Abstract
To enhance the sensitivity of lateral flow assays (LFAs), a simple strategy is proposed using a nitrocellulose membrane modified with a superabsorbent polymer (SAP). SAP was incorporated into a nitrocellulose membrane for the flow control of detection probes. When absorbing aqueous solutions, SAP promoted the formation of biomolecule complexes to achieve up to a tenfold sensitivity improvement for the detection of human IgG. The assay time was optimized experimentally and numerically to within 20 min using this strategy. Moreover, fluid saturation in LFAs modified with SAP was mathematically simulated to better understand the underlying process, and molecular dynamics simulations were carried out to determine the effect of SAP. The proposed design was also applied to samples spiked with human immunoglobulin-depleted serum to test its applicability. The strategy presented is unique in that it preserves the characteristics of conventional LFAs, as it minimizes user intervention and is simple to manufacture at scale.
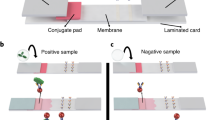
Graphical abstract






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jung W, Han J, Choi JW, Ahn CH (2015) Point-of-care testing (POCT) diagnostic systems using microfluidic lab-on-a-chip technologies. Microelectron Eng 132:46–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mee.2014.09.024
Gong MM, Sinton D (2017) Turning the page: advancing paper-based microfluidics for broad diagnostic application. Chem Rev 117:8447–8480. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.7b00024
Wu G, Zaman MH (2012) Low-cost tools for diagnosing and monitoring HIV infection in low-resource settings. Bull World Health Organ 90:914–920. https://doi.org/10.2471/BLT.12.102780
Li F, You M, Li S et al (2019) Paper-based point-of-care immunoassays: Recent advances and emerging trends. Biotechnol Adv. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2019.107442
Xiong X, Zhang J, Wang Z et al (2020) Simultaneous multiplexed detection of protein and metal ions by a colorimetric microfluidic paper-based analytical device. Biochip J 14:429–437. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-020-4407-9
Hyung S, Karima G, Shin K et al (2021) A simple paper-based α-amylase separating system for potential application in biological sciences. Biochip J. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00022-3
Hidayat MA, Maharani DA, Purwanto DA et al (2020) Simple and sensitive paper-based colorimetric biosensor for determining total polyphenol content of the green tea beverages. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 25:255–263. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-019-0299-8
Lim SH, Ryu YC, Hwang BH (2021) Aptamer-immobilized gold nanoparticles enable facile and on-site detection of staphylococcus aureus. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 26:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12257-020-0161-z
Koczula KM, Gallotta A (2016) Lateral flow assays. Essays Biochem 60:111–120. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20150012
Quesada-González D, Merkoçi A (2015) Nanoparticle-based lateral flow biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 73:47–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.05.050
Carrilho E, Martinez AW, Whitesides GM (2009) Understanding wax printing: A simple micropatterning process for paper-based microfluidics. Anal Chem 81:7091–7095. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac901071p
Renault C, Koehne J, Ricco AJ, Crooks RM (2014) Three-dimensional wax patterning of paper fluidic devices. Langmuir 30:7030–7036. https://doi.org/10.1021/la501212b
Sena-Torralba A, Ngo DB, Parolo C et al (2020) Lateral flow assay modified with time-delay wax barriers as a sensitivity and signal enhancement strategy. Biosens Bioelectron 168:112559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2020.112559
Preechakasedkit P, Siangproh W, Khongchareonporn N et al (2018) Development of an automated wax-printed paper-based lateral flow device for alpha-fetoprotein enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biosens Bioelectron 102:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.051
He X, Liu Z, Yang Y et al (2019) Sensitivity enhancement of nucleic acid lateral flow assays through a physical-chemical coupling method: dissoluble saline barriers. ACS Sensors 4:1691–1700. https://doi.org/10.1021/acssensors.9b00594
Lutz B, Liang T, Fu E et al (2013) Dissolvable fluidic time delays for programming multi-step assays in instrument-free paper diagnostics. Lab Chip 13:2840–2847. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50178g
Zohuriaan-Mehr MJ, Kabiri K (2008) Superabsorbent polymer materials: A review. Iran Polym J English Ed 17:451–477
Zohuriaan-Mehr MJ, Omidian H, Doroudiani S, Kabiri K (2010) Advances in non-hygienic applications of superabsorbent hydrogel materials. J Mater Sci 45:5711–5735. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-010-4780-1
Biswas GC, Rana MM, Kazuhiro T, Suzuki H (2019) A simple micropump based on a freeze-dried superabsorbent polymer for multiplex solution processing in disposable devices. R Soc Open Sci 6(3):182213. https://doi.org/10.1098/rsos.182213
Oyama Y, Osaki T, Kamiya K et al (2017) A sensitive point-of-care testing chip utilizing superabsorbent polymer for the early diagnosis of infectious disease. Sensors Actuators, B Chem 240:881–886. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.09.046
Ambrosi A, Castañeda MT, Killard AJ et al (2007) Double-codified gold nanolabels for enhanced immunoanalysis. Anal Chem 79:5232–5240. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac070357m
Masoodi R, Pillai KM (2010) Darcy’s law-based model for wicking in paper-like swelling porous media. AIChE J 59:NA-NA. https://doi.org/10.1002/aic.12163
Parolo C, Medina-Sánchez M, de la Escosura-Muñiz A, Merkoçi A (2013) Simple paper architecture modifications lead to enhanced sensitivity in nanoparticle based lateral flow immunoassays. Lab Chip 13:386–390. https://doi.org/10.1039/C2LC41144J
Liu M, Suo S, Wu J et al (2019) Tailoring porous media for controllable capillary flow. J Colloid Interface Sci 539:379–387. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2018.12.068
Hess B, Kutzner C, Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E (2008) GRGMACS 4: Algorithms for highly efficient, load-balanced, and scalable molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4:435–447. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct700301q
Lindahl E, Hess B, van der Spoel D (2001) GROMACS 3.0: A package for molecular simulation and trajectory analysis. J Mol Model 7:306–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/S008940100045
Van Der Spoel D, Lindahl E, Hess B et al (2005) GROMACS: Fast, flexible, and free. J Comput Chem 26:1701–1718. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.20291
Brooks BR, Brooks CL, Mackerell AD et al (2009) CHARMM: The biomolecular simulation program. J Comput Chem 30:1545–1614. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc.21287
Brooks BR, Bruccoleri RE, Olafson BD, States DJ, Swaminathan S, Karplus M (1983) Charmm - a program for macromolecular energy, minimization, and dynamics calculations. J Comput Chem 4:187–217
Sunhwan JO, Taehoon KIM, Vidyashankara G, Iyer WI (2008) CHARMM-GUI: A Web-Based Graphical User Interface for CHARMM. J Comput Chem 29:1859–1865. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcc
Jorgensen WL, Chandrasekhar J, Madura JD et al (1983) Comparison of simple potential functions for simulating liquid water. J Chem Phys 79:926–935. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.445869
Bussi G, Donadio D, Parrinello M (2007) Canonical sampling through velocity rescaling. J Chem Phys 126(1):014101. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.2408420
Parrinello M, Rahman A (1981) Polymorphic transitions in single crystals: A new molecular dynamics method. J Appl Phys 52:7182–7190
Essmann U, Perera L, Berkowitz ML et al (1995) A smooth particle mesh Ewald method. J Chem Phys 103:8577–8593. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.470117
Hess B (2008) P-LINCS: A parallel linear constraint solver for molecular simulation. J Chem Theory Comput 4:116–122. https://doi.org/10.1021/ct700200b
Hess B, Bekker H, Berendsen HJC, Fraaije JGEM (1997) LINCS: A Linear Constraint Solver for molecular simulations. J Comput Chem 18:1463–1472. https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-987X(199709)18:12%3c1463::AID-JCC4%3e3.0.CO;2-H
Omidian H, Hashemi SA, Sammes PG, Meldrum I (1999) Modified acrylic-based superabsorbent polymers (dependence on particle size and salinity). Polymer (Guildf) 40:1753–1761. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-3861(98)00394-2
Sawut A, Yimit M, Sun W, Nurulla I (2014) Photopolymerisation and characterization of maleylatedcellulose-g- poly(acrylic acid) superabsorbent polymer. Carbohydr Polym 101:231–239. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2013.09.054
Fredrickson GH (1996) The theory of polymer dynamics. Curr Opin Solid State Mater Sci 1:812–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1359-0286(96)80106-9
Cheeveewattanagul N, Morales-Narváez E, Hassan ARHA et al (2017) Straightforward immunosensing platform based on graphene oxide-decorated nanopaper: a highly sensitive and fast biosensing approach. Adv Funct Mater 27:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201702741
Gao Y, Zhu Z, Xi X et al (2019) An aptamer-based hook-effect-recognizable three-line lateral flow biosensor for rapid detection of thrombin. Biosens Bioelectron 133:177–182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.03.036
Acknowledgements
This work was carried out with the support of the ‘‘Cooperative Research Program for Agriculture Science and Technology Development (Project No. PJ014238042021)” Rural Development Administration, Republic of Korea, as well as the Inha University Research Grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
You, T., Jeong, W., Lee, H. et al. A simple strategy for signal enhancement in lateral flow assays using superabsorbent polymers. Microchim Acta 188, 364 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05026-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-05026-2