Abstract
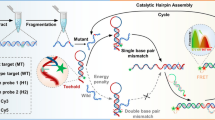
Based on the prominent electrochemiluminescence (ECL) performances of molybdenum disulfide-graphene quantum dots (MoS2-GQDs) nanocomposite and combined with enzyme-assisted recycling DNA walker signal amplification, an “on-off” switch ECL biosensor was proposed for sensitive assay of specific DNA sequences. Noticeably, MoS2 with two-dimensional nanosheet structure increased the loading capacity of GQDs to support abundant hairpin DNA (H). The composites of MoS2 and GQDs facilitated the charge transfer in ECL process, which significantly improved the ECL signal to achieve an “on” state. Then, the DNA walker cyclic amplification was performed by adding the target DNA and exonuclease III (Exo III). Finally, the DNA2-Fc-DNA1 was introduced into the system as ECL signal quencher, turning the ECL signal into an “off” state. The sensitive assay of ultra-low concentration specific DNA sequences was realized according to the variation of ECL signal strength before and after the existence of target DNA. The proposed ECL biosensor showed a good linear relationship ranging from 1 nM to 100 aM with a detection limit of 25.1 aM, providing a powerful strategy for biomedical research and clinical analysis.
Graphical abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang L, Wen Y, Yang X, Xu L, Liang W, Zhu Y, Wang L, Li Y, Li Y, Ding M, Ren S, Yang Z, Lv M, Zhang J, Ma K, Liu G (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemical DNA biosensor based on a label-free assembling strategy using a triblock polyA DNA probe. Anal Chem 91(24):16002–16009. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04757
Ding W, Song C, Li T, Ma H, Yao Y, Yao C (2019) TiO2 nanowires as an effective sensing platform for rapid fluorescence detection of single-stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. Talanta 199:442–448. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2019.02.002
Han Y, An F, Liu J, Kong J, Zhang X (2020) Highly sensitive determination of DNA via a new type of electrochemical zirconium signaling probe. New J Chem 44(47):20770–20775. https://doi.org/10.1039/d0nj04405a
Dutta S, Dutta Chowdhury A, Biswas S, Park EY, Agnihotri N, De A, De S (2018) Development of an effective electrochemical platform for highly sensitive DNA detection using MoS2- polyaniline nanocomposites. Biochem Eng J 140:130–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bej.2018.09.016
Chen J, Qiu H, Zhang M, Gu T, Shao S, Huang Y, Zhao S (2015) Hairpin assembly-triggered cyclic activation of a DNA machine for label-free and ultrasensitive chemiluminescence detection of DNA. Biosens Bioelectron 68:550–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.01.054
Wu H, Su Y, Jiang J, Liang Y, Zhang C (2020) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of p53 gene by a novel cloth-based microfluidic biosensor with luminol-gold nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction amplification. J Luminesc 226:117485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jlumin.2020.117485
Tang H, Chen W, Li D, Duan X, Ding S, Zhao M, Zhang J (2019) Luminol-based ternary electrochemiluminescence nanospheres as signal tags and target-triggered strand displacement reaction as signal amplification for highly sensitive detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA. Sensors Actuators B Chem 293:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.05.013
Wu Z, Luo F, Wen W, Zhang X, Wang S (2019)Enrichment-stowage-cycle strategy for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescent detection of HIV-DNA with wide dynamic range. Anal Chem 91(19):12238–12245. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b01969
Zhou S, Gou T, Hu J, Wu W, Ding X, Fang W, Hu Z, Mu Y (2019) A highly integrated real-time digital PCR device for accurate DNA quantitative analysis. Biosens Bioelectron 128:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.12.055
Tao C, Yan Y, Xiang H, Zhu D, Cheng W, Ju H, Ding S (2015) A new mode for highly sensitive and specific detection of DNA based on exonuclease III-assisted target recycling amplification and mismatched catalytic hairpin assembly. Chem Commun 51(20):4220–4222. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cc00385g
He Y, Chen D, Li M, Fang L, Yang W, Xu L, Fu F (2014) Rolling circle amplification combined with gold nanoparticles-tag for ultra sensitive and specific quantification of DNA by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. Biosens Bioelectron 58:209–213. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.02.072
Li X, Guo J, Zhai Q, Xia J, Yi G (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical biosensor for specific detection of DNA based on molecular beacon mediated circular strand displacement polymerization and hyperbranched rolling circle amplification. Anal Chim Acta 934:52–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2016.06.034
Jia L, Shi S, Ma R, Jia W, Wang H (2016) Highly sensitive electrochemical biosensor based on nonlinear hybridization chain reaction for DNA detection. Biosens Bioelectron 80:392–397. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.02.007
An N, Li K, Zhang Y, Wen T, Liu W, Liu G, Li L, Jin W (2021) A multiplex and regenerable surface plasmon resonance (MR-SPR) biosensor for DNA detection of genetically modified organisms. Talanta 231:122361. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2021.122361
Pan J, Li F, Cha TG, Chen H, Choi JH (2015) Recent progress on DNA based walkers. Curr Opin Biotechnol 34:56–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copbio.2014.11.017
Shin JS, Pierce NA (2004) A synthetic DNA walker for molecular transport. J Am Chem Soc 126(35):10834–10835. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja047543j
Wang L, Deng R, Li J (2015) Target-fueled DNA walker for highly selective miRNA detection. Chem Sci 6(12):6777–6782. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5sc02784e
Chen Y, Xiang Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2015) A restriction enzyme-powered autonomous DNA walking machine: its application for a highly sensitive electrochemiluminescence assay of DNA. Nanoscale 7(3):981–986. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr05387g
Ma C, Cao Y, Gou X, Zhu JJ (2020) Recent progress in electrochemiluminescence sensing and imaging. Anal Chem 92(1):431–454. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.9b04947
Huang B, Liu XP, Chen JS, Mao CJ, Niu HL, Jin BK (2020) Electrochemiluminescence immunoassay for the prostate-specific antigen by using a CdS/chitosan/g-C3N4 nanocomposite. Mikrochim Acta 187(3):155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-4125-y
Li M, Wang C, Chen L, Liu D (2019) A novel electrochemiluminescence sensor based on resonance energy transfer system between nitrogen doped graphene quantum dots and boron nitride quantum dots for sensitive detection of folic acid. Anal Chim Acta 1090:57–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2019.09.018
Shekari Z, Zare HR, Falahati A (2019) Electrochemical sandwich aptasensor for the carcinoembryonic antigen using graphene quantum dots, gold nanoparticles and nitrogen doped graphene modified electrode and exploiting the peroxidase-mimicking activity of a G-quadruplex DNAzyme. Mikrochim Acta 186(8):530. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3572-9
Zhang X-L, Li X, Li X-T, Gao Y, Feng F, Yang G-J (2019) Electrochemiluminescence sensor for pentoxifylline detection using Au nanoclusters@graphene quantum dots as an amplified electrochemiluminescence luminophore. Sensors Actuators B Chem 282:927–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.11.113
Wang H, Yuan H, Sae Hong S, Li Y, Cui Y (2015) Physical and chemical tuning of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem Soc Rev 44(9):2664–2680. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4cs00287c
Song Y, Qiao J, Li W, Ma C, Chen S, Li H, Hong C (2020) Bimetallic PtCu nanoparticles supported on molybdenum disulfide-functionalized graphitic carbon nitride for the detection of carcinoembryonic antigen. Mikrochim Acta 187(9):538. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-020-04498-y
Lin Y, Chen X, Lin Y, Zhou Q, Tang D (2015) Non-enzymatic sensing of hydrogen peroxide using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite made from carbon nanotubes and molybdenum disulfide. Microchim Acta 182(9–10):1803–1809. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1517-5
Ma X, Du C, Zhang J, Shang M, Song W (2019) A system composed of vanadium(IV) disulfide quantum dots and molybdenum(IV) disulfide nanosheets for use in an aptamer-based fluorometric tetracycline assay. Mikrochim Acta 186(12):837. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3983-7
Govindasamy M, Chen S-M, Mani V, Akilarasan M, Kogularasu S, Subramani B (2016) Nanocomposites composed of layered molybdenum disulfide and graphene for highly sensitive amperometric determination of methyl parathion. Microchim Acta 184(3):725–733. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-2062-6
Li Z, Ye R, Feng R, Kang Y, Zhu X, Tour JM, Fang Z (2015) Graphene quantum dots doping of MoS2 monolayers. Adv Mater 27(35):5235–5240. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201501888
Vasilescu I, Eremia SA, Kusko M, Radoi A, Vasile E, Radu GL (2016) Molybdenum disulphide and graphene quantum dots as electrode modifiers for laccase biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 75:232–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.051
Chen C, Qiao H, Lin S, Man Luk C, Liu Y, Xu Z, Song J, Xue Y, Li D, Yuan J, Yu W, Pan C, Ping Lau S, Bao Q (2015) Highly responsive MoS2 photodetectors enhanced by graphene quantum dots. Sci Rep 5:11830. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep11830
Yang Y, Fang G, Wang X, Zhang F, Liu J, Zheng W, Wang S (2017) Electrochemiluminescent graphene quantum dots enhanced by MoS2 as sensing platform: a novel molecularly imprinted electrochemiluminescence sensor for 2-methyl-4-chlorophenoxyacetic acid assay. Electrochim Acta 228:107–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.043
Xie J, Zhang H, Li S, Wang R, Sun X, Zhou M, Zhou J, Lou XW, Xie Y (2013) Defect-rich MoS2 ultrathin nanosheets with additional active edge sites for enhanced electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Adv Mater 25(40):5807–5813. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201302685
Xie S, Dong Y, Yuan Y, Chai Y, Yuan R (2016) Ultrasensitive lipopolysaccharides detection based on doxorubicin conjugated N-(Aminobutyl)-N-(ethylisoluminol) as electrochemiluminescence indicator and self-assembled tetrahedron DNA dendrimers as nanocarriers. Anal Chem 88(10):5218–5224. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.analchem.6b00276
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21775055, 22074053, 21874055); Excellent Youth Innovation Team in Universities of Shandong (2019KJC016); The Project of “20 items of University” of Jinan (2020GXRC047, 2018GXRC001); the Taishan Scholars program and Case-by-Case Project for Top Outstanding Talents of Jinan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 416 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, Y., Huang, C., Sun, X. et al. Electrochemiluminescence biosensor based on molybdenum disulfide-graphene quantum dots nanocomposites and DNA walker signal amplification for DNA detection. Microchim Acta 188, 353 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04962-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04962-3