Abstract
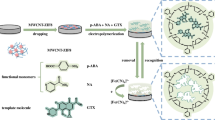
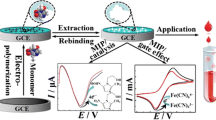
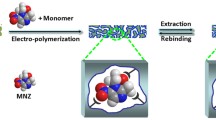
A novel tulathromycin (TLTMC) electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polymer (MIP) membranes was constructed. p-Aminothiophenol (p-ATP) and TLTMC were assembled on the surface of gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) modified on the gold electrode (GE) by the formation of Au-S bonds and hydrogen-bonding interactions. Besides, polymer membranes were formed by electropolymerization in a polymer solution containing p-ATP, tetrachloroaurate(III) acid (HAuCl4), tetrabutylammonium perchlorate (TBAP), and a template molecule TLTMC. A novel molecular imprinted sensor (MIS) in this experiment was achieved after the removal of TLTMC. Cyclic voltammetry (CV) and differential pulse voltammetry (DPV) measurements were used to illustrate the process of electropolymerization and its optimal conditions. The electrode with MIP obtained the linear of response range, which was between 3.0 × 10–12 mol L–1 and 7.0 × 10–9 mol L–1, and the limit of detection was 1.0 × 10–12 mol L–1. All the obtained results indicate that the MIS tends to be an effective electrochemical technique for the determination of TLTMC in real-time and in a complicated matrix.

Schematic illustration of the facrication of the tulathromycin (TLTMC) electrochemical sensors








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang X-H, Zhao Y-D, He L-M, Liang Z-S, Guo L-L, Zeng Z-L, Chen Z-L, Zhang M, Fang B-H (2012) Development of high performance liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for the detection of tulathromycin in swine plasma. J Integrative Agric 11(3):465–473
Gáler D, Hessong S, Beato B, Risk J, Inskeep P, Weerasinghe C, Schneider RP, Langer C, LaPerle J, Renouf D (2004) An analytical method for the analysis of tulathromycin, an equilibrating triamilide, in bovine and porcine plasma and lung. J Agric Food Chem 52(8):2179–2191
Bolard J (1986) How do the polyene macrolide antibiotics affect the cellular membrane properties? Biochim Biophys Acta 864(3):257–304
Godinho K, Rae A, Windsor G, Tilt N, Rowan T, Sunderland S (2004) Efficacy of tulathromycin in the treatment of bovine respiratory disease associated with induced Mycoplasma bovis infections in young dairy calves. Vet Therapeut: Res Appl Vet Med 6(2):96–112
Nowakowski M, Inskeep P, Risk J, Skogerboe T, Benchaoui H, Meinert T, Sherington J, Sunderland S (2003) Pharmacokinetics and lung tissue concentrations of tulathromycin, a new triamilide antibiotic, in cattle. Vet Therapeut: Res Appl Vet Med 5(1):60, Vet Therapeut: Res Appl Vet Med 74
Evans NA (2005) Tulathromycin: an overview of a new triamilide antibiotic for livestock respiratory disease. Vet Therapeut 6(2):83–95
González de la Huebra MJ, Vincent U, von Holst C (2007) Sample preparation strategy for the simultaneous determination of macrolide antibiotics in animal feedingstuffs by liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection (HPLC-ECD). J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 43(5):1628–1637
Codony R, Compano R, Granados M, García-Regueiro JA, Prat MD (2002) Residue analysis of macrolides in poultry muscle by liquid chromatography–electrospray mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A 959(1):131–141
Civitareale C, Fiori M, Ballerini A, Brambilla G (2004) Identification and quantification method of spiramycin and tylosin in feedingstuffs with HPLC-UV/DAD at 1 ppm level. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 36(2):317–325
Shaikh K, Patil S, Devkhile A (2008) Development and validation of a reversed-phase HPLC method for simultaneous estimation of ambroxol hydrochloride and azithromycin in tablet dosage form. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 48(5):1481–1484
Khashaba PY (2002) Spectrofluorimetric analysis of certain macrolide antibiotics in bulk and pharmaceutical formulations. J Pharmaceut Biomed Anal 27(6):923–932
Holthoff EL, Bright FV (2007) Molecularly templated materials in chemical sensing. Anal Chim Acta 594(2):147–161
Matsui J, Nicholls IA, Takeuchi T (1998) Molecular recognition in cinchona alkaloid molecular imprinted polymer rods. Anal Chim Acta 365(1):89–93
Matsui J, Kato T, Takeuchi T, Suzuki M, Yokoyama K, Tamiya E, Karube I (1993) Molecular recognition in continuous polymer rods prepared by a molecular imprinting technique. Anal Chem 65(17):2223–2224
Lin L-Q, Li Y-C, Fu Q, He L-C, Zhang J, Zhang Q-Q (2006) Preparation of molecularly imprinted polymer for sinomenine and study on its molecular recognition mechanism. Polymer 47(11):3792–3798
Takeuchi T, Matsui J (2000) Miniaturized molecularly imprinted continuous polymer rods. J High Resolut Chromatogr 23(1):44–46
Li ZY, Liu ZS, Zhang QW, Duan HQ (2007) Chiral separation by (<i > S</i>)-naproxen imprinted monolithic column with mixed functional monomers. Chinese Chem Lett 18(3):322–324
Xu YL, Liu ZS, Wang HF, Yan C, Gao RY (2005) Chiral recognition ability of an (S)‐naproxen‐imprinted monolith by capillary electrochromatography. Electrophoresis 26(4/5):804–811
Liu Z-S, Xu Y-L, Yan C, Gao R-Y (2004) Preparation and characterization of molecularly imprinted monolithic column based on 4-hydroxybenzoic acid for the molecular recognition in capillary electrochromatography. Anal Chim Acta 523(2):243–250
Aşır S, Uzun L, Türkmen D, Say R, Denizli A (2005) Ion‐selective imprinted superporous monolith for cadmium removal from human plasma. Sep Sci Technol 40(15):3167–3185
Zou H, Huang X, Ye M, Luo Q (2002) Monolithic stationary phases for liquid chromatography and capillary electrochromatography. J Chromatogr A 954(1):5–32
Feng L, Liu Y, Hu J (2004) Molecularly imprinted TiO2 thin film by liquid phase deposition for the determination of L-glutamic acid. Langmuir 20(5):1786–1790
Mao Y, Bao Y, Gan S, Li F, Niu L (2011) Electrochemical sensor for dopamine based on a novel graphene-molecular imprinted polymers composite recognition element. Biosens Bioelectron 28(1):291–297
Yuan L, Zhang J, Zhou P, Chen J, Wang R, Wen T, Li Y, Zhou X, Jiang H (2011) Electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted membranes at platinum nanoparticles-modified electrode for determination of 17β-estradiol. Biosenso Bioelectron 29(1):29–33
Wang Y, Zhou Y, Sokolov J, Rigas B, Levon K, Rafailovich M (2008) A potentiometric protein sensor built with surface molecular imprinting method. Biosens Bioelectron 24:162–166
Suryanarayanan V, Wu CT, Ho KC (2010) Molecularly imprinted electrochemical sensors. Electroanalysis 22(16):1795–1811
Wang J (2003) Nanoparticle-based electrochemical DNA detection. Anal Chim Acta 500(1):247–257
Pingarrón JM, Yáñez-Sedeño P, González-Cortés A (2008) Gold nanoparticle-based electrochemical biosensors. Electrochim Acta 53(19):5848–5866
Riskin M, Tel-Vered R, Bourenko T, Granot E, Willner I (2008) Imprinting of molecular recognition sites through electropolymerization of functionalized Au nanoparticles: development of an electrochemical TNT sensor based on π-donor − acceptor interactions. J Am Chem Soc 130(30):9726–9733
Gholivand MB, Torkashvand M, Malekzadeh G (2012) Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on computationally designed molecularly imprinted polymers for determination of cyanazine in food samples. Anal Chim Acta 713:36–44
Matsui J, Akamatsu K, Nishiguchi S, Miyoshi D, Nawafune H, Tamaki K, Sugimoto N (2004) Composite of Au nanoparticles and molecularly imprinted polymer as a sensing material. Anal Chem 76(5):1310–1315
Xie C, Li H, Li S, Wu J, Zhang Z (2009) Surface molecular self-assembly for organophosphate pesticide imprinting in electropolymerized poly (p-aminothiophenol) membranes on a gold nanoparticle modified glassy carbon electrode. Anal Chem 82(1):241–249
Fodey T, Leonard P, O’Mahony J, O’Kennedy R, Danaher M (2011) Developments in the production of biological and synthetic binders for immunoassay and sensor-based detection of small molecules. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 30(2):254–269
Scheuch E, Spieker J, Venner M, Siegmund W (2007) Quantitative determination of the macrolide antibiotic tulathromycin in plasma and broncho-alveolar cells of foals using tandem mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr B 850(1):464–470
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31371768), Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology Ministry of Education(KLIB-KF201109), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in Jiangnan University, and Priority Academic Program Development of Jiangsu Higher Education Institutions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 246 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, J., Ji, J., Wang, Y. et al. Electrochemical sensor for determination of tulathromycin built with molecularly imprinted polymer film. Anal Bioanal Chem 407, 1951–1959 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8440-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-014-8440-1