Abstract
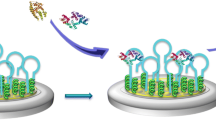
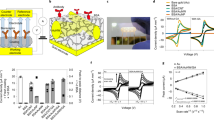
A reliable and brief ultralow fouling electrochemical sensing system capable of monitoring targets in complex biological media was constructed and validated based on gold nanoparticles-peptide hydrogel-modified screen-printed electrode. The self-assembled zwitterionic peptide hydrogel was prepared by a newly designed peptide sequence of Phe-Phe-Cys-Cys-(Glu-Lys)3 with the N-terminal modified with a fluorene methoxycarbonyl group. The thiol groups on cysteine of the designed peptide are able to self-assemble with AuNPs to form a three-dimensional nanonetwork structure, which showed satisfactory antifouling capability in complex biological media (human serum). The developed gold nanoparticles-peptide hydrogel-based electrochemical sensing platform displayed notably sensing properties for dopamine determination, with a wide linear range (from 0.2 nM to 1.9 μM), a low limit of detection (0.12 nM), and an excellent selectivity. This highly sensitive and ultralow fouling electrochemical sensor was fabricated via simple preparation with concise components that avoid the accumulation of layers with single functional material and complex activation processes. This ultralow fouling and highly sensitive strategy based on the gold nanoparticles-peptide hydrogel with a three-dimensional nanonetwork offers a solution to the current situation of various low-fouling sensing systems facing impaired sensitivity and provides a potential path for the practical application of electrochemical sensors.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
We confirm that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the article and its supplementary materials.
References
Ekker M (2021) Dopamine in health and disease. Biomedicines 9:1644–1646. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines9111644
Speranza L, di Porzio U, Viggiano D et al (2021) Dopamine: the neuromodulator of long-term synaptic plasticity, reward and movement control. Cells 10:735–753. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells10040735
Illenberger JM, Harrod SB, Mactutus CF et al (2020) HIV infection and neurocognitive disorders in the context of chronic drug abuse: evidence for divergent findings dependent upon prior drug history. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 15:715–728. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11481-020-09928-5
Kim H-S, Yang SM, Jang T-M et al (2018) Bioresorbable silicon nanomembranes and iron catalyst nanoparticles for flexible, transient electrochemical dopamine monitors. Adv Healthc Mater 7:1801071. https://doi.org/10.1002/adhm.201801071
Hou X, Huang W, Tong Y et al (2019) Hollow dummy template imprinted boronate-modified polymers for extraction of norepinephrine, epinephrine and dopamine prior to quantitation by HPLC. Microchim Acta 186:686–694. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3801-2
Wang J, Hu Y, Zhou Q et al (2019) Peroxidase-like activity of metal–organic framework [Cu(PDA)(DMF)] and its application for colorimetric detection of dopamine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11:44466–44473. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b17488
Zhu J, Peng X, Nie W et al (2019) Hollow copper sulfide nanocubes as multifunctional nanozymes for colorimetric detection of dopamine and electrochemical detection of glucose. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111450. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111450
Roychoudhury A, Francis KA, Patel J et al (2020) A decoupler-free simple paper microchip capillary electrophoresis device for simultaneous detection of dopamine, epinephrine and serotonin. RSC Adv 10:25487–25495. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0RA03526B
Rusheen AE, Gee TA, Jang DP et al (2020) Evaluation of electrochemical methods for tonic dopamine detection in vivo. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 132:116049–116060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2020.116049
Sajid M, Baig N, Alhooshani K (2019) Chemically modified electrodes for electrochemical detection of dopamine: challenges and opportunities. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 118:368–385. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.05.042
Kannan K, Radhika D, Nesaraj AS et al (2020) Photocatalytic, antibacterial and electrochemical properties of novel rare earth metal oxides-based nanohybrids. Mater Sci Energy Technol 3:853–861. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mset.2020.10.008
Kim D-S, Kang E-S, Baek S et al (2018) Electrochemical detection of dopamine using periodic cylindrical gold nanoelectrode arrays. Sci Rep 8:14049–14058. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-32477-0
Senel M, Dervisevic E, Alhassen S et al (2020) Microfluidic electrochemical sensor for cerebrospinal fluid and blood dopamine detection in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Anal Chem 92:12347–12355. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.0c02032
Dalirirad S, Steckl AJ (2020) Lateral flow assay using aptamer-based sensing for on-site detection of dopamine in urine. Anal Biochem 596:113637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2020.113637
Wu S, Sun T, Wang H et al (2020) A sandwich-structured, layered CoTMPyP/Sr2Nb3O10 nanocomposite for simultaneous voltammetric determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. J Electroanal Chem 873:114403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2020.114403
Li G, Zhong P, Ye Y et al (2019) A highly sensitive and stable dopamine sensor using shuttle-like α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles/electro-reduced graphene oxide composites. J Electrochem Soc 166:1552–1561. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1071915jes
Jiang C, Wang G, Hein R et al (2020) Antifouling strategies for selective in vitro and in vivo sensing. Chem Rev 120:3852–3889. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.9b00739
Liu N, Song J, Lu Y et al (2019) Electrochemical aptasensor for ultralow fouling cancer cell quantification in complex biological media based on designed branched peptides. Anal Chem 91:8334–8340. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01129
Lin P-H, Li B-R (2020) Antifouling strategies in advanced electrochemical sensors and biosensors. Analyst 145:1110–1120. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AN02017A
Liu N, Hui N, Davis JJ et al (2018) Low fouling protein detection in complex biological media supported by a designed multifunctional peptide. ACS Sens 3:1210–1216. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.8b00318
Hui N, Sun X, Niu S et al (2017) PEGylated polyaniline nanofibers: antifouling and conducting biomaterial for electrochemical DNA sensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2914–2923. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b11682
He X, Sathishkumar G, Gopinath K et al (2021) One-step self-assembly of biogenic Au NPs/PEG-based universal coatings for antifouling and photothermal killing of bacterial pathogens. Chem Eng J 421:130005. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130005
Baggerman J, Smulders MMJ, Zuilhof H (2019) Romantic surfaces: a systematic overview of stable, biospecific, and antifouling zwitterionic surfaces. Langmuir 35:1072–1084. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.8b03360
Zhao S, Liu N, Wang W et al (2021) An electrochemical biosensor for alpha-fetoprotein detection in human serum based on peptides containing isomer D-Amino acids with enhanced stability and antifouling property. Biosens Bioelectron 190:113466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2021.113466
Ren R, Cai G, Yu Z et al (2018) Metal-polydopamine framework: an innovative signal-generation tag for colorimetric immunoassay. Anal Chem 90:11099–11105. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b03538
Yu Z, Gong H, Xu J et al (2022) Liposome-embedded Cu2–xAgxS nanoparticle-mediated photothermal immunoassay for daily monitoring of cTnI protein using a portable thermal imager. Anal Chem 94:7408–7416. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c01133
Sabaté del Río J, Henry OYF, Jolly P et al (2019) An antifouling coating that enables affinity-based electrochemical biosensing in complex biological fluids. Nat Nanotechnol 14:1143–1149. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41565-019-0566-z
Hanssen BL, Siraj S, Wong DKY (2016) Recent strategies to minimise fouling in electrochemical detection systems. Reviews in Anal Chem 35:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1515/revac-2015-0008
Lu L, Zhou L, Chen J et al (2018) Nanochannel-confined graphene quantum dots for ultrasensitive electrochemical analysis of complex samples. ACS Nano 12:12673–12681. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b07564
Gao N, Fan B, Li L et al (2021) Label-free antifouling photoelectrochemical sensing strategy for detecting breast tumor cells based on ligand–receptor interactions. ACS Appl Bio Mater 4:4479–4485. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsabm.1c00215
Zhou L, Hou H, Wei H et al (2019) In vivo monitoring of oxygen in rat brain by carbon fiber microelectrode modified with antifouling nanoporous membrane. Anal Chem 91:3645–3651. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.8b05658
Sun Q, Yan F, Yao L et al (2016) Anti-biofouling isoporous silica-micelle membrane enabling drug detection in human whole blood. Anal Chem 88:8364–8368. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02091
Wang W, Han R, Tang K et al (2021) Biocompatible peptide hydrogels with excellent antibacterial and catalytic properties for electrochemical sensing application. Anal Chim Acta 1154:338295. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338295
Divyashri G, Badhe RV, Sadanandan B et al (2022) Applications of hydrogel-based delivery systems in wound care and treatment: an up-to-date review. Polym Adv Technol 33:2025–2043. https://doi.org/10.1002/pat.5661
Nasalapure AV, Chalannavar RK, Kasai DR et al (2021) Novel polymeric hydrogel composites: synthesis, physicochemical, mechanical and biocompatible properties. Nano Express 2:030003. https://doi.org/10.1088/2632-959X/ac11bf
Ziegler C, Eychmüller A (2011) Seeded growth synthesis of uniform gold nanoparticles with diameters of 15-300 nm. J Phys Chem C 115:4502–4506. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp1106982
Li Y, Zeng R, Wang W et al (2022) Size-controlled engineering photoelectrochemical biosensor for human papillomavirus-16 based on CRISPR-Cas12a-induced disassembly of Z-scheme heterojunctions. ACS Sensors 7:1593–1601. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.2c00691
Gao Y, Zeng Y, Liu X et al (2022) Liposome-mediated in situ formation of type-I heterojunction for amplified photoelectrochemical immunoassay. Anal Chem 94:4859–4865. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00283
Yu Z, Gong H, Xu J et al (2022) Exploiting photoelectric activities and piezoelectric properties of NaNbO3 semiconductors for point-of-care immunoassay. Anal Chem 94:3418–3426. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.2c00066
Medintz IL, Stewart MH, Trammell SA et al (2010) Quantum-dot/dopamine bioconjugates function as redox coupled assemblies for in vitro and intracellular pH sensing. Nat Mater 9:676–684. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2811
Chakraborty P, Guterman T, Adadi N et al (2019) A self-healing, all-organic, conducting, composite peptide hydrogel as pressure sensor and electrogenic cell soft substrate. ACS Nano 13:163–175. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsnano.8b05067
Kim JH, Lim SY, Nam DH et al (2011) Self-assembled, photoluminescent peptide hydrogel as a versatile platform for enzyme-based optical biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1860–1865. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2010.01.026
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21974075) and the Taishan Scholar Program of Shandong Province of China (ts20110829).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, N., Zhao, S., Li, Y. et al. Gold nanoparticles-decorated peptide hydrogel for antifouling electrochemical dopamine determination. Microchim Acta 190, 199 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05785-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-023-05785-0