Abstract
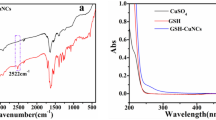
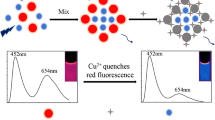
The simple preparation of a nanohybrid of terbium-doped carbon dots/glutathione-capped copper nanoclusters (Tb@CDs/GSH-CuNCs) was for the first time developed for ratiometric detection of phosphate anion (Pi). Blue-emission of Tb@CDs can trigger non-luminescence of GSH-CuNCs for aggregation-induced emission (AIE) performance due to the strong reserved coordination capacity of Tb3+. Thus, Tb@CDs/GSH-CuNCs rapidly generated dual-emission signals at 630 nm and 545 nm by directly mixing the two individual materials via the AIE effect, alongside fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET) process. However, by the introduction of Pi, both AIE and FRET processes were blocked because of the stronger binding affinity of Tb3+ and Pi than that of Tb3+ and –COOH on Tb@CDs, thus realizing successful ratiometric detection of Pi. The linear concentration range was 0–16 μM, with the limit of detection (LOD) of 0.32 μM. The proposed method provided new ideas for designing nanohybrid of CDs and nanoclusters (MNCs) as ratiometric fluorescent probes for analytical applications.
Graphical abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included within the article and its supplementary information files.
References
Jia X, Li J, Wang E (2013) Cu nanoclusters with aggregation induced emission enhancement. Small 9(22):3873–3879. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201300896
Wu Z, Liu J, Gao Y et al (2015) Assembly-induced enhancement of Cu nanoclusters luminescence with mechanochromic property. J Am Chem Soc 137(40):12906–12913. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b06550
Ye M, Yu Y, Lin B et al (2019) Copper nanoclusters reversible switches based on ions-triggered for detection of inorganic pyrophosphatase activity. Sensors Actuators B Chem 284:36–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.12.092
Yin Z, Wang Z, Dai X et al (2020) Highly luminescent AuAg nanoclusters with aggregation-induced emission for high-performance white LED application. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 8(40):15336–15343. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.0c05722
Bai H, Tu Z, Liu Y et al (2020) Dual-emission carbon dots-stabilized copper nanoclusters for ratiometric and visual detection of Cr2O72− ions and Cd2+ ions. J Hazard Mater 386:121654. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121654
Huang Y, Huang J, Wang Y et al (2020) Progressive aggregation-induced emission strategy for imaging of aluminum ions in cellular microenvironment. Talanta 211:120699. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.120699
Bera D, Goswami N (2021) Driving forces and routes for aggregation-induced emission-based highly luminescent metal nanocluster assembly. J Phys Chem Lett 12(37):9033–9046. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jpclett.1c02406
Li X, Zhang X, Cao H et al (2021) Tb3+ tuning AIE self-assembly of copper nanoclusters for sensitively sensing trace fluoride ions. Sensors Actuators B Chem 342:130071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130071
Huang Y, Liu W, Feng H et al (2016) Luminescent nanoswitch based on organic-phase copper nanoclusters for sensitive detection of trace amount of water in organic solvents. Anal Chem 88(14):7429–7434. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02149
Ru Y, Waterhouse GIN, Lu S (2022) Aggregation in carbon dots. Aggregate 3:296. https://doi.org/10.1002/agt2.296
Wang B, Cai H, Waterhouse GIN et al (2022) Carbon dots in bioimaging, biosensing and therapeutics: a comprehensive review. Small Sci 2(6):2200012
Ru Y, Ai L, Jia T et al (2020) Recent advances in chiral carbonized polymer dots: from synthesis and properties to applications. Nano Today 34:100953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2020.100953
Chen B, Liu M, Zhan L et al (2018) Terbium(III) modified fluorescent carbon dots for highly selective and sensitive ratiometry of stringent. Anal Chem 90(6):4003–4009. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.7b05149
Lin L, Luo Y, Tsai P et al (2018) Metal ions doped carbon quantum dots: synthesis, physicochemical properties, and their applications. Trends Anal Chem 103:87–101. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2018.03.015
Liu L, Zhang C, Yu Y et al (2018) Determination of DNA based on fluorescence quenching of terbium doped carbon dots. Microchimica Acta 185(11):514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3053-6
Tian X, Fan Z (2022) Comparison between terbium-doped carbon dots and terbium-functionalized carbon dots: characterization, optical properties, and applications in anthrax biomarker detection. J Lumin 244:118732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2022.118732
Shen J, Fan Z (2023) Ce3+-induced fluorescence amplification of copper nanoclusters based on aggregation-induced emission for specific sensing 2,6-pyridine dicarboxylic acid. J Fluoresc 33(1):135–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10895-022-03044-8
Gao H, Zhang P, Guan T et al (2021) Rapid and accurate detection of phosphate in complex biological fluids based on highly improved antenna sensitization of lanthanide luminescence. Talanta 231:122243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122243
Han L, Liu S, Yang Y et al (2020) A lanthanide coordination polymer as a ratiometric fluorescent probe for rapid and visual sensing of phosphate based on the target-triggered competitive effect. J Mater Chem C 8:13063–13071. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0tc02436h
Spivakov BY, Maryutina TA, Muntau H (1999) Phosphorus speciation in water and sediments. Pure Appl Chem 71:2161–2176. https://doi.org/10.1351/pac199971112161
Sarwar M, Leichner J, Naja GM et al (2019) Smart-phone, paper-based fluorescent sensor for ultra-low inorganic phosphate detection in environmental samples. Microsystems and nanoengineering 5:56. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41378-019-0096-8
Warwick C, Guerreiro A, Soares A (2013) Sensing and analysis of soluble phosphates in environmental samples: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 41:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2012.07.012
Wu Z, Yang H, Pan S et al (2020) Fluorescence-scattering dual-signal response of carbon dots@ZIF-90 for phosphate ratiometric detection. ACS sensors 5(7):2211–2220. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.0c00853
Zhao H, Liu L, Liu Z et al (2011) Highly selective detection of phosphate in very complicated matrixes with an off-on fluorescent probe of europium-adjusted carbon dots. Chem Commun 47(9):2604–2606. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cc04399k
Vervloet MG, Sezer S, Massy ZA et al (2017) The role of phosphate in kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(1):27–38. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2016.164
Han M, Kim DH (2002) Naked-eye detection of phosphate ions in water at physiological pH: a remarkably selective and easy-to-assemble colorimetric phosphate-sensing probe. Angewandte Chemie Int Ed 41(20):3809–3811
Samy R, Faustino PJ, Adams W et al (2010) Development and validation of an ion chromatography method for the determination of phosphate-binding of lanthanum carbonate. J Pharm Biomed Anal 51(5):1108–1112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2009.11.017
Chai S, He J, Zhan L et al (2019) Dy(III)-induced aggregation emission quenching effect of single-layered graphene quantum dots for selective detection of phosphate in the artificial wetlands. Talanta 196:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.12.032
Huang Y, Feng H, Liu W et al (2017) Cation-driven luminescent self-assembled dots of copper nanoclusters with aggregation-induced emission for beta-galactosidase activity monitoring. J Mater Chem B 5(26):5120–5127. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7tb00901a
Sahu DK, Singha D, Sahu K (2019) Sensing of iron(III)-biomolecules by surfactant-free fluorescent copper nanoclusters. Sens Bio-sensing Res 22:100250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2018.100250
Zhang Q, Mei H, Zhou W et al (2021) Cerium ion(III)-triggered aggregation-induced emission of copper nanoclusters for trace-level p-nitrophenol detection in water. Microchem J 162:105842. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2020.105842
Lu W, Qin X, Liu S et al (2012) Economical, green synthesis of fluorescent carbon nanoparticles and their use as probes for sensitive and selective detection of mercury(II) ions. Anal Chem 84(12):5351–5357. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac3007939
Zhang R, Chen W (2014) Nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots: facile synthesis and application as a “turn-off” fluorescent probe for detection of Hg2+ ions. Biosens Bioelectron 55:83–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2013.11.074
Wang S, Liu S, Zhang J et al (2019) Highly fluorescent nitrogen-doped carbon dots for the determination and the differentiation of the rare earth element ions. Talanta 198:501–509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.01.113
Jiang K, Zhang L, Lu J et al (2016) Triple-mode emission of carbon dots: applications for advanced anti-counterfeiting. Angew Chem 55(25):7231–7235
Hu X, Wang W, Huang Y (2016) Copper nanocluster-based fluorescent probe for sensitive and selective detection of Hg2+ in water and food stuff. Talanta 154:409–415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.095
Zhang Q, Zhao D, Zhang C et al (2018) An effective signal amplifying strategy for copper (II) sensing by using in situ fluorescent proteins as energy donor of FRET. Sensors Actuators B Chem 259:633–641. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.118
Xie H, Bei F, Hou J et al (2018) A highly sensitive dual-signaling assay via inner filter effect between g-C3N4 and gold nanoparticles for organophosphorus pesticides. Sensors Actuators B Chem 255:2232–2239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.024
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection and analysis were performed by Jingxiang Shen; the first draft of the manuscript was written by Jingxiang Shen; review, supervision, and editing were performed by Zhefeng Fan. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.14 mb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, J., Fan, Z. Construction of nanohybrid Tb@CDs/GSH-CuNCs as a ratiometric probe to detect phosphate anion based on aggregation-induced emission and FRET mechanism. Microchim Acta 190, 427 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06005-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-06005-5