Abstract
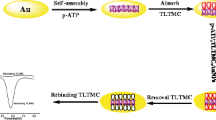
A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor was designed for the selective determination of gatifloxacin (GTX) based on dual functional monomers. Multi-walled carbon nanotube (MWCNT) enhanced the current intensity and zeolitic imidazolate framework 8 (ZIF8) provided a large surface area to produce more imprinted cavities. In the electropolymerization of molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP), p-aminobenzoic acid (p-ABA) and nicotinamide (NA) were used as dual functional monomers, and GTX was the template molecule. Taking [Fe(CN)6]3−/4− as an electrochemical probe, an oxidation peak on the glassy carbon electrode was located at about 0.16 V (vs. saturated calomel electrode). Due to the diverse interactions among p-ABA, NA, and GTX, the MIP-dual sensor exhibited higher specificity towards GTX than MIP-p-ABA and MIP-NA sensors. The sensor had a wide linear range from 1.00 × 10−14 to 1.00 × 10−7 M with a low detection limit of 2.61 × 10−15 M. Satisfactory recovery between 96.5 and 105% with relative standard deviation from 2.4 to 3.7% in real water samples evidenced the potential of the method in antibiotic contaminant determination.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
No data was used for the research described in the article.
References
Jiang Z, Li G, Zhang M (2016) Electrochemical sensor based on electro-polymerization of β-cyclodextrin and reduced-graphene oxide on glassy carbon electrode for determination of gatifloxacin. Sens Actuators B Chem 228:59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.013
Chen A, Li R, Zhong Y, Deng Q, Yin X, Li H, Kong L, Yang R (2022) A novel chiral fluorescence probe based on carbon dots-copper(II) system for ratio fluorescence detection of gatifloxacin. Sens. Actuators B Chem 359:131602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2022.131602
Huang F, Chen L, Zhang C, Liu F, Li H (2022) Prioritization of antibiotic contaminants in China based on decennial national screening data and their persistence, bioaccumulation and toxicity. Sci. Total Environ 806:150636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150636
Jia A, Wan Y, Xiao Y, Hu J (2012) Occurrence and fate of quinolone and fluoroquinolone antibiotics in a municipal sewage treatment plant. Water Res 46:387–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2011.10.055
Domingos LC, Moreira MV, Keller KM, Viana FA, Melo MM, Soto-Blanco B (2017) Simultaneous quantification of gatifloxacin, moxifloxacin, and besifloxacin concentrations in cornea and aqueous humor by LC-QTOF/MS after topical ocular dosing. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods 83:87–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vascn.2016.09.006
Zhang J, Shu B, Gao Y, Gui X, He L-F, Zhang K (2022) Multicolor fluorescence digital mapping of rare-earth ion-labeled porous silica nanoprobes for the recognition of various antibiotic residues in milk. Chin J Anal Chem 50:100181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjac.2022.100181
Yi J, Meng M, Liu ZQ, Zhi JF, Zhang YY, Xu J, Wang YB, Liu JT, Xi RM (2012) Development of an electrochemical immunoassay for detection of gatifloxacin in swine urine. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B 13:118–125. https://doi.org/10.1631/jzus.B1100073
Zan G, Wu T, Dong W, Zhou J, Tu T, Xu R, Chen Y, Wang Y, Wu Q (2022) Two-level biomimetic designs enable intelligent stress dispersion for super-foldable C/NiS nanofiber free-standing electrode. Adv Fiber Mater 4:1177–1190. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00162-7
Huang Y, Ye D, Yang J, Lu H, Li L, Ding Y (2022) A novel dual-signal molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor based on NiFe prussian blue analogue and SnS2 for detection of p-Hydroxyacetophenone. Chem Eng J 435:134981. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.134981
Mohammadinejad A, Abouzari-Lotf E, Aleyaghoob G, Rezayi M, KazemiOskuee R (2022) Application of a transition metal oxide/carbon-based nanocomposite for designing a molecularly imprinted poly (l-cysteine) electrochemical sensor for curcumin. Food Chem 386:132845. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132845
Zan G, Wu T, Zhu F, He P, Cheng Y, Chai S, Wang Y, Huang X, Zhang W, Wan Y, Peng X, Wu Q (2021) A biomimetic conductive super-foldable material. Matter 4:3232–3247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matt.2021.07.021
Chai S, Zan G, Dong K, Wu T, Wu Q (2021) Approaching superfoldable thickness-limit carbon nanofiber membranes transformed from water-soluble PVA. Nano Lett 21:8831–8838. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.nanolett.1c03241
Sui R, Zan G, Wen M, Li W, Liu Z, Wu Q, Fu Y (2022) Dual carbon design strategy for anodes of sodium-ion battery: mesoporous CoS2/CoO on open framework carbon-spheres with rGO encapsulating. ACS Appl Mater 14:28004–28013. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.2c06551
Zan G, Wu T, Zhang Z, Li J, Zhou J, Zhu F, Chen H, Wen M, Yang X, Peng X, Chen J, Wu Q (2022) Bioinspired nanocomposites with self-adaptive stress dispersion for super-foldable electrodes. Adv Sci 9:e2103714. https://doi.org/10.1002/advs.202103714
Huang Y, Lin J, Duan Y, Yu C, Li L, Ding Y (2022) Preparation of carbon fiber composite modified by cobalt lanthanum oxides and its electrochemical simultaneous determination of amlodipine and acetaminophen. Adv Fiber Mater 4:1153–1163. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42765-022-00159-2
Li Y, Zhang L, Dang Y, Chen Z, Zhang R, Li Y, Ye BC (2019) A robust electrochemical sensing of molecularly imprinted polymer prepared by using bifunctional monomer and its application in detection of cypermethrin. Biosens Bioelectron 127:207–214. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.002
Pan Y, Shang L, Zhao F, Zeng B (2015) A novel electrochemical 4-nonyl-phenol sensor based on molecularly imprinted poly (o-phenylenediamine-co-o-toluidine)−nitrogen-doped graphene nanoribbons−ionic liquid composite film. Electrochim Acta 151:423–428. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.044
Regasa MB, Soreta TR, Femi OE, Ramamurthy PC, Subbiahraj S (2020) Novel multifunctional molecular recognition elements based on molecularly imprinted poly (aniline-co-itaconic acid) composite thin film for melamine electrochemical detection. Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research 27:100318. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sbsr.2019.100318
Jin H, Ye D, Shen L, Fu R, Tang Y, Jung JC, Zhao H, Zhang J (2022) Perspective for single atom nanozymes based sensors: advanced materials, sensing mechanism, selectivity regulation, and applications. Anal Chem 94:1499–1509. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.1c04496
Shen L, Khan MA, Wu X, Cai J, Lu T, Ning T, Liu Z, Lu W, Ye D, Zhao H, Zhang J (2022) Fe-N-C single-atom nanozymes based sensor array for dual signal selective determination of antioxidants. Biosens. Bioelectron 205:114097. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2022.114097
Han W, Wang W, Fan J, Jia R, Yang X, Wu T, Wu Q (2022) A novel Ag/ZnO core–shell structure for efficient sterilization synergizing antibiotics and subsequently removing residuals. Green Energy Environ. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gee.2022.07.004
Zhang Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Kuang X, Ma H, Wei Q (2020) Directly assembled electrochemical sensor by combining self-supported CoN nanoarray platform grown on carbon cloth with molecularly imprinted polymers for the detection of Tylosin. J Hazard Mater 398:122778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.122778
Fu K, Zhang R, He J, Bai H, Zhang G (2019) Sensitive detection of ketamine with an electrochemical sensor based on UV-induced polymerized molecularly imprinted membranes at graphene and MOFs modified electrode. Biosens Bioelectron 143:111636. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111636
Hatamluyi B, Rezayi M, Beheshti HR, Boroushaki MT (2020) Ultra-sensitive molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor for patulin detection based on a novel assembling strategy using Au@Cu-MOF/N-GQDs. Sens Actuators B Chem 318:128219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128219
Yang S, Yang M, Yao X, Fa H, Wang Y, Hou C (2020) A zeolitic imidazolate framework/carbon nanofiber nanocomposite based electrochemical sensor for simultaneous detection of co-existing dihydroxybenzene isomers. Sens Actuators B Chem 320:128294. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128294
Tong P, Meng Y, Liang J, Li J (2021) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical luminescence sensor based on core–shell magnetic particles with ZIF-8 imprinted material. Sens Actuators B Chem 330:129405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.129405
Ding K, Zhao C, Cao Z, Liu Z, Liu J, Zhan J, Ma C, Xi R (2009) Chemiluminescent detection of gatifloxacin residue in milk. Anal Lett 42:505–518. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032710802677100
Razzaq SN, Mariam I, Khan IU, Ashfaq M (2012) Development and validation of liquid chromatographic method for gatifloxacin and ketorolac tromethamine in combined dosage form. J Liq Chromatogr R T 35:651–661. https://doi.org/10.1080/10826076.2011.606584
Taherizadeh M, Jahani S, Moradalizadeh M, Foroughi MM (2023) Synthesis of a dual-functional terbium doped copper oxide nanoflowers for high-efficiently electrochemical sensing of ofloxacin, pefloxacin and gatifloxacin. Talanta 255:124216. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2022.124216
Zhu M, Li R, Lai M, Ye H, Long N, Ye J, Wang J (2020) Copper nanoparticles incorporating a cationic surfactant-graphene modified carbon paste electrode for the simultaneous determination of gatifloxacin and pefloxacin. J Electroanal Chem 857:113730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.113730
Phonklam K, Wannapob R, Sriwimol W, Thavarungkul P, Phairatana T (2020) A novel molecularly imprinted polymer PMB/MWCNTs sensor for highly-sensitive cardiac troponin T detection. Sens Actuators B Chem 308:127630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127630
Tan F, Zhai M, Meng X, Wang Y, Zhao H, Wang X (2021) Hybrid peptide-molecularly imprinted polymer interface for electrochemical detection of vancomycin in complex matrices. Biosens Bioelectron 184:113220. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113220
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 22274096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Y., Sun, X., Yang, J. et al. A molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensor with dual functional monomers for selective determination of gatifloxacin. Microchim Acta 190, 261 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05839-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05839-3