolymer. (F) (a) DPV curves in BSA in the presence of interferents; (b) bar chart representation of current density variations in the presence of interferents; (c) stability of the response in BSA; (d) long-term stability test in BSA. Reproduced with permission from reference [102]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society

Reproduced with permission from reference [110]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society. (B) Illustration of five-functional peptide-based CTCs biosensor. Reproduced with permission from reference [111]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. (C) The functional design of a phosphorylated zwitterionic oligopeptide and the assembling procedure of phosphorylated oligopeptide-based biosensor. Reproduced with permission from reference [38]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society. (D) Illustrative representation of the construction and sensing of the PHHP-microsensor. Reproduced with permission from reference [29]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society. (E) Illustration of the structure of inverted Y-shaped peptides. Reproduced with permission from reference [116]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (F) Schematic structure of the designed multifunctional isopeptide. Reproduced with permission from reference [115]. Copyright 2023 American Chemical Society

Reproduced with permission from reference [124]. Copyright 2021 American Chemical Society. (B) The construction processes of the UA sensor based on antifouling PTB. Reproduced with permission from reference [33]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (C) A diagrammatic representation of the HER2 biosensor construction, utilizing antifouling PEG and peptide. Reproduced with permission from reference [131]. Copyright 2023 Elsevier. (D) The antifouling HER2 biosensor fabrication process. Reproduced with permission from reference [132]. Copyright 2024 American Chemical Society. (E) Stepwise fabrication of the platelet membrane-based electrochemical immunosensor for detection of CD44. Reproduced with permission from reference [133]. Copyright 2022 American Chemical Society. (F) Illustration of the construction of the LM-Masked CFEs. Reproduced with permission from reference [26]. Copyright 2020 American Chemical Society
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Magin CM, Cooper SP, Brennan AB (2010) Non-toxic antifouling strategies. Mater Today 13:36–44
Blaszykowski C, Sheikh S, Thompson M (2012) Surface chemistry to minimize fouling from blood-based fluids. Chem Soc Rev 41:5599–5612
Sabaté del Río J, Henry OYF, Jolly P, Ingber DE (2019) An antifouling coating that enables affinity-based electrochemical biosensing in complex biological fluids. Nat Nanotechnol 14:1143–1149
Jiang C, Wang G, Hein R, Liu N, Luo X, Davis JJ (2020) Antifouling strategies for selective in vitro and in vivo sensing. Chem Rev 120:3852–3889
Tong X, Liu S, Crittenden J, Chen Y (2021) Nanofluidic membranes to address the challenges of salinity gradient power harvesting. ACS Nano 15:5838–5860
Wongkaew N, Simsek M, Griesche C, Baeumner AJ (2019) Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing electrochemical biosensors and Lab-on-a-Chip performances: recent progress, applications, and future perspective. Chem Rev 119:120–194
Wang C, Xia K, Wang H, Liang X, Yin Z, Zhang Y (2019) Advanced carbon for flexible and wearable electronics. Adv Mater 31:1801072
Taniselass S, Arshad MKM, Gopinath SCB (2019) Graphene-based electrochemical biosensors for monitoring noncommunicable disease biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 130:276–292
Lin P-H, Li B-R (2020) Antifouling strategies in advanced electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Analyst 145:1110–1120
Zhang M, Yu P, Mao L (2012) Rational design of surface/interface chemistry for quantitative in vivo monitoring of brain chemistry. Acc Chem Res 45:533–543
Zhang L, Tian Y (2018) Designing recognition molecules and tailoring functional surfaces for in vivo monitoring of small molecules in the brain. Acc Chem Res 51:688–696
Wang Y, Qian Y, Zhang L, Zhang Z, Chen S, Liu J, He X, Tian Y (2023) Conductive metal–organic framework microelectrodes regulated by conjugated molecular wires for monitoring of dopamine in the mouse brain. J Am Chem Soc 145:2118–2126
Liu B, Liu X, Shi S, Huang R, Su R, Qi W, He Z (2016) Design and mechanisms of antifouling materials for surface plasmon resonance sensors. Acta Biomater 40:100–118
Vaisocherová H, Brynda E, Homola J (2015) Functionalizable low-fouling coatings for label-free biosensing in complex biological media: advances and applications. Anal Bioanal Chem 407:3927–3953
Caracciolo G, Farokhzad OC, Mahmoudi M (2017) Biological identity of nanoparticles in vivo: clinical implications of the protein corona. Trends Biotechnol 35:257–264
Bertrand N, Grenier P, Mahmoudi M, Lima EM, Appel EA, Dormont F, Lim J-M, Karnik R, Langer R, Farokhzad OC (2017) Mechanistic understanding of in vivo protein corona formation on polymeric nanoparticles and impact on pharmacokinetics. Nat Commun 8:777
Zhou L, Li X, Zhu B, Su B (2022) An overview of antifouling strategies for electrochemical analysis. Electroanalysis 34:966–975
Wei T, Tang Z, Yu Q, Chen H (2017) Smart antibacterial surfaces with switchable bacteria-killing and bacteria-releasing capabilities. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:37511–37523
Zhang L, Cao Z, Bai T, Carr L, Ella-Menye J-R, Irvin C, Ratner BD, Jiang S (2013) Zwitterionic hydrogels implanted in mice resist the foreign-body reaction. Nat Biotechnol 31:553–556
Zhang D, Chen Q, Bi Y, Zhang H, Chen M, Wan J, Shi C, Zhang W, Zhang J, Qiao Z, Li J, Chen S, Liu R (2021) Bio-inspired poly-DL-serine materials resist the foreign-body response. Nat Commun 12:5327
Colman RW (1993) Chapter 3 Mechanisms of thrombus formation and dissolution. Cardiovasc Pathol 2:23–31
Anderson JM (1993) Chapter 4 Mechanisms of inflammation and infection with implanted devices. Cardiovasc Pathol 2:33–41
Ingelsson M, Yasri N, Roberts EPL (2020) Electrode passivation, faradaic efficiency, and performance enhancement strategies in electrocoagulation-a review. Water Res 187:116433
Schmuki P (2002) From bacon to barriers: a review on the passivity of metals and alloys. J Solid State Electrochem 6:145–164
Li Y, Zhao S, Xu Z, Qiao X, Li M, Li Y, Luo XL (2023) Peptide nucleic acid and antifouling peptide based biosensor for the non-fouling detection of COVID-19 nucleic acid in saliva. Biosens Bioelectron 225:115101
Wei H, Wu F, Li L, Yang X, Xu C, Yu P, Ma F, Mao L (2020) Natural leukocyte membrane-masked microelectrodes with an enhanced antifouling ability and biocompatibility for in vivo electrochemical sensing. Anal Chem 92:11374–11379
Hu X, Tian J, Li C, Su H, Qin R, Wang Y, Cao X, Yang P (2020) Amyloid-like protein aggregates: a new class of bioinspired materials merging an interfacial anchor with antifouling. Adv Mater 32:2000128
Zhao Z, Pan M, Qiao C, Xiang L, Liu X, Yang W, Chen XZ, Zeng H (2023) Bionic engineered protein coating boosting anti-biofouling in complex biological fluids. Adv Mater 35:2208824
Han R, Li Y, Shi MJ, Ding CF, Luo XL (2023) Designed polyhydroxyproline helical peptide with ultrarobust antifouling capability for electrochemical sensing in diverse complex biological fluids. Anal Chem 95:18540–18548
Schlenoff JB (2014) Zwitteration: coating surfaces with zwitterionic functionality to reduce nonspecific adsorption. Langmuir 30:9625–9636
Chen S, Li L, Zhao C, Zheng J (2010) Surface hydration: principles and applications toward low-fouling/nonfouling biomaterials. Polymer 51:5283–5293
Zhao SJ, Qiao XJ, Chen M, Li Y, Wang X, Xu ZY, Wu YM, Luo XL (2022) d-Amino acid-based antifouling peptides for the construction of electrochemical biosensors capable of assaying proteins in serum with enhanced stability. ACS Sens 7:1740–1746
Song Z, Li R, Yang XQ, Ambrosi A, Luo XL (2023) Ultralow fouling electrochemical detection of uric acid directly in serum based on phase-transited bovine serum albumin and conducting polymer. Chin Chem Lett 34:108314
Gu ST, Shi X-M, Zhang D, Fan G-C, Luo XL (2021) Peptide-based photocathodic biosensors: integrating a recognition peptide with an antifouling peptide. Anal Chem 93:2706–2712
Hu Z, Xu Y, Wang H, Fan G-C, Luo XL (2022) Self-powered anti-interference photoelectrochemical immunosensor based on Au/ZIS/CIS heterojunction photocathode with zwitterionic peptide anchoring. Chin Chem Lett 33:4750–4755
Megelski S, Stephens JS, Chase B, Rabolt J (2002) Micro- and nanostructured surface morphology on electrospun polymer fibers. Macromolecules 35:8456–8466
Chen Q, Yu S, Zhang D, Zhang W, Zhang H, Zou J, Mao Z, Yuan Y, Gao C, Liu R (2019) Impact of antifouling PEG layer on the performance of functional peptides in regulating cell behaviors. J Am Chem Soc 141:16772–16780
Qiao XJ, Qian Z-H, Sun W, Zhu C-Y, Li Y, Luo XL (2023) Phosphorylation of oligopeptides: design of ultra-hydrophilic zwitterionic peptides for anti-fouling detection of nucleic acids in saliva. Anal Chem 95:11091–11098
Leng C, Hung H-C, Sieggreen O, Li Y, Jiang S, Chen Z (2015) Probing the surface hydration of nonfouling zwitterionic and poly(ethylene glycol) materials with isotopic dilution spectroscopy. J Phys Chem C 119:8775–8780
Leng C, Hung H-C, Sun S, Wang D, Li Y, Jiang S, Chen Z (2015) Probing the surface hydration of nonfouling zwitterionic and PEG materials in contact with proteins. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:16881–16888
Xie Y, Pan Y, Zhang R, Liang Y, Li Z (2015) Modulating protein behaviors on responsive surface by external electric fields: a molecular dynamics study. Appl Surf Sci 326:55–65
Jeon SI, Lee JH, Andrad J, De Gennes PG (1991) Protein-surface interactions in the presence of polyethylene oxide: I. Simplified theory. J Colloid Interface Sci 142:149–158
Zheng J, Li L, Tsao H-K, Sheng Y-J, Chen S, Jiang S (2005) Strong repulsive forces between protein and oligo (ethylene glycol) self-assembled monolayers: a molecular simulation study. Biophys J 89:158–166
Wu S-T, Huang C-Y, Weng C-C, Chang C-C, Li B-R, Hsu C-S (2019) Rapid prototyping of an open-surface microfluidic platform using wettability-patterned surfaces prepared by an atmospheric-pressure plasma jet. ACS Omega 4:16292–16299
Gao A, Yan Y, Li T, Liu F (2019) Biomimetic urchin-like surface based on poly (lactic acid) membrane for robust anti-wetting and anti-bacteria properties. Mater Lett 237:240–244
Murakami D, Jinnai H, Takahara A (2014) Wetting transition from the cassie-baxter state to the wenzel state on textured polymer surfaces. Langmuir 30:2061–2067
Cao X, Pettitt ME, Wode F, Arpa Sancet MP, Fu J, Ji J, Callow ME, Callow JA, Rosenhahn A, Grunze M (2010) Interaction of zoospores of the green alga ulva with bioinspired micro- and nanostructured surfaces prepared by polyelectrolyte layer-by-layer self-assembly. Adv Funct Mater 20:1984–1993
Bers AV, Wahl M (2004) The influence of natural surface microtopographies on fouling. Biofouling 20:43–51
Patel J, Radhakrishnan L, Zhao B, Uppalapati B, Daniels RC, Ward KR, Collinson MM (2013) Electrochemical properties of nanostructured porous gold electrodes in biofouling solutions. Anal Chem 85:11610–11618
Daggumati P, Matharu Z, Seker E (2015) Effect of nanoporous gold thin film morphology on electrochemical DNA sensing. Anal Chem 87:8149–8156
Chapman CAR, Chen H, Stamou M, Biener J, Biener MM, Lein PJ, Seker E (2015) Nanoporous gold as a neural interface coating: effects of topography, surface chemistry, and feature size. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:7093–7100
Silva TA, Khan MRK, Fatibello-Filho O, Collinson MM (2019) Simultaneous electrochemical sensing of ascorbic acid and uric acid under biofouling conditions using nanoporous gold electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 846:113160
Sabaté del Río J, Woo H-K, Park J, Ha HK, Kim J-R, Cho Y-K (2022) SEEDING to enable sensitive electrochemical detection of biomarkers in undiluted biological samples. Adv Mater 34:2200981
González-Martínez E, Saem S, Beganovic NE, Moran-Mirabal JM (2023) Electrochemical nano-roughening of gold microstructured electrodes for enhanced sensing in biofluids. Angew Chem Int Ed 62:e202218080
Martins TS, Bott-Neto JL, Machado SAS, Oliveira ON Jr (2022) Label-free electrochemical immunosensor made with tree-like gold dendrites for monitoring 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 metabolite. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 14:31455–31462
Yang J, He D, Zhang N, Hu C (2022) Disposable carbon nanotube-based antifouling electrochemical sensors for detection of morphine in unprocessed coffee and milk. J Electroanal Chem 905:115997
Ramya R, Thivya P, Nathiya D, Wilson J (2021) Polypyrrole and enzyme free cholesterol flakes based composite: selective determination of theophylline. J Pharm Biomed Anal 199:114065
Wu S, Lan X, Huang F, Luo Z, Ju H, Meng C, Duan C (2012) Selective electrochemical detection of cysteine in complex serum by graphene nanoribbon. Biosens Bioelectron 32:293–296
Sun Q, Yan F, Yao L, Su B (2016) Anti-biofouling isoporous silica-micelle membrane enabling drug detection in human whole blood. Anal Chem 88:8364–8368
Yan F, Zheng W, Yao L, Su B (2015) Direct electrochemical analysis in complex samples using ITO electrodes modified with permselective membranes consisting of vertically ordered silica mesochannels and micelles. Chem Commun 51:17736–17739
Zhou L, Ding H, Yan F, Guo W, Su B (2018) Electrochemical detection of Alzheimer’s disease related substances in biofluids by silica nanochannel membrane modified glassy carbon electrodes. Analyst 143:4756–4763
Liu Y, Wang X, Zeng X, Waterhouse GIN, Jiang X, Zhang Z, Yu L (2023) Antifouling improvement in Pb2+ ion selective electrodes by using an environmentally friendly capsaicin derivative. Talanta 258:124436
Feng T, Ji W, Tang Q, Wei H, Zhang S, Mao J, Zhang Y, Mao L, Zhang M (2019) Low-fouling nanoporous conductive polymer-coated microelectrode for in vivo monitoring of dopamine in the rat brain. Anal Chem 91:10786–10791
Zhou L, Hou H, Wei H, Yao L, Sun L, Yu P, Su B, Mao L (2019) In vivo monitoring of oxygen in rat brain by carbon fiber microelectrode modified with antifouling nanoporous membrane. Anal Chem 91:3645–3651
Hao J, Xiao T, Wu F, Yu P, Mao L (2016) High antifouling property of ion-selective membrane: toward in vivo monitoring of pH change in live brain of rats with membrane-coated carbon fiber electrodes. Anal Chem 88:11238–11243
Hang T, Xiao S, Yang C, Li X, Guo C, He G, Li B, Yang C, Chen H-j, Liu F, Deng S, Zhang Y, Xie X (2019) Hierarchical graphene/nanorods-based H2O2 electrochemical sensor with self-cleaning and anti-biofouling properties. Sens Actuators B 289:15–23
Ruiz-Valdepeñas Montiel V, Sempionatto JR, Esteban-Fernández de Ávila B, Whitworth A, Campuzano S, Pingarrón JM, Wang J (2018) Delayed sensor activation based on transient coatings: biofouling protection in complex biofluids. J Am Chem Soc 140:14050–14053
Daggumati P, Matharu Z, Wang L, Seker E (2015) Biofouling-resilient nanoporous gold electrodes for DNA sensing. Anal Chem 87:8618–8622
Zhou J, Zhang L, Tian Y (2016) Micro electrochemical pH sensor applicable for real-time ratiometric monitoring of pH values in rat brains. Anal Chem 88:2113–2118
Bocquet L, Lauga E (2011) A smooth future? Nat Mater 10:334–337
Zhang D, Li L, Wu Y, Zhu B, Song H (2019) One-step method for fabrication of bioinspired hierarchical superhydrophobic surface with robust stability. Appl Surf Sci 473:493–499
Maan AMC, Hofman AH, de Vos WM, Kamperman M (2020) Recent developments and practical feasibility of polymer-based antifouling coatings. Adv Funct Mater 30:2000936
Greene GW, Martin LL, Tabor RF, Michalczyk A, Ackland LM, Horn R (2015) Lubricin: a versatile, biological anti-adhesive with properties comparable to polyethylene glycol. Biomaterials 53:127–136
Li B, Jain P, Ma J, Smith JK, Yuan Z, Hung H-C, He Y, Lin X, Wu K, Pfaendtner J, Jiang S (2019) Trimethylamine N-oxide–derived zwitterionic polymers: a new class of ultralow fouling bioinspired materials. Sci Adv 5:eaaw9562
Ostuni E, Chapman RG, Holmlin RE, Takayama S, Whitesides GM (2001) A survey of structure−property relationships of surfaces that resist the adsorption of protein. Langmuir 17:5605–5620
Lee JH, Kopecek J, Andrade JD (1989) Protein-resistant surfaces prepared by PEO-containing block copolymer surfactants. J Biomed Mater Res 23:351–368
Norman ME, Williams P, Illum L (1992) Human serum albumin as a probe for surface conditioning (opsonization) of block copolymer-coated microspheres. Biomaterials 13:841–849
Freij-Larsson C, Nylander T, Jannasch P, Wesslén B (1996) Adsorption behaviour of amphiphilic polymers at hydrophobic surfaces: effects on protein adsorption. Biomaterials 17:2199–2207
Hui N, Sun X, Niu S, Luo X (2017) PEGylated polyaniline nanofibers: antifouling and conducting biomaterial for electrochemical DNA sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2914–2923
Ma B, Yao T, Meng X, Xu Y, Ma Z, Ha H (2022) Novel immunoprobe based on MOF-818 synergizing with an antifouling sensing interface to improve immunosensors. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 10:12041–12047
Kim J, Baek KJ, Yu S, Yang HS, Khaliq NU, Choi WI, Kim H, Sung D (2023) Ferrocene-based acrylate copolymer multilayers with efficient antifouling and electrochemical redox properties. Electrochim Acta 463:142824
Hu Z, Zhu R, Figueroa-Miranda G, Zhou L, Feng L, Offenhäusser A, Mayer D (2023) Truncated electrochemical aptasensor with enhanced antifouling capability for highly sensitive serotonin detection. Biosensors 13:881
Santos A, Bueno PR, Davis JJ (2018) A dual marker label free electrochemical assay for Flavivirus dengue diagnosis. Biosens Bioelectron 100:519–525
Liu X, Li Y, He L, Feng Y, Tan H, Chen X, Yang W (2021) Simultaneous detection of multiple neuroendocrine tumor markers in patient serum with an ultrasensitive and antifouling electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 194:113603
Zhao S, Zhou Y, Wei L, Chen L (2020) Low fouling strategy of electrochemical biosensor based on chondroitin sulfate functionalized gold magnetic particle for voltammetric determination of mycoplasma ovipneumonia in whole serum. Anal Chim Acta 1126:91–99
Wang W, Fan X, Xu S, Davis JJ, Luo X (2015) Low fouling label-free DNA sensor based on polyethylene glycols decorated with gold nanoparticles for the detection of breast cancer biomarkers. Biosens Bioelectron 71:51–56
Cui M, Song Z, Wu Y, Guo B, Fan X, Luo X (2016) A highly sensitive biosensor for tumor maker alpha fetoprotein based on poly(ethylene glycol) doped conducting polymer PEDOT. Biosens Bioelectron 79:736–741
Wang G, Xu Q, Liu L, Su X, Lin J, Xu G, Luo X (2017) Mixed self-assembly of polyethylene glycol and aptamer on polydopamine surface for highly sensitive and low-fouling detection of adenosine triphosphate in complex media. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:31153–31160
Pidhatika B, Rodenstein M, Chen Y, Rakhmatullina E, Mühlebach A, Acikgöz C, Textor M, Konradi R (2012) Comparative stability studies of poly(2-methyl-2-oxazoline) and poly(ethylene glycol) brush coatings. Biointerphases 7:1
Krause JE, Brault ND, Li Y, Xue H, Zhou Y, Jiang S (2011) Photoiniferter-mediated polymerization of zwitterionic carboxybetaine monomers for low-fouling and functionalizable surface coatings. Macromolecules 44:9213–9220
Zhu Y, Xu X, Brault ND, Keefe AJ, Han X, Deng Y, Xu J, Yu Q, Jiang S (2014) Cellulose paper sensors modified with zwitterionic poly(carboxybetaine) for sensing and detection in complex media. Anal Chem 86:2871–2875
Bai T, Sun F, Zhang L, Sinclair A, Liu S, Ella-Menye J-R, Zheng Y, Jiang S (2014) Restraint of the differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by a nonfouling zwitterionic hydrogel. Angew Chem Int Ed 53:12729–12734
Anthi J, Vaněčková E, Spasovová M, Houska M, Vrabcová M, Vogelová E, Holubová B, Vaisocherová-Lísalová H, Kolivoška V (2023) Probing charge transfer through antifouling polymer brushes by electrochemical methods: the impact of supporting self-assembled monolayer chain length. Anal Chim Acta 1276:341640
Le NL, Ulbricht M, Nunes SP (2017) How do polyethylene glycol and poly(sulfobetaine) hydrogel layers on ultrafiltration membranes minimize fouling and stay stable in cleaning chemicals? Ind Eng Chem Res 56:6785–6795
Chang Y, Shih Y-J, Lai C-J, Kung H-H, Jiang S (2013) Blood-inert surfaces via ion-pair anchoring of zwitterionic copolymer brushes in human whole blood. Adv Funct Mater 23:1100–1110
Rodriguez Emmenegger C, Brynda E, Riedel T, Sedlakova Z, Houska M, Alles AB (2009) Interaction of blood plasma with antifouling surfaces. Langmuir 25:6328–6333
Konai MM, Bhattacharjee B, Ghosh S, Haldar J (2018) Recent progress in polymer research to tackle infections and antimicrobial resistance. Biomacromol 19:1888–1917
Watkins Z, Karajic A, Young T, White R, Heikenfeld J (2023) Week-long operation of electrochemical aptamer sensors: new insights into self-assembled monolayer degradation mechanisms and solutions for stability in serum at body temperature. ACS Sens 8:1119–1131
Yang H, Wang P, Geng F, Wu Q, Song F, Ding C (2023) Copolymerization of zwitterionic sulfobetaine and hydrophobic acrylamide based antifouling electrochemical biosensors for detection of CA125 in clinical serum samples. Sens Actuators B 387:133820
Xu Z, Han R, Liu N, Gao F, Luo X (2020) Electrochemical biosensors for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen with low fouling and high sensitivity based on copolymerized polydopamine and zwitterionic polymer. Sens Actuators B 319:128253
Wei H, Ni S, Cao C, Yang G, Liu G (2018) Graphene oxide signal reporter based multifunctional immunosensing platform for amperometric profiling of multiple cytokines in serum. ACS Sens 3:1553–1561
Olejnik A, Ficek M, Szkodo M, Stanisławska A, Karczewski J, Ryl J, Dołęga A, Siuzdak K, Bogdanowicz R (2022) Tailoring diffusional fields in zwitterion/dopamine copolymer electropolymerized at carbon nanowalls for sensitive recognition of neurotransmitters. ACS Nano 16:13183–13198
Jiang C, Alam MT, Silva SM, Taufik S, Fan S, Gooding JJ (2016) Unique sensing interface that allows the development of an electrochemical immunosensor for the detection of tumor necrosis factor α in whole blood. ACS Sens 1:1432–1438
Wu B, Castagnola E, Cui XT (2023) Zwitterionic polymer coated and aptamer functionalized flexible micro-electrode arrays for in vivo cocaine sensing and electrophysiology. Micromachines 14:323
Goda T, Toya M, Matsumoto A, Miyahara Y (2015) Poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) bearing phosphorylcholine groups for metal-free, antibody-free, and low-impedance biosensors specific for C-reactive protein. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:27440–27448
Cui M, Wang Y, Jiao M, Jayachandran S, Wu Y, Fan X, Luo X (2017) Mixed self-assembled aptamer and newly designed zwitterionic peptide as antifouling biosensing interface for electrochemical detection of alpha-etoprotein. ACS Sens 2:490–494
Keefe AJ, Caldwell KB, Nowinski AK, White AD, Thakkar A, Jiang S (2013) Screening nonspecific interactions of peptides without background interference. Biomaterials 34:1871–1877
Ye H, Wang L, Huang R, Su R, Liu B, Qi W, He Z (2015) Superior antifouling performance of a zwitterionic peptide compared to an amphiphilic, non-ionic peptide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7:22448–22457
Liu N, Hui N, Davis JJ, Luo X (2018) Low fouling protein detection in complex biological media supported by a designed multifunctional peptide. ACS Sens 3:1210–1216
Song Z, Chen M, Ding C, Luo X (2020) Designed three-in-one peptides with anchoring, antifouling, and recognizing capabilities for highly sensitive and low-fouling electrochemical sensing in complex biological media. Anal Chem 92:5795–5802
Han R, Li Y, Chen M, Li W, Ding C, Luo X (2022) Antifouling electrochemical biosensor based on the designed functional peptide and the electrodeposited conducting polymer for CTC analysis in human blood. Anal Chem 94:2204–2211
Wang G, Han R, Li Q, Han Y, Luo X (2020) Electrochemical biosensors capable of detecting biomarkers in human serum with unique long-term antifouling abilities based on designed multifunctional peptides. Anal Chem 92:7186–7193
Liu N, Song J, Lu Y, Davis JJ, Gao F, Luo X (2019) Electrochemical aptasensor for ultralow fouling cancer cell quantification in complex biological media based on designed branched peptides. Anal Chem 91:8334–8340
Chen M, Han R, Wang W, Li Y, Luo X (2021) Antifouling aptasensor based on self-assembled loop-closed peptides with enhanced stability for CA125 assay in complex biofluids. Anal Chem 93:13555–13563
Han R, Li Y, Hou W, Ding C, Luo X (2023) Designed multifunctional isopeptide for enhanced annexin A1 biosensing based on peptide-protein interactions in human blood. Anal Chem 95:9025–9033
Song Z, Ma Y, Chen M, Ambrosi A, Ding C, Luo X (2021) Electrochemical biosensor with enhanced antifouling capability for COVID-19 nucleic acid detection in complex biological media. Anal Chem 93:5963–5971
Wang W, Han R, Chen M, Luo X (2021) Antifouling peptide hydrogel based electrochemical biosensors for highly sensitive detection of cancer biomarker HER2 in human serum. Anal Chem 93:7355–7361
Qiao X, Cai Y, Kong Z, Xu Z, Luo X (2023) A wearable electrochemical sensor based on anti-fouling and self-healing polypeptide complex hydrogels for sweat monitoring. ACS Sens 8:2834–2842
Ma GJ, Ferhan AR, Jackman JA, Cho N-J (2020) Conformational flexibility of fatty acid-free bovine serum albumin proteins enables superior antifouling coatings. Commun Mater 1:45
Fang B, Ling Q, Zhao W, Ma Y, Bai P, Wei Q, Li H, Zhao C (2009) Modification of polyethersulfone membrane by grafting bovine serum albumin on the surface of polyethersulfone/poly(acrylonitrile-co-acrylic acid) blended membrane. J Membr Sci 329:46–55
Chaturvedi SK, Ma J, Zhao H, Schuck P (2017) Use of fluorescence-detected sedimentation velocity to study high-affinity protein interactions. Nat Protoc 12:1777–1791
Tian C, Wang L, Luan F, Fu X, Zhuang X, Chen L (2019) A novel electrochemiluminescent emitter of europium hydroxide nanorods and its application in bioanalysis. Chem Commun 55:12479–12482
Zupančič U, Jolly P, Estrela P, Moschou D, Ingber DE (2021) Graphene enabled low-noise surface chemistry for multiplexed sepsis biomarker detection in whole blood. Adv Funct Mater 31:2010638
Li Y, Han R, Chen M, Zhang L, Wang G, Luo X (2021) Bovine serum albumin-cross-linked polyaniline nanowires for ultralow fouling and highly sensitive electrochemical protein quantification in human serum samples. Anal Chem 93:4326–4333
Li Y, Han R, Chen M, Yang X, Zhan Y, Wang L, Luo X (2021) Electrochemical biosensor with enhanced antifouling capability based on amyloid-like bovine serum albumin and a conducting polymer for ultrasensitive detection of proteins in human serum. Anal Chem 93:14351–14357
Liu X, Huang R, Su R, Qi W, Wang L, He Z (2014) Grafting hyaluronic acid onto gold surface to achieve low protein fouling in surface plasmon resonance biosensors. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6:13034–13042
Wang W, Jayachandran S, Li M, Xu S, Luo X (2018) Hyaluronic acid functionalized nanostructured sensing interface for voltammetric determination of microRNA in biological media with ultra-high sensitivity and ultra-low fouling. Microchim Acta 185:156
Wang J, Hui N (2018) A nonfouling voltammetric immunosensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen based on the use of polyaniline nanowires wrapped with hyaluronic acid. Microchim Acta 185:329
Lv S, Sheng J, Zhao S, Liu M, Chen L (2018) The detection of brucellosis antibody in whole serum based on the low-fouling electrochemical immunosensor fabricated with magnetic Fe3O4@Au@PEG@HA nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 117:138–144
Song Z, Li R, Yang XQ, Zhang ZH, Luo XL (2022) Functional DNA-peptide conjugates with enhanced antifouling capabilities for electrochemical detection of proteins in complex human serum. Sens Actuators B 367:132110
Yang XQ, Chen P, Zhang X, Zhou H, Song Z, Yang WL, Luo XL (2023) An electrochemical biosensor for HER2 detection in complex biological media based on two antifouling materials of designed recognizing peptide and PEG. Anal Chim Acta 1252:341075
Li Y, Han R, Feng J, Li J, Luo XL (2024) Phospholipid bilayer integrated with multifunctional peptide for ultralow-fouling electrochemical detection of her2 in human serum. Anal Chem 96:531–537
Lian M, Shi Y, Chen L, Qin Y, Zhang W, Zhao J, Chen D (2022) Cell membrane and V2C MXene-based electrochemical immunosensor with enhanced antifouling capability for detection of CD44. ACS Sens 7:2701–2709
Acknowledgements
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (22174082, 22374085), the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2022QB049), and the Postdoctoral Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (SDCX-ZG-202203020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This work did not involve human or animal samples.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, Z., Han, R., Yu, K. et al. Antifouling strategies for electrochemical sensing in complex biological media. Microchim Acta 191, 138 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06218-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-024-06218-2