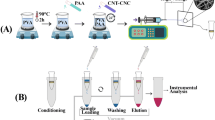
Abstract
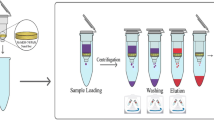
Composite nanofibers, namely, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), citric acid (CA), β-cyclodextrin (β–CD), and copper oxide nanoparticles (PVA/CA/β-cyclodextrin/CuO NPs), were developed as a novel, green, and efficient adsorbent in the pipette tip-micro-solid-phase extraction method (PT-µSPE), for the simultaneous extraction of three antidepressants drugs namely imipramine (IMP), citalopram (CIT), and clozapine (CLZ) in biological fluids before quantification by gas chromatography (GC-FID). Based on the obtained results from field emission scanning electron microscopy (FE-SEM), energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX), Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR), and X-ray diffraction (XRD), the successful synthesis of composite nanofibers was approved. Due to the presence of β-cyclodextrins and CuO NPs rich of functional groups on their surface, the nanofibers have high extraction efficiency. Under the optimal conditions, the linear range for imipramine, citalopram, and clozapine was 0.1 to 1000.0 ng mL−1 with a determination coefficient ≥ 0.99. The limits of detection (LODs) were in the range 0.03 to 0.15 ng mL−1. The relative standard deviation was 4.8 to 8.7% (within-day, n = 4) and 5.1 to 9.2% (between-day, n = 3) for 3 consecutive days. In addition, excellent clean-up was achieved which is a great advantage over other sample preparation methods. Finally, the ability of the developed method to extract the target analytes from the biological samples was evaluated.
Graphical Abstract










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schultz MM, Furlong ET (2008) Trace analysis of antidepressant pharmaceuticals and their select degradates in aquatic matrixes by LC/ESI/MS/MS. Anal Chem 80:1756–1762. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac702154e
Woolf AD, Erdman AR, Nelson LS, Caravati EM, Cobaugh DJ, Booze LL, Wax PM, Manoguerra AS, Scharman EJ, Olson KR (2007) Tricyclic antidepressant poisoning: an evidence-based consensus guideline for out-of-hospital management. Clin Toxicol 45:203–233. https://doi.org/10.1080/15563650701226192
Maj J, Dziedzicka-Wasylewska M, Rogoż R, Rogóż Z (1998) Effect of antidepressant drugs administered repeatedly on the dopamine D3 receptors in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 351:31–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0014-2999(98)00297-0
Farajzadeh MA, Abbaspour M (2018) Development of new extraction method based on liquid–liquid–liquid extraction followed by dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction for extraction of three tricyclic antidepressants in plasma samples. Biomed Chromatogr 32:e4251. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.4251
Behpour M, Nojavan S, Asadi S, Shokri A (2020) Combination of gel-electromembrane extraction with switchable hydrophilicity solvent-based homogeneous liquid-liquid microextraction followed by gas chromatography for the extraction and determination of antidepressants in human serum, breast milk and wastewater. J Chromatogr A 1621:461041. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2020.46104
Chen Y, Guo Z, Wang X, Qiu C (2008) Sample preparation. J Chromatogr A 1184:191–219. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2007.10.026
Frahnert C, Rao ML, Grasmäder K (2003) Analysis of eighteen antidepressants, four atypical antipsychotics and active metabolites in serum by liquid chromatography: a simple tool for therapeutic drug monitoring. J Chromatogr B 794:35–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1570-0232(03)00393-3
Xu R, Lee HK (2014) Application of electro-enhanced solid phase microextraction combined with gas chromatography–mass spectrometry for the determination of tricyclic antidepressants in environmental water samples. J Chromatogr A 1350:15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2014.05.024
Xiong C, Ruan J, Cai Y, Tang Y (2009) Extraction and determination of some psychotropic drugs in urine samples using dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction followed by high-performance liquid chromatography. J Pharm Biomed Anal 49:572–578. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2008.11.036
Prosen H, Zupančič-Kralj L (1999) Solid-phase microextraction. TrAC - Trends Anal Chem 18:272–282. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0165-9936(98)00109-5
Habila MA, Alothman ZA, El-Toni AM, Labis JP, Soylak M (2016) Synthesis and application of Fe3O4@ SiO2@ TiO2 for photocatalytic decomposition of organic matrix simultaneously with magnetic solid phase extraction of heavy metals prior to ICP-MS analysis. Talanta 154:539–547. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.03.081
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Goudarzi A, Soylak M, Langroodi SM (2015) Magnetic nanoparticle based dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction for the determination of malachite green in water samples: optimized experimental design. NJC 39:9813–9823. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5NJ01730K
Tabani H, Alexovič M, Sabo J, Payán MR (2021) An overview on the recent applications of agarose as a green biopolymer in micro-extraction-based sample preparation techniques. Talanta 224:121892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.121892
HejabriKandeh S, Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H (2021) Simultaneous trace-level monitoring of seven opioid analgesic drugs in biological samples by pipette-tip micro solid phase extraction based on PVA-PAA/CNT-CNC composite nanofibers followed by HPLC-UV analysis. MCA 188:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04931-w
Uhlschmied C, Krieg C, Abel G, Popp M, Huck C, Bonn G (2013) Evaluation of Commercial Solid-Phase Extraction (SPE) Carrier materials for the selective automated enrichment of monoterpenoides and their analysis in cough drops, mouthwashes and bath additives by gas-chromatography mass spectrometry (GC-MS). J Anal Chem 7: https://doi.org/10.2174/1874065001307010012
Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2021) Preparation of Polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF electrospun nanofiber as an efficient fiber coating material for headspace solid-phase microextraction of diazinon and chlorpyrifos followed by CD-IMS analysis. Food Chem 350:129242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129242
Cui J, Lu T, Li F, Wang Y, Lei J, Ma W, Zou Y, Huang C (2021) Flexible and transparent composite nanofibre membrane that was fabricated via a “green” electrospinning method for efficient particulate matter 2.5 capture. J Colloid Interface Sci 582:506–514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2020.08.075
Amini S, Ebrahimzadeh H (2022) PVA/Stevia/MIL-88A@ AuNPs composite nanofibers as a novel sorbent for simultaneous extraction of eight agricultural pesticides in food and vegetable samples followed by HPLC-UV analysis. Food Chem 386:132734. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2022.132734
Amini S, Ebrahimzdeh H, Seidi S, Jalilian N (2020) Preparation of electrospun polyacrylonitrile/Ni-MOF-74 nanofibers for extraction of atenolol and captopril prior to HPLC-DAD. MCA 187:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04483-5
Celebioglu A, Uyar T (2013) Electrospinning of nanofibers from non-polymeric systems: electrospun nanofibers from native cyclodextrins. J Colloid Interface Sci 404:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2013.04.034
Sathiyavimal S, Vasantharaj S, Veeramani V, Saravanan M, Rajalakshmi G, Kaliannan T, Al-Misned FA, Pugazhendhi A (2021) Green chemistry route of biosynthesized copper oxide nanoparticles using Psidium guajava leaf extract and their antibacterial activity and effective removal of industrial dyes. J Environ Chem Eng 9:105033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2021.105033
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajjadi M, Sajadi SM, Issaabadi Z (2019) Green nanotechnology. In. Interface science and technology: Elsevier. 145–198.
Nasrollahzadeh M, Sajadi SM, Maham M (2015) Tamarix gallica leaf extract mediated novel route for green synthesis of CuO nanoparticles and their application for N-arylation of nitrogen-containing heterocycles under ligand-free conditions. RSC Adv 5:40628–40635. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5RA04012D
Maghsoudi M, Nojavan S, Alexovič M, Tabani H (2021) Two-phase agarose gel-electromembrane extraction: effect of organic solvent as an acceptor phase in electroendosmosis flow phenomenon. Pharm Biomed Anal 195:113862. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2020.113862
Velsankar K, Vinothini V, Sudhahar S, Kumar MK, Mohandoss S (2020) Green Synthesis of CuO nanoparticles via Plectranthus amboinicus leaves extract with its characterization on structural, morphological, and biological properties. Appl Nanosci 10:3953–3971. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-020-01504-w
Raghu A, Jeong HM (2008) Synthesis, characterization of novel dihydrazide containing polyurethanes based on N1, N2-bis [(4-hydroxyphenyl) methylene] ethanedihydrazide and various diisocyanates. J Appl Polym Sci 107:3401–3407. https://doi.org/10.1002/app.27447
Işik C, Teke M (2022) β-cyclodextrin based electrospun nanofibers for arginase immobilization and its application in the production of L-ornithine. J Polym Res 29:1–17. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10965-022-02968-w
Vidovix TB, Quesada HB, Januário EFD, Bergamasco R, Vieira AMS (2019) Green synthesis of copper oxide nanoparticles using Punica granatum leaf extract applied to the removal of methylene blue. Mater Lett 257:126685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2019.126685
Gunalan S, Sivaraj R, Venckatesh R (2012) Aloe barbadensis Miller mediated green synthesis of mono-disperse copper oxide nanoparticles: optical properties. SAA 97:1140–1144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2012.07.096
Antonoglou O, Lafazanis K, Mourdikoudis S, Vourlias G, Lialiaris T, Pantazaki A, Dendrinou-Samara C (2019) Biological relevance of CuFeO2 nanoparticles: antibacterial and anti-inflammatory activity, genotoxicity, DNA and protein interactions. Mater Sci Eng C 99:264–274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2019.01.112
Pooresmaeil M, Namazi H (2019) Preparation and characterization of polyvinyl alcohol/β-cyclodextrin/GO-Ag nanocomposite with improved antibacterial and strength properties. Polym Adv Technol 30:447–456. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.4484
Moghadam AG, Rajabi M, Asghari A (2018) Efficient and relatively safe emulsification microextraction using a deep eutectic solvent for influential enrichment of trace main anti-depressant drugs from complicated samples. J Chromatogr B 1072:50–59. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2017.09.042
Safari M, Shahlaei M, Yamini Y, Shakorian M, Arkan E (2018) Magnetic framework composite as sorbent for magnetic solid phase extraction coupled with high performance liquid chromatography for simultaneous extraction and determination of tricyclic antidepressants. Anal Chim Acta 1034:204–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2018.06.023
Nojavan S, Shaghaghi H, Rahmani T, Shokri A, Nasiri-Aghdam M (2018) Combination of electromembrane extraction and electro-assisted liquid-liquid microextraction: A tandem sample preparation method. J Chromatogr A 1563:20–27. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2018.05.068
Esrafili A, Yamini Y, Shariati S (2007) Hollow fiber-based liquid phase microextraction combined with high-performance liquid chromatography for extraction and determination of some antidepressant drugs in biological fluids. Anal Chim Acta 604:127–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.10.012
Sarıkaya M, Ulusoy HI, Morgul U, Ulusoy S, Tartaglia A, Yılmaz E, Soylak M, Locatelli M, Kabir A (2021) Sensitive determination of Fluoxetine and Citalopram antidepressants in urine and wastewater samples by liquid chromatography coupled with photodiode array detector. J Chromatogr A 1648:462215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2021.462215
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kharazmi, F., Hosseini, F.S. & Ebrahimzadeh, H. Polyvinyl alcohol/citric acid/β-cyclodextrin/CuONP composite nanofibers as an effective and green absorbent for the simultaneous extraction of three antidepressant drugs in biological fluids prior to GC-FID analysis. Microchim Acta 190, 218 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05800-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05800-4