Abstract
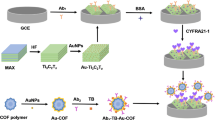
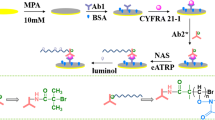
Relying on the electrochemiluminescence (ECL) and microfluidic technology, an immunosensor chip with high bioactivity was designed for sensitive determination of cytokeratin 19 fragment 21–1 (CYFRA 21–1). The mesoporous nanomaterial Fe3O4@Cu@Cu2O as the co-reaction accelerator was used to catalyze the S2O82− to produce more SO4•− to achieve the amplification of the ECL signal. In fact, the generating of SO4•− could not only be done with the aid of the reversible cycles of Fe2+ and Fe3+ and Cu+ and Cu2+, but could be achieved also through the catalase-like function of Fe3O4. What is more, it has also been proved that Fe3O4@Cu@Cu2O exhibited better catalytic performance than single Fe3O4, Cu2O, and Cu@Cu2O, which supported its application in this system. In addition, a portable microfluidic immunosensor chip for CYFRA 21–1-sensitive determination was assembled, which showed high selectivity, sensitivity, and strong universality in clinical cancer screening and diagnosis. It should be noted that HWRGWVC (HWR) was introduced as the antibody fixator to improve the incubation and binding efficiency of the antibody, which increased the ECL intensity and improved the sensitivity of the immunosensor. This strategy provided a new idea for cancer identification and diagnosis in clinical medicine.
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao L, Yang H, Zheng X, Li J, Jian L, W, Feng, J. Kong, (2020) Dual signal amplification by polysaccharide and eATRP for ultrasensitive detection of CYFRA 21–1 DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 150:111895
Abbas J, Hossain-Ali R, Mehdi S (2022) A new strategy to design label-free electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive diagnosis of CYFRA 21–1 as a biomarker for detection of non-small cell lung cancer. Chemosphere 301:134636
Liu D, Qian Y, Xu R, Zhang Y, Ren X, Ma H, Wei Q (2021) A dual-signal amplification photoelectrochemical immunosensor for ultrasensitive detection of CYFRA 21–1 based on the synergistic effect of SnS2/SnS/Bi2S3 and ZnCdS@NPC-ZnO. Sens Actuators, B 346:130456
Zhao L, Song X, Ren X, Fan D, Wei Q, Wu D (2021) Rare self-luminous mixed-valence Eu-MOF with a self-enhanced characteristic as a near-infrared fluorescent ECL probe for nondestructive immunodetection. Anal Chem 93:8613–8621
Cheng Q, Feng J, Wu T, Guo Y, Sun X, Ren X, Lee J, Liu L, Wei Q (2021) Hollow performances quenching label of Au NPs@CoSnO3 nanoboxes-based sandwich photoelectrochemical immunosensor for sensitive CYFRA 21–1 detection. Talanta 233:122552
Jian L, Wang X, Hao L, Liu Y, Yang H, Zheng X, Feng W (2021) Electrochemiluminescence immunosensor for cytokeratin fragment antigen 21–1 detection using electrochemically mediated atom transfer radical polymerization. Microchim Acta 188:115
Xue J, Yang L, Jia Y, Wang H, Zhang N, Ren X et al (2019) Electrochemiluminescence double quenching system based on novel emitter GdPO4: Eu with low-excited positive potential for ultrasensitive procalcitonin detection. ACS Sensors 4:2825–2831
Song X, Shao X, Dai L, Fan D, Ren X, Sun X et al (2020) Triple amplification of 3,4,9,10-perylenetetracarboxylic acid by Co2+-based metal-organic frameworks and silver-cysteine and its potential application for ultrasensitive assay of procalcitonin. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 12:9098–9106
Jia Y, Yang L, Xue J, Ren X, Zhang N, Fan D et al (2019) Highly-branched Cu2O as well-ordered co-reaction accelerator for amplifying electrochemiluminescence response of gold nanoclusters and procalcitonin analysis based on protein bioactivity maintenance. Biosens Bioelectron 144:111676
Yang L, Wu T, Du Y, Zhang N, Feng R, Ma H et al (2021) Pegylation Improved electrochemiluminescence supramolecular assembly of iridium(III) complexes in apoferritin for immunoassays using 2D/2D MXene/TiO2 hybrids as signal amplifiers. Anal Chem 93:16906–16914
Damien T, Cedric L, Isabelle D, Philippe P, Cedric A, Jean-Baptiste S (2018) Engineering polymer MEMS using combined microfluidic pervaporation and micro-molding. Microsyst Nanoeng 4:15
Verpoorte E, Rooij NFD (2003) Microfluidics meets MEMS. Proc IEEE 91:930–953
Ranjan G, Ishwar KP (2010) Microfluidic transport in magnetic MEMS and bioMEMS. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev.: Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol 2:382–399
Pattanayak P, Singh SK, Gulati M et al (2021) Microfluidic chips: recent advances, critical strategies in design, applications and future perspectives. Microfluid Nanofluid 25:1–28
Zhuang Q, Ning R, Ma Y, Lin J (2016) Recent developments in microfluidic chip for in vitro cell-based research. Chin J Anal Chem 44:522–531
Zhao Y, Hu X, Hu S, Peng Y (2020) Applications of fiber-optic biochemical sensor in microfluidic chips: a review. Biosens Bioelectron 166:112447
Cui P, Wang S (2019) Application of microfluidic chip technology in pharmaceutical analysis: a review. J Pharm Anal 9:238–247
de Arquer F, Talapin D et al (2021) Semiconductor quantum dots: technological progress and future challenges. Science 373:640–655
Alexander LE, Louis EB (2021) Nanocrystal quantum dots: from discovery to modern development. ACS Nano 15:6192–6210
Liu Y, Yu J (2010) In situ synthesis of highly luminescent glutathione-capped CdTe/ZnS quantum dots with biocompatibility. J Colloid Interface Sci 351:1–9
Yong K, Law W, Indrajit R, Zhu L, Huang H, Swihart MT et al (2011) Aqueous phase synthesis of CdTe quantum dots for biophotonics. J Biophotonics 4:9–20
Kalsoom UE, Yi R, Qu J, Liu L et al (2021) Nonlinear optical properties of CdSe and CdTe core-shell quantum dots and their applications. Front Phys 9:612070
Wang Z, Chen M, Shu J, Li Y et al (2016) One-step solvothermal synthesis of Fe3O4@Cu@Cu2O nanocomposite as magnetically recyclable mimetic peroxidase. J Alloys Compd 682:432–440
Li J, Wang X, Liu W, Li X, Yang L, Ma H, et al (2021) Highly selective electrochemiluminescence aptasensor coupled with mesoporous Fe3O4@Cu@Cu2O as co-reaction accelerator for ATP assay based on target-triggered emitter release. Sens Actuators, B 346:130581
Song X, Wu T, Luo C, Zhao L, Ren X, Zhang Y et al (2021) Peptide-based electrochemiluminescence biosensors using silver nanoclusters as signal probes and Pd-Cu2O hybrid nanoconcaves as coreactant promoters for immunoassays. Anal Chem 93:13045–13053
Nishiyama K, Fukuyama M, Maeki M, Ishida A, Tani H, Hibara A, et al (2020) One-step non-competitive fluorescence polarization immunoassay based on a Fab fragment for C-reactive protein quantification. Sens Actuators, B 326:128982
Urios P, Cittanova N (1990) Adaptation of fluorescence polarization immunoassay to the assay of macromolecules. Anal Biochem 185:308–312
Ma M, Zhou Y, Yuan R, Chai Y et al (2015) New signal amplification strategy using semicarbazide as co-reaction accelerator for highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent aptasensor construction. Anal Chem 87:11389–11397
Feng J, Dai L, Ren X, Ma H, Wang X, Fan D et al (2021) Self-powered cathodic photoelectrochemical aptasensor comprising a photocathode and a photoanode in microfluidic analysis systems. Anal Chem 93:7125–7132
Cui X, Zhang S, Geng Y, Zhen J, Zhan J, Cao C, Ni S (2021) Synergistic catalysis by Fe3O4-biochar/peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of bisphenol a. Sep Purif Technol 276:119351
Dang X, Sun M, Sinha A, Niu J, Zhao H (2019) Coupling O2 and K2S2O8 dual Co-reactant with Fe-N-C modified electrode for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence signal amplification. ChemistrySelect 4(5):1673–1680
Xie C, Wang W, Yang Y, Jiang L, Chen Y, He J, Wang J (2020) Enhanced stability and activity for solvent-free selective oxidation of cyclohexane over Cu2O/CuO fabricated by facile alkali etching method. Mol Catal 495:111134
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L, Zhang J, Zhang Y, Gu N et al (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583
Zhou B, Wang H, Liu Z, Yang Y, Huang X, Lue Z et al (2011) Enhanced photocatalytic activity of flowerlike Cu2O/Cu prepared using solvent-thermal route. Mater Chem Phys 126:847–852
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 51904114), Shandong Provincial Natural Science Foundation (No. ZR2020QB097), Jinan Scientific Research Leader Workshop Project (2019GXRC027), Special Foundation for Taishan Scholar Professorship of Shandong Province.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Feng, T., Song, X., Wang, W. et al. High-bioactivity microfluidic immunosensing platform for electrochemiluminescence determination of CYFRA 21–1 with the introduction of Fe3O4@Cu@Cu2O. Microchim Acta 189, 336 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05436-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05436-w