Abstract
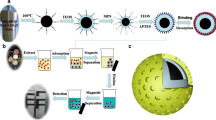
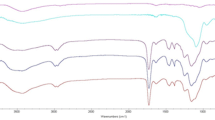
In this study, novel magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (MMIPs) with specific adsorption for glutathione were prepared. Based on MMIPs as adsorbents for magnetic solid-phase extraction, we combined magnetic solid-phase extraction with high-performance liquid chromatography (MPSE-HPLC) for the separation, enrichment, and detection of glutathione in nine kinds of wild edible bolete extracts. MMIPs were characterized by Fourier transform infrared spectrometer (FT-IR), X-ray diffraction (XRD), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), and vibrating sample magnetometer (VSM). In addition, the properties of MMIPs were studied by adsorption isotherm, adsorption kinetic, and selective adsorption experiments. The results showed that MMIPs had high selectivity for glutathione (Kd = 245.33 mL/g), and adsorption time and saturated adsorption capacity were 30 min and 17.88 μmol/g, respectively. Under the optimized conditions, there was a good linear relationship in the concentration range of 100~3000 μg/L, the correlation coefficient R2 = 0.9997, and the limit of detection (LOD) and the limit of quantitation (LOQ) that were 24.828 μg/L and 82.760 μg/L, respectively. The spiked recovery and RSD were 93.28~103.03% and 2.77~5.11, respectively. We successfully combined MSPE-HPLC for the detection of glutathione in nine kinds of wild edible bolete extracts. It was found that the content of glutathione in Leccinum extremiorientale (L. Vass.) Sing. was the highest (19.800 mg/g) and that in Boletus aereus was the lowest (6.791 mg/g).











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguilar-Arteaga K, Rodriguez J, Barrado E (2010) Magnetic solids in analytical chemistry: a review. Anal Chim Acta 674:157–165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.06.043
Asfaram A, Ghaedi M, Purkait M (2017) Novel synthesis of nanocomposite for the extraction of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) from water and urine samples: process screening and optimization. Ultrason Sonochem 38:463–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ultsonch.2017.03.045
Asfaram A, Arabi M, Ostovan A, Sadeghi H, Ghaedi M (2018) Simple and selective detection of quercetin in extracts of plants and food samples by dispersive-micro-solid phase extraction based on core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. New J Chem 42:16144–16153. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8nj03349h
Beitollahi H, Gholami A, Ganjali M (2015) Preparation, characterization and electrochemical application of Ag-ZnO nanoplates for voltammetric determination of glutathione and tryptophan using modified carbon paste electrode. Mat Sci Eng C-Mater 57:107–112. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2015.07.034
Bellini E, Borso M, Betti C, Bruno L, Andreucci A, Castiglione M, Saba A, Sanita di Toppi L (2019) Characterization and quantification of thiol-peptides in Arabidopsis thaliana using combined dilution and high sensitivity HPLC-ESI-MS-MS. Phytochemistry 164:215–222. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phytochem.2019.05.007
Borowczyk K, Olejarz P, Kaminska A, Glowacki R, Chwatko G (2019) Application of butylamine as a conjugative reagent to on-column derivatization for the determination of antioxidant amino acids in brain tissue, plasma, and urine samples. Int J Mol Sci 20:3340. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133340
Chang C, Tseng W (2010) Gold nanoparticle extraction followed by capillary electrophoresis to determine the total, free, and protein-bound aminothiols in plasma. Anal Chem 82:2696–2702. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac902342c
Chen L, Zhang X, Xu Y, Du X, Sun X, Sun L, Wang H, Zhao Q, Yu A, Zhang H, Ding L (2010a) Determination of fluoroquinolone antibiotics in environmental water samples based on magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer extraction followed by liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Anal Chim Acta 662:31–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2010.01.001
Chen X, Zhou Y, Peng X, Yoon J (2010b) Fluorescent and colorimetric probes for detection of thiols. Chem Soc Rev 39:2120–2135. https://doi.org/10.1039/b925092a
Chwatko G, Kuzniak E, Kubalczyk P, Borowczyk K, Wyszczelska-Rokiel M, Glowacki R (2014) Determination of cysteine and glutathione in cucumber leaves by HPLC with UV detection. Anal Methods-UK 6:8039–8044. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4ay01574f
Dai J, Pan J, Xu L, Li X, Zhou Z, Zhang R, Yan Y (2012) Preparation of molecularly imprinted nanoparticles with superparamagnetic susceptibility through atom transfer radical emulsion polymerization for the selective recognition of tetracycline from aqueous medium. J Hazard Mater 205:179–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.12.056
Dil E, Asfaram A, Sadeghfar F (2019a) Magnetic dispersive micro-solid phase extraction with the CuO/ZnO@Fe3O4-CNTs nanocomposite sorbent for the rapid pre-concentration of chlorogenic acid in the medical extract of plants, food, and water samples. Analyst 144:2684–2695. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8an02484g
Dil E, Ghaedi M, Asfaram A (2019b) Application of hydrophobic deep eutectic solvent as the carrier for ferrofluid: a novel strategy for pre-concentration and determination of mefenamic acid in human urine samples by high performance liquid chromatography under experimental design optimization. Talanta 202:526–530. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.05.027
Ferin R, Pavao M, Baptista J (2012) Methodology for a rapid and simultaneous determination of total cysteine, homocysteine, cysteinylglycine and glutathione in plasma by isocratic RP-HPLC. J Chromatogr B 911:15–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.10.022
Forgacsova A, Galba J, Mojzisova J, Mikus P, Piestansky J, Kovac A (2019) Ultra-high performance hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography—triple quadrupole tandem mass spectrometry method for determination of cysteine, homocysteine, cysteinyl-glycine and glutathione in rat plasma. J Pharmaceut Biomed 164:442–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpba.2018.10.053
Gao R, Mu X, Zhang J, Tang Y (2014) Specific recognition of bovine serum albumin using superparamagnetic molecularly imprinted nanomaterials prepared by two-stage core-shell sol-gel polymerization. J Mater Chem B 2:783–792. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3tb21424a
Heleno S, Barros L, Sousa M, Martins A, Santos-Buelga C, Ferreira I (2011) Targeted metabolites analysis in wild Boletus species. LWT- Food Sci Technol 44:1343–1348. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2011.01.017
Herrero-Latorre C, Barciela-Garcia J, Garcia-Martin S, Pena-Crecente R, Otarola-Jimenez J (2015) Magnetic solid-phase extraction using carbon nanotubes as sorbents: a review. Anal Chim Acta 892:10–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.07.046
Isokawa M, Funatsu T, Tsunoda M (2013) Fast and simultaneous analysis of biothiols by high-performance liquid chromatography with fluorescence detection under hydrophilic interaction chromatography conditions. Analyst 138:3802–3808. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3an00527e
Ji B, Ito K, Sekine S, Tajima A, Horie T (2004) Ethacrynic-acid-induced glutathione depletion and oxidative stress in normal and Mrp2-deficient rat liver. Free Radic Biol Med 37:1718–1729. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2004.08.020
Ju J, Zhang R, Chen W (2016) Photochemical deposition of surface-clean silver nanoparticles on nitrogen-doped graphene quantum dots for sensitive colorimetric detection of glutathione. Sensors Actuators B Chem 228:66–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.01.007
Kalaras M, Richie J, Calcagnotto A, Beelman R (2017) Mushrooms: a rich source of the antioxidants ergothioneine and glutathione. Food Chem 233:429–433. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2017.04.109
Kan X, Zhao Q, Shao D, Geng Z, Wang Z, Zhu J (2010) Preparation and recognition properties of bovine hemoglobin magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. J Phys Chem B 114:3999–4004. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp910060c
Karakosta T, Tzanavaras P, Themelis D (2013) Determination of glutathione and cysteine in yeasts by hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography followed by on-line postcolumn derivatization. J Sep Sci 36:1877–1882. https://doi.org/10.1002/jssc.201300202
Kato T, Tada-Oikawa S, Takahashi K, Saito K, Wang L, Nishio A, Hakamada-Taguchi R, Kawanishi S, Kuribayashi K (2006) Endocrine disruptors that deplete glutathione levels in APC promote Th2 polarization in mice leading to the exacerbation of airway inflammation. Eur J Immunol 36:1199–1209. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.200535140
Kong X, Gao R, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2012) Synthesis and characterization of the core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers (Fe3O4@MIPs) adsorbents for effective extraction and determination of sulfonamides in the poultry feed. J Chromatogr A 1245:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.04.061
Lee W, Chiu L, Yeung J (2008) Cytotoxicity of major tanshinones isolated from Danshen (Salvia miltiorrhiza) on HepG2 cells in relation to glutathione perturbation. Food Chem Toxicol 46:328–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2007.08.013
Li Y, Yin X, Chen F, Yang H, Zhuang Z, Wang X (2006) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanowires using a nanoporous alumina template. Macromolecules 39:4497–4499. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma0526185
Li Y, Elmer G, LeBoeuf R (2008) Tanshinone IIA reduces macrophage death induced by hydrogen peroxide by upregulating glutathione peroxidase. Life Sci 83:557–562. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2008.08.003
Li L, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2009) Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem-Asian J 4:286–293. https://doi.org/10.1002/asia.200800300
Li H, Xu W, Wang N, Ma X, Niu D, Jiang B, Liu L, Huang W, Yang W, Zhou Z (2012) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer particles for selective adsorption and separation of dibenzothiophene. Microchim Acta 179:123–130. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-012-0873-7
Li C, Shi L, Chen D, Ren A, Gao T, Zhao M (2015a) Functional analysis of the role of glutathione peroxidase (GPx) in the ROS signaling pathway, hyphal branching and the regulation of ganoderic acid biosynthesis in Ganoderma lucidum. Fungal Genet Biol 82:168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fgb.2015.07.008
Li X, Wang X, Li L, Duan H, Luo C (2015b) Electrochemical sensor based on magnetic graphene oxide@gold nanoparticles-molecular imprinted polymers for determination of dibutyl phthalate. Talanta 131:354–360. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.07.028
Liu X, Yu D, Yu Y, Ji S (2014) Preparation of a magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer for selective recognition of rhodamine B. Appl Surf Sci 320:138–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2014.08.122
Liu Y, Chen D, You Y, Zeng S, Li Y, Tang Q, Han G, Liu A, Feng C, Li C, Su Y, Su Z, Chen D (2016) Nutritional composition of boletus mushrooms from Southwest China and their antihyperglycemic and antioxidant activities. Food Chem 211:83–91. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.05.032
Meng X, Chen S, Meng M, Peng J, He X, Han Y, Zhu J, Xiao Q, Lv R, Lin R (2018) Development of the HPLC-ELSD method for the determination of phytochelatins and glutathione in Perilla frutescens under cadmium stress conditions. R Soc Open Sci 5:171659. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.171659
Miao S, Wu M, Zuo H, Jiang C, Jin S, Lu Y, Yang H (2015) Core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers as sorbent for sulfonylurea herbicide residues. J Agric Food Chem 63:3634–3645. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf506239b
Mishra R, Hayat A, Catanante G, Istamboulie G, Marty J (2016) Sensitive quantitation of ochratoxin A in cocoa beans using differential pulse voltammetry based aptasensor. Food Chem 192:799–804. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.080
Moradi Z, Dil E, Asfaram A (2019) Dispersive micro-solid phase extraction based on Fe3O4@SiO2@Ti-MOF as a magnetic nanocomposite sorbent for the trace analysis of caffeic acid in the medical extracts of plants and water samples prior to HPLC-UV analysis. Analyst 144:4351–4361. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9an00120d
Pereira E, Barros L, Martins A, Ferreira I (2012) Towards chemical and nutritional inventory of Portuguese wild edible mushrooms in different habitats. Food Chem 130:394–403. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.07.057
Perez-Rafols C, Subirats X, Serrano N, Diaz-Cruz J (2019) New discrimination tools for harvest year and varieties of white wines based on hydrophilic interaction liquid chromatography with amperometric detection. Talanta 201:104–110. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.03.099
Pownall T, Udenigwe C, Aluko R (2010) Amino acid composition and antioxidant properties of pea seed (Pisum sativum L.) enzymatic protein hydrolysate fractions. J Agric Food Chem 58:4712–4718. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf904456r
Schirhagl R, Ren K, Zare R (2012) Surface-imprinted polymers in microfluidic devices. Sci China Chem 55:469–483. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11426-012-4544-7
Shen A, Li X, Dong X, Wei J, Guo Z, Liang X (2013) Glutathione-based zwitterionic stationary phase for hydrophilic interaction/cation-exchange mixed-mode chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1314:63–69. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2013.09.002
Troyano A, Fernandez C, Sancho P, de Blas E, Aller P (2001) Effect of glutathione depletion on antitumor drug toxicity (apoptosis and necrosis) in U-937 human promonocytic cells—the role of intracellular oxidation. J Biol Chem 276:47107–47115. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M104516200
Tsai S, Tsai H, Mau J (2007) Antioxidant properties of Agaricus blazei, Agrocybe cylindracea, and Boletus edulis. LWT- Food Sci Technol 40:1392–1402. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lwt.2006.10.001
van 't Erve T, Wagner B, Ryckman K, Raife T, Buettner G (2013) The concentration of glutathione in human erythrocytes is a heritable trait. Free Radic Biol Med 65:742–749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2013.08.002
Vasapollo G, Del Sole R, Mergola L, Lazzoi M, Scardino A, Scorrano S, Mele G (2011) Molecularly imprinted polymers: present and future prospective. Int J Mol Sci 12:5908–5945. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms12095908
Wackerlig J, Lieberzeit P (2015) Molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles in chemical sensing—synthesis, characterisation and application. Sensors Actuators B Chem 207:144–157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.09.094
Wang D, Sun S, Wu W, Yang S, Tan J (2014) Characterization of a water-soluble polysaccharide from Boletus edulis and its antitumor and immunomodulatory activities on renal cancer in mice. Carbohydr Polym 105:127–134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.12.085
Wei L, Song Y, Liu P, Kang X (2018) Polystyrene nanofibers capped with copper nanoparticles for selective extraction of glutathione prior to its determination by HPLC. Microchim Acta 185(321):321. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2845-z
Whitcombe M, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky S, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40:1547–1571. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0cs00049c
Wu X, Tang L, Du Y, Xu Z (2010) Improving glutathione extraction from crude yeast extracts by optimizing aqueous two-phase system composition and operation conditions. Korean J Chem Eng 27:1829–1835. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-010-0308-2
Wu X, Wang X, Lu W, Wang X, Li J, You H, Xiong H, Chen L (2016) Water-compatible temperature and magnetic dual-responsive molecularly imprinted polymers for recognition and extraction of bisphenol A. J Chromatogr A 1435:30–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.01.040
Xiao D, Dramou P, Xiong N, He H, Li H, Yuan D, Dai H (2013) Development of novel molecularly imprinted magnetic solid-phase extraction materials based on magnetic carbon nanotubes and their application for the determination of gatifloxacin in serum samples coupled with high performance liquid chromatography. J Chromatogr A 1274:44–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2012.12.011
Yola M, Atar N (2017) A highly efficient nanomaterial with molecular imprinting polymer: carbon nitride nanotubes decorated with graphene quantum dots for sensitive electrochemical determination of chlorpyrifos. J Electrochem Soc 164:B223–B229. https://doi.org/10.1149/2.1411706jes
Zhang Y, Liu R, Hu Y, Li G (2009) Microwave heating in preparation of magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer beads for trace triazines analysis in complicated samples. Anal Chem 81:967–976. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac8018262
Zhong S, Zhou C, Zhang X, Zhou H, Li H, Zhu X, Wang Y (2014) A novel molecularly imprinted material based on magnetic halloysite nanotubes for rapid enrichment of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid in water. J Hazard Mater 276:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.05.013
Zimmerman S, Wendland M, Rakow N, Zharov I, Suslick K (2002) Synthetic hosts by monomolecular imprinting inside dendrimers. Nature 418:399–403. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature00877
Funding
The project was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 31660437), Major Projects of Yunnan Provincial Science and Technology Department (no. 2018ZF004), and China Agriculture Research System (CARS-21).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
Zenghui Xie declares that he has no conflict of interest. Lanyun Zhang declares that she has no conflict of interest. Yanli Chen declares that she has no conflict of interest. Xujia Hu declares that she has no conflict of interest.
Ethical Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Informed Consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, Z., Zhang, L., Chen, Y. et al. Magnetic Molecularly Imprinted Polymer Combined with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography for the Selective Separation and Determination of Glutathione in Various Wild Edible Boletes. Food Anal. Methods 12, 2908–2919 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01646-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-019-01646-w