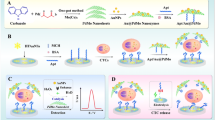
Abstract
An ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor was designed for the rapid label-free detection of circulating tumor DNA (ctDNA, EGFR 19 Dels for non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC). We linked the highly conjugated tricatecholate, 2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxytriphenylene (HHTP) with Ni(II) ions into the two-dimensional porous conductive metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), which is termed Ni-catecholates (Ni-CAT). Then, the AuNPs/Ni-catecholates/carbon black/polarized pencil graphite electrode (AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGE) was obtained by electrodeposition of AuNPs on the surface of PPGE modified with Ni-CAT/CB composite materials. The AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGE were used for label-less detection of ctDNA, with a total detection time of only 30 min. Under optimal detection conditions, the AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGE sensor exhibited excellent detection performance with good linear response to ctDNA over a wide concentration range and the detection limit down to the femtomolar level. The sensor was applied to the determination of ctDNA in serum samples with high sensitivity. This simple, efficient, and expeditious method has practical value in liquid biopsy of ctDNA and has potential for development in early detection, treatment, and prognosis of tumors.
Graphical abstract
Herein, an ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor was designed for the rapid label-free detection of ctDNA (EGFR 19 Dels for non-small cell lung cancer, NSCLC). We linked the highly conjugated tricatecholate, 2,3,6,7,10,11-hexahydroxytriphenylene (HHTP) with Ni(II) ions into the two-dimensional porous conductive metal–organic frameworks (MOFs), which is termed as Ni-catecholates (Ni-CAT). Then, the AuNPs/Ni-catecholates/carbon black/polarized pencil graphite electrode (AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGE) was obtained by electrodeposition of AuNPs on the surface of PPGE modified with Ni-CAT/CB composite materials. The AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGEs were used for label-less detection of ctDNA, with a total detection time of only 30 min. Under optimal detection conditions, the AuNPs/Ni-CAT/CB/PPGE sensor exhibited excellent detection performance with good linear response to ctDNA in the concentration range of 1 × 10−15 M to 1 × 10−6 M and with a detection limit as low as 0.32 fM. The sensor was applied for determination of ctDNA in serum samples and gave high sensitivity. This simple, efficient and expeditious method has practical value in liquid biopsy of ctDNA and has potential for development in early detection, treatment and prognosis of tumors.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bronkhorst AJ, Ungerer V, Holdenrieder S (2019) The emerging role of cell-free DNA as a molecular marker for cancer management. Biomolecular Detection and Quantification 17:100087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bdq.2019.100087
de Lima LTF, Broszczak D, Zhang X, Bridle K, Crawford D, Punyadeera C (2020) The use of minimally invasive biomarkers for the diagnosis and prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) Reviews on Cancer 1874(2):188451
Volckmar AL, Sultmann H, Riediger A, Fioretos T, Schirmacher P, Endris V et al (2018) A field guide for cancer diagnostics using cell-free DNA: from principles to practice and clinical applications. Genes Chromosom Cancer 57(3):123–139. https://doi.org/10.1002/gcc.22517
Newton CR, Graham A, Heptinstall LE, Powell SJ, Summers C, Kalsheker N et al (1989) Analysis of any point mutation in DNA. The amplification refractory mutation system (ARMS). Nucleic Acids Research 17(7):2503–2516
Mao X, Pan S, Zhou D, He X, Zhang Y (2019) Fabrication of DNAzyme-functionalized hydrogel and its application for visible detection of circulating tumor DNA. Sens Actuators, B Chem 285:385–390. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.01.076
Zhang J, Dong Y, Zhu W, Xie D, Zhao Y, Yang D et al (2019) Ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor dna of lung cancer via an enzymatically amplified SERS-based frequency shift assay. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 11(20):18145–18152. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b02953
Chaibun T, Puenpa J, Ngamdee T, Boonapatcharoen N, Athamanolap P, O’Mullane AP et al (2021) Rapid electrochemical detection of coronavirus SARS-CoV-2. Nat Commun 12(1):802. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-021-21121-7
Miao P, Tang YG (2020) DNA walking and rolling nanomachine for electrochemical detection of miRNA. Small 16(47):2004518. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.202004518
Wang L-L, Chen W-Q, Wang Y-R, Zeng L-P, Chen T-T, Chen G-Y et al (2020) Numerous long single-stranded DNAs produced by dual amplification reactions for electrochemical detection of exosomal microRNAs. Biosens Bioelectron 169:112555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112555
Zhang R, Chen W (2015) Fe3C-functionalized 3D nitrogen-doped carbon structures for electrochemical detection of hydrogen peroxide. Science Bulletin 60(5):522–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11434-015-0740-0
Ramachandran R, Leng X, Zhao C, Xu Z-X, Wang F (2020) 2D siloxene sheets: a novel electrochemical sensor for selective dopamine detection. Appl Mater Today 18:100477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmt.2019.100477
Small LJ, Henkelis SE, Rademacher DX, Schindelholz ME, Krumhansl JL, Vogel DJ et al (2020) Near-zero power MOF-based sensors for NO2 detection. Adv Func Mater 30(50):2006598. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.202006598
Song J, Huang M, Lin X, Li SFY, Jiang N, Liu Y et al (2022) Novel Fe-based metal–organic framework (MOF) modified carbon nanofiber as a highly selective and sensitive electrochemical sensor for tetracycline detection. Chem Eng J 427:130913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130913
Rubio-Gimenez V, Almora-Barrios N, Escorcia-Ariza G, Galbiati M, Sessolo M, Tatay S et al (2018) Origin of the chemiresistive response of ultrathin films of conductive metal-organic frameworks. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 57(46):15086–15090. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201808242
Duan H, Zhao Z, Lu J, Hu W, Zhang Y, Li S et al (2021) When conductive MOFs meet MnO2: high electrochemical energy storage performance in an aqueous asymmetric supercapacitor. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 13(28):33083–33090. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.1c08161
Cai D, Lu MJ, Li L, Cao JM, Chen D, Tu HR et al (2019) A highly conductive MOF of graphene analogue Ni3(HITP)2 as a sulfur host for high-performance lithium-sulfur batteries. Small 15(44):1902605. https://doi.org/10.1002/smll.201902605
Xu Z, Wang Q, Zhangsun H, Zhao S, Zhao Y, Wang L (2021) Carbon cloth-supported nanorod-like conductive Ni/Co bimetal MOF: a stable and high-performance enzyme-free electrochemical sensor for determination of glucose in serum and beverage. Food Chem 349:129202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.129202
Ko M, Mendecki L, Eagleton AM, Durbin CG, Stolz RM, Meng Z et al (2020) Employing conductive metal–organic frameworks for voltammetric detection of neurochemicals. J Am Chem Soc 142(27):11717–11733. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.9b13402
Vicentini FC, Ravanini AE, Figueiredo-Filho LCS, Iniesta J, Banks CE, Fatibello-Filho O (2015) Imparting improvements in electrochemical sensors: evaluation of different carbon blacks that give rise to significant improvement in the performance of electroanalytical sensing platforms. Electrochim Acta 157:125–133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2014.11.204
Hmadeh M, Lu Z, Liu Z, Gándara F, Furukawa H, Wan S et al (2012) New porous crystals of extended metal-catecholates. Chem Mater 24(18):3511–3513. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm301194a
Nagarajan S, Vairamuthu R, Angamuthu R, Venkatachalam G (2019) Electrochemical fabrication of reusable pencil graphite electrodes for highly sensitive, selective and simultaneous determination of hydroquinone and catechol. J Electroanal Chem 846:113156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2019.05.038
Nguyen NTT, Furukawa H, Gándara F, Trickett CA, Jeong HM, Cordova KE et al (2015) Three-dimensional metal-catecholate frameworks and their ultrahigh proton conductivity. J Am Chem Soc 137(49):15394–15397. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b10999
Lee S-M, Lee S-H, Roh J-S (2021) Analysis of activation process of carbon black based on structural parameters obtained by XRD analysis. Crystals 11(2):153 (https://www.mdpi.com/2073-4352/11/2/153)
Qiao Y, Liu Q, Lu S, Chen G, Gao S, Lu W et al (2020) High-performance non-enzymatic glucose detection: using a conductive Ni-MOF as an electrocatalyst. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 8(25):5411–5415. https://doi.org/10.1039/D0TB00131G
Tezerjani MD, Benvidi A, Jahanbani S, Moshtaghioun SM, Mazloum-Ardakani M (2016) A comparative investigation for prostate cancer detection using two electrochemical biosensors based on various nanomaterials and the linker of thioglycolic acid. J Electroanal Chem 778:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2016.08.009
Hájková A, Barek J, Vyskočil V (2017) Electrochemical DNA biosensor for detection of DNA damage induced by hydroxyl radicals. Bioelectrochemistry 116:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioelechem.2017.02.003
Guo L, Mu Z, Yan B, Wang J, Zhou J, Bai L (2022) A novel electrochemical biosensor for sensitive detection of non-small cell lung cancer ctDNA using NG-PEI-COFTAPB-TFPB as sensing platform and Fe-MOF for signal enhancement. Sens Actuators, B Chem 350:130874. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2021.130874
Chen M, Wu D, Tu S, Yang C, Chen D, Xu Y (2021) CRISPR/Cas9 cleavage triggered ESDR for circulating tumor DNA detection based on a 3D graphene/AuPtPd nanoflower biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 173:112821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112821
Huang Y, Tao M, Luo S, Zhang Y, Situ B, Ye X et al (2020) A novel nest hybridization chain reaction based electrochemical assay for sensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA. Anal Chim Acta 1107:40–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2020.02.006
Li D, Xu Y, Fan L, Shen B, Ding X, Yuan R et al (2020) Target-driven rolling walker based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA using doxorubicin@tetrahedron-Au tags. Biosens Bioelectron 148:111826. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111826
Chen K, Zhao H, Wang Z, Lan M (2021) A novel signal amplification label based on AuPt alloy nanoparticles supported by high-active carbon for the electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA. Anal Chim Acta 1169:338628. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2021.338628
Chen KC, Zhao HL, Wang ZX, Lan MB (2022) Three-dimensional graphene-like homogeneous carbon architecture loaded with gold-platinum for the electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA. Materials Today Chemistry 24:100892. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mtchem.2022.100892
Su J, Zhong WZ, Zhang XC, Huang Y, Yan HH, Yang JJ et al (2017) Molecular characteristics and clinical outcomes of EGFR exon 19 indel subtypes to EGFR TKIs in NSCLC patients. Oncotarget 8(67):111246–111257. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.22768
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 81271930 and 31000425), the Research Project of Chongqing Science and Technology Commission of China (cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0861), the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (No. 2020CDJ-LHZZ-033), and we would like to thank the Analytical and Testing Center of Chongqing University for SEM images, XRD, and XPS spectrum.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Yang, S., Shen, J. et al. Conductive metal–organic framework based label-free electrochemical detection of circulating tumor DNA. Microchim Acta 189, 391 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05482-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05482-4