Abstract
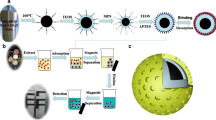
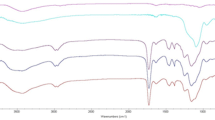
Magnetic molecular imprinted polymers (MIPs) based on 4-vinylbenzyltrimethylammonium chloride (VBTAC) and 4-vinylbenzoic acid (VBA) deep eutectic solvent as dual functional monomers was successfully synthesized for the specific recognition of laminarin. The MIPs were characterized by transmission electron microscopy, scanning electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, thermal gravimetric analysis, and vibrating sample magnetometer analysis. The results showed that the MIPs were spheres of a uniform size, with the surface rich in cavities and excellent superparamagnetism properties. The adsorption experiments showed that MIPs conform to pseudo-second-order kinetics and Langmuir isotherm adsorption. The maximum adsorption capacity under optimal conditions was 322.58 μg·mg−1 and the imprinting factor was 2.13. Under the optimized conditions, the limit of detection (LOD) of the developed material was 6.6 µM. Linearity of the material was obtained within the range 20–800 µM with a coefficient of determination (r2) being better 0.999. Relative standard deviations (RSDs) were less than 3.96%, and satisfactory recoveries were between 94.55 and 97.39%. The actual sample analysis manifested that MIPs could effectively separate laminarin from Laminarin japonica Aiesch.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Youssouf L, Lallemand L, Giraud P, Soulé F, Bhaw-Luximon A, Meilhac O, Hellencourt CLD, Jhurry D, Couprie J (2017) Ultrasound-assisted extraction and structural characterization by NMR of alginates and carrageenans from seaweeds. Carbohyd Polym 166:55–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.01.041
Abraham RE, Su P, Puri M, Raston CL, Zhang W (2019) Optimisation of biorefinery production of alginate, fucoidan and laminarin from brown seaweed Durvillaea potatorum. Algal Res 38:101389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.algal.2018.101389
Rhein-Knudsen N, Ale MT, Ajalloueian F, Yu L, Meyer AS (2017) Rheological properties of agar and carrageenan from Ghanaian red seaweeds. Food Hydrocolloid 63:50–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2016.08.023
Helbert W (2017) marine polysaccharide sulfatases. Front Mar Sci 4:486–498. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmars.2017.00006
Yang J, Lim SY (2021) Fucoidans and bowel health. Mar Drugs 19:436. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19080436
Li YT, Huo YF, Wang F, Wang C, Zhu Q, Wang YB, Fu LL, Zhou T (2020) Improved antioxidant and immunomodulatory activities of enzymatically degradedPorphyra haitanensis polysaccharides. J Food Biochem 44:e13189. https://doi.org/10.1111/jfbc.13189
Peng Y, Song Y, Wang Q, Hu Y, He Y, Ren D, Wu L, Liu S, Cong H, Zhou H (2019) In vitro and in vivo immunomodulatory effects of fucoidan compound agents. Int J Biol Macromol 127:48–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.197
Rasin AB, Silchenko AS, Kusaykin MI, Malyarenko OS, Zueva AO, Kalinovsky AI, Airong J, Surits VV, Ermakova SP (2020) Enzymatic transformation and anti-tumor activity of Sargassum horneri fucoidan. Carbohyd Polym 246:116635. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116635
Khotimchenko M, Tiasto V, Kalitnik A, Begun M, Khotimchenko R, Leonteva E, Bryukhovetskiy I, Khotimchenko Y (2020) Antitumor potential of carrageenans from marine red algae. Carbohyd Polym 246:116568. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2020.116568
Lai H, Yang L, Lin P, Lai S, Wang M (2020) Phagocytosis activity of three sulfated polysaccharides purified from a marine diatom cultured in a semi-continuous system. Int J Biol Macromol 155:951–960. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.11.054
Tang W, Liu D, Yin J, Nie S (2020) Consecutive and progressive purification of food-derived natural polysaccharide: Based on material, extraction process and crude polysaccharide. Trends Food Sci Tech 99:76–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2020.02.015
Zhou T, Ding L, Che G, Jiang W, Sang L (2019) Recent advances and trends of molecularly imprinted polymers for specific recognition in aqueous matrix: preparation and application in sample pretreatment. Trends Anal Chem 114:11–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2019.02.028
Huang Y, Pan J, Liu Y, Wang M, Deng S, Xia Z (2019) A SPE method with two MIPs in two Steps for improving the selectivity of MIPs. Anal Chem 91:8436–8442. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01453
Chen Z, Wright C, Dincel O, Chi T, Kameoka J (2020) A low-cost paper glucose sensor with molecularly imprinted polyaniline electrode. Sensors-Basel 20:1098. https://doi.org/10.3390/s20041098
Claude B, Morin P, Lafosse M, Belmont A, Haupt K (2008) Selective solid-phase extraction of a triterpene acid from a plant extract by molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 75:344–350. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2007.11.037
Karrat A, Palacios-Santander JM, Amine A, Cubillana-Aguilera L (2022) A novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective extraction and determination of quercetin in plant samples. Anal Chim Acta 1203:339709. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2022.339709
Zhao Q, Zhao H, Huang W, Yang X, Yao L, Liu J, Li J, Wang J (2019) Dual functional monomer surface molecularly imprinted microspheres for polysaccharide recognition in aqueous solution. Anal Methods-UK 11(21):2800–2808. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9AY00132H
Huang W, Yang X, Zhao S, Zhang M, Hu X, Wang J, Zhao H (2013) Fast and selective recognizes polysaccharide by surface molecularly imprinted film coated onto aldehyde-modified magnetic nanoparticles. Analyst 138:6653–6661. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an01149f
Li G, Row KH (2017) Magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and enrichment of polysaccharides from seaweed. J Sep Sci 44:4765–4772. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201700947
Zhang R, Zhang T, Lv Y, Qin P, Li H, Li J, Tan T (2019) Selective binding of heparin oligosaccharides in a magnetic thermoresponsive molecularly imprinted polymer. Talanta 201:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.04.050
Orihara K, Hikichi A, Arita T, Muguruma H, Yoshimi Y (2018) Heparin molecularly imprinted polymer thin flm on gold electrode by plasma-induced graft polymerization for label-free biosensor. J Pharmaceut Biomed 151:324–330. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.01.012
Ansari S (2017) Application of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer as a versatile and highly selective tool in food and environmental analysis: recent developments and trends. TrAC, Trends Anal Chem 90:89–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2017.03.001
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Li J, Wang X, Zhang Z, Choo J, Chen L (2021) Molecular Imprinting: green perspectives and strategies. Adv Mater 33:2100543. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.202100543
Arabi M, Ostovan A, Bagheri AR, Guo X, Li J, Ma J, Chen L (2020) Hydrophilic molecularly imprinted nanospheres for the extraction of rhodamine B followed by HPLC analysis: A green approach and hazardous waste elimination. Talanta 215:120933. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2020.120933
He X, Wang Y, Li H, Chen J, Liu Z, Xu F, Zhou Y (2021) Specific recognition of protein by deep eutectic solvent–based magnetic β-cyclodextrin molecularly imprinted polymer. Microchim Acta 188:702–715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04887-x
Costa AMS, Rodrigues JMM, Pérez-Madrigal MM, Dove AP, Mano JF (2020) Modular functionalization of Laminarin to create value-added naturally derived macromolecules. J Am Chem Soc 142:19689–19697. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.0c09489
Pessagno F, Hasanah AN, Manesiotis P (2018) Molecularly imprinted ‘traps’ for sulfonylureas prepared using polymerisable ion pairs. RSC Adv 8:14212–14220. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8RA01135D
Liu B, Han M, Guan G, Wang S, Liu R, Zhang Z (2011) Highly-controllable molecular imprinting at superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for ultrafast enrichment and separation. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C 115:17320–17327. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp205327q
Funding
This work was financially supported by Jiangxi Provincial Natural Science Foundation Key Project (No.20192ACBL20028), National Natural Science Foundation of China (No.81760708), Jiangxi Provincial Academic and Technology Project for Main Disciplines Leader (No.20162BCB22016), Major Foundation of Jiangxi Provincial Education Ministry (No.GJJ160809), and Harbin Special Foundation for Excellent Academic Leader Project (No.2014RFXXJ113).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Zhao, Q., Zhou, X. et al. A deep eutectic solvent magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for extraction of laminarin from seaweeds. Microchim Acta 189, 399 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05488-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05488-y