Abstract
Monitoring hydroxyl radical (·OH) in living cells remains a big challenge on account of its high reactivity and short half-life. In this work, we designed a fluorescent probe based on manganese-doped silicon quantum dots (Mn-SiQDs) for detecting and imaging of ·OH with good water solubility. The manganese was doped in its ethylene diamine tetra-acetic acid (EDTA) complex form and effectively improved the metal ion tolerance of fluorescence of SiQDs. And m-dihydroxybenzene was used as the reductant to extend the emission of SiQDs to the green region at 515 nm when the excitation wavelength was 424 nm. Basing on the fluorescence quenching of Mn-SiQDs, a linear response of ·OH was observed in the range 0.8–50 μM with a limit of detection (LOD) of 88.4 nM, which is lower than those reported with SiQDs. The interference from other ROS or RNS has been assessed and no impact was found. In fully aqueous systems, the Mn-SiQDs have been applied to monitor and image the endogenous ·OH in HeLa cells. Our work provided a new strategy for designing SiQDs with good biocompatibility, high selectivity and long monitoring wavelength.
Graphical abstract
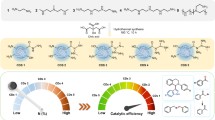
Synthesis of green-emitting silicon quantum dots with N-[3 -(trimethoxysilyl) propyl] ethylenediamine (DAMO), Ethylenediamine tetraacetic acid disodium salt dehydrate (EDTA-2Na·2H2O), manganese acetate tetrahydrate (Mn(CH3COO)2·4H20) and m-dihydroxybenzene. The green fluorescence of the silicon quantum dots can be selectively quenched by hydroxyl radicals.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dobashi K, Ghosh B, Orak JK, Singh I, Singh AK (2000) Kidney ischemia-reperfusion: Modulation of antioxidant defenses. Mol Cell Biochem 205:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1007047505107
Rupec RA, Baeuerle PA (1995) The genomic response of tumor-cells to hypoxia and reoxygenation - differential activation of transcription factors AP-1 and NF-KAPPA-B. Eur J Biochem 234:632–640. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.632_b.x
Lemar KM, Aon MA, Cortassa S, O’Rourke B, Muller CT, Lloyd D (2007) Diallyl disulphide depletes glutathione in Candida albicans: oxidative stress-mediated cell death studied by two-photon microscopy. Yeast 24:695–706. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1503
Fejer J, Kron I, Grulova D, Eliasova A (2020) Seasonal Variability of Juniperus communis L. Berry ethanol extracts: 1. In Vitro Hydroxyl Radical Scavenging Activity. Molecules 25. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules25184114
Soh N, Makihara K, Sakoda E, Imato T (2004) A ratiometric fluorescent probe for imaging hydroxyl radicals in living cells. Chem Commun (Camb). https://doi.org/10.1039/b314204c:496-497.
Zhao QQ, Zhang R, Ye DX, Zhang S, Chen H, Kong JL (2017) Ratiometric fluorescent silicon quantum dots-Ce6 complex probe for the live cell imaging of highly reactive oxygen species. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:2052–2058. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.6b12047
Zhou J, Ma H (2016) Design principles of spectroscopic probes for biological applications. Chem Sci 7:6309–6315. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6sc02500e
Ma Y, Cen Y, Sohail M, Xu G, Wei F, Shi M, Xu X, Song Y, Ma Y, Hu Q (2017) A ratiometric fluorescence universal platform based on N, Cu codoped carbon dots to detect metabolites participating in H2O2-generation reactions. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:33011–33019. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b10548
Chen D, Zhuang X, Zhai J, Zheng Y, Lu H, Chen L (2018) Preparation of highly sensitive Pt nanoparticles-carbon quantum dots/ionic liquid functionalized graphene oxide nanocomposites and application for H2O2 detection. Sens Actuators, B Chem 255:1500–1506. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.08.156
Li X, Shi H, Wang T, Zhang Y, Zuo S, Luo S, Yao C (2018) Photocatalytic removal of NO by Z-scheme mineral based heterojunction intermediated by carbon quantum dots. Appl Surf Sci 456:835–844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.06.133
Zhang P, Wang H, Zhang D, Zeng X, Zeng R, Xiao L, Tao H, Long Y, Yi P, Chen J (2018) Two-photon fluorescent probe for lysosome-targetable hypochlorous acid detection within living cells. Sens Actuators, B Chem 255:2223–2231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.09.025
Chen B, Fu H, Lv Y, Li X, Han Y (2018) An oxidative cyclization reaction based fluorescent “Turn-On” probe for highly selective and rapid detection of hypochlorous acid. Tetrahedron Lett 59:1116–1120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2018.02.018
Gai L, Mack J, Liu H, Xu Z, Lu H, Li Z (2013) A BODIPY fluorescent probe with selective response for hypochlorous acid and its application in cell imaging. Sens Actuators, B Chem 182:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2013.02.106
He Y, Xu Y, Shang Y, Zheng S, Chen W, Pang Y (2018) An ESIPT-based fluorescent probe for the determination of hypochlorous acid (HClO): mechanism study and its application in cell imaging. Anal Bioanal Chem 410:7007–7017. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-018-1332-z
Zhu G, Huang D, Liu L, Yi Y, Wu Y, Huang Y (2020) One-step green preparation of N-doped silicon quantum dots for the on-off fluorescent determination of hydrogen peroxide. Anal Lett 53:1834–1849. https://doi.org/10.1080/00032719.2020.1720222
Li Y, Zhang H, Yao Y, Gong T, Dong R, Li D, Liu Y, Lei B (2020) Promoted off-on recognition of H2O2 based on the fluorescence of silicon quantum dots assembled two-dimensional PEG-MnO2 nanosheets hybrid nanoprobe. Mikrochim Acta 187:347. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04276-w
Ji X, Wang H, Song B, Chu B, He Y (2018) Silicon Nanomaterials for Biosensing and Bioimaging Analysis. Front Chem 6:38. https://doi.org/10.3389/fchem.2018.00038
Dong R, Yao Y, Li D, Zhang H, Li W, Molokee M, Liu Y, Lei B (2020) Ratio fluorescent hybrid probe for visualized fluorescence detection of H2O2 in vitro and in vivo. Sens Actuators, B Chem 321. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2020.128643
Liang J, Huang C, Gong X (2019) Silicon nanocrystals and their composites: syntheses, fluorescence mechanisms, and biological applications. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 7:18213–18227. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssuschemeng.9b04359
Peng F, Su YY, Zhong YL, Fan CH, Lee ST, He Y (2014) Silicon nanomaterials platform for bioimaging, biosensing, and cancer therapy. Accounts Chem Res 47:612–623. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar400221g
Qiu M, Singh A, Wang D, Qu J, Swihart M, Zhang H, Prasad PN (2019) Biocompatible and biodegradable inorganic nanostructures for nanomedicine: silicon and black phosphorus. Nano Today 25:135–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nantod.2019.02.012
Li Z, Ren X, Hao C, Meng X, Li Z (2018) Silicon quantum dots with tunable emission synthesized via one-step hydrothermal method and their application in alkaline phosphatase detection. Sens Actuators, B Chem 260:426–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.12.175
Wu W, Zhan L, Fan W, Song J, Li X, Li Z, Wang R, Zhang J, Zheng J, Wu M, Zeng H (2015) Cu-N dopants boost electron transfer and photooxidation reactions of carbon dots. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 54:6540–6544. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201501912
Han Y, Chen Y, Feng J, Na M, Liu J, Ma Y, Ma S, Chen X (2019) Investigation of nitrogen content effect in reducing agent to prepare wavelength controllable fluorescent silicon nanoparticles and its application in detection of 2-nitrophenol. Talanta 194:822–829. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.11.008
Zhong Y, Peng F, Bao F, Wang S, Ji X, Yang L, Su Y, Lee ST, He Y (2013) Large-scale aqueous synthesis of fluorescent and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles and their use as highly photostable biological probes. J Am Chem Soc 135:8350–8356. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja4026227
Ma SD, Chen YL, Feng J, Liu JJ, Zuo XW, Chen XG (2016) One-step synthesis of water-dispersible and biocompatible silicon nanoparticles for selective heparin sensing and cell imaging. Anal Chem 88:10474–10481. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b02448
Pang L-F, Wu H, Fu M-J, Guo X-F, Wang H (2019) Red emissive boron and nitrogen co-doped “on-off-on” carbon dots for detecting and imaging of mercury(II) and biothiols. MicrochimActa 186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3852-4
Qu D, Zheng M, Du P, Zhou Y, Zhang L, Li D, Tan H, Zhao Z, Xie Z, Sun Z (2013) Highly luminescent S, N co-doped graphene quantum dots with broad visible absorption bands for visible light photocatalysts. Nanoscale 5. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3nr04402e
Han Y, Chen Y, Feng J, Liu J, Ma S, Chen X (2017) One-pot synthesis of fluorescent silicon nanoparticles for sensitive and selective determination of 2,4,6-trinitrophenol in aqueous solution. Anal Chem 89:3001–3008. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b04509
Geng X, Li Z, Hu Y, Liu H, Sun Y, Meng H, Wang Y, Qu L, Lin Y (2018) One-Pot Green Synthesis of Ultrabright N-Doped Fluorescent Silicon Nanoparticles for Cellular Imaging by Using Ethylenediaminetetraacetic Acid Disodium Salt as an Effective Reductant. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:27979–27986. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b09242
Yang X, Feng Y, Zhu S, Luo Y, Zhuo Y, Dou Y (2014) One-step synthesis and applications of fluorescent Cu nanoclusters stabilized by L-cysteine in aqueous solution. Anal Chim Acta 847:49–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2014.07.019
Li D, Jiang Y, Chen S, Zhao Q, Zhang Y, Wang W, Sun Y, Ma P, Song D, Wang X (2020) A simple and sensitive assay of alkaline phosphatase activity in serum by fluorescent silicon nanoparticles based on inner filter effect. Sens Actuators, B Chem 307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.127589
Wang J, Li R, Long X, Li Z (2016) Synthesis of imidazole-functionalized silicon quantum dots as “off-on” fluorescence probe for highly selective and sensitive detection of l-histidine. Sens Actuators, B Chem 237:740–748. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.06.157
Zhuang M, Ding C, Zhu A, Tian Y (2014) Ratiometric fluorescence probe for monitoring hydroxyl radical in live cells based on gold nanoclusters. Anal Chem 86:1829–1836. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac403810g
Zhai W, Wang C, Yu P, Wang Y, Mao L (2014) Single-layer MnO2 nanosheets suppressed fluorescence of 7-hydroxycoumarin: mechanistic study and application for sensitive sensing of ascorbic acid in vivo. Anal Chem 86:12206–12213. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503215z
Hai X, Guo Z, Lin X, Chen X, Wang J (2018) Fluorescent TPA@GQDs Probe for sensitive assay and quantitative imaging of hydroxyl radicals in living cells. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:5853–5861. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b16094
Huang Z, Ying P, Huang L, Xu Q, Hu X-Y (2019) Molecularly imprinted polymer functionalized reduced graphene oxide: a new platform for the detection of hydroxyl radicals in the atmosphere. Anal Methods 11:5126–5133. https://doi.org/10.1039/c9ay01414d
Bai X, Huang Y, Lu M, Yang D (2017) HKOH-1: a highly sensitive and selective fluorescent probe for detecting endogenous hydroxyl radicals in living cells. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56:12873–12877. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201705873
Liu F, Du J, Song D, Xu M, Sun G (2016) A sensitive fluorescent sensor for the detection of endogenous hydroxyl radicals in living cells and bacteria and direct imaging with respect to its ecotoxicity in living zebra fish. Chem Commun (Camb) 52:4636–4639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc10658c
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Large-Scale Instrument and Equipment Sharing Foundation of Wuhan University for the support.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21777126 and 32070398, Beijing, China).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
Additional information and figures are listed in the supplementary information.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, YC., Pang, LF., Guo, XF. et al. Synthesis of metal ion–tolerant Mn-doped fluorescence silicon quantum dots with green emission and its application for selective imaging of ·OH in living cells. Microchim Acta 189, 60 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05082-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05082-8