Abstract
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) have been accepted as promising non-invasive biomarkers for cancer early diagnosis. Developing amplified sensing strategies for detecting ultralow concentration of miRNAs in clinical samples still requires much effort. Herein, an integrated fluorescence biosensor using nicking enzyme-powered numerous-feet DNA walking machine was developed for ultrasensitive detection of miRNA. A long numerous-feet walker produced by target-triggered rolling circle amplification autonomously moves along the defined DNA tracks on gold nanorods (AuNRs) with the help of nicking enzyme, leading to the recovery of fluorescence. This results in an amplified fluorescence signal, typically measured at 518 nm emission wavelength. Benefiting from the long walker that dramatically improves movement range, the homogenous and one-step strategy realizes ultrahigh sensitivity with a limit of detection of 0.8 fM. Furthermore, this walking machine has been successfully used to quantification of miRNA in clinical serum samples. The consistency of the gained results between of the developed strategy and reverse transcription quantitative polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) shows that the sensing method has great promise for tumor diagnostics based on nucleic acid.
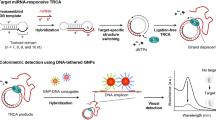
Graphical abstract

Schematic representation of the fluorescent biosensing strategy, numerous-legged DNA walker prepared by rolling circle amplification on gold nanorods (AuNRs) for microRNA analysis, which can be applied in real samples with good results.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu P, Zhang S, Wu T, Ni D, Fan W, Zhu Y, Qian R, Shi J (2018) Fe-Au nanoparticle-coupling for ultrasensitive detections of circulating tumor DNA. Adv Mater 30(31):e1801690
Murtaza M, Dawson SJ, Tsui DW, Gale D, Forshew T, Piskorz AM, Parkinson C, Chin SF, Kingsbury Z, Wong AS, Marass F, Humphray S, Hadfield J, Bentley D, Chin TM, Brenton JD, Caldas C, Rosenfeld N (2013) Non-invasive analysis of acquired resistance to cancer therapy by sequencing of plasma DNA. Nature 497(7447):108–112
Jin CE, Koo B, Lee TY, Han K, Lim SB, Park IJ, Shin Y (2018) Simple and low-cost sampling of cell-free nucleic acids from blood plasma for rapid and sensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA. Adv Sci 5(10):1800614
van Rooij E, Sutherland LB, Qi X, Richardson JA, Hill J, Olson EN (2007) Control of stress-dependent cardiac growth and gene expression by a microRNA. Science 316(5824):575–579
Dong H, Lei J, Ding L, Wen Y, Ju H, Zhang X (2013) MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113(8):6207–6233
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, Alvarez-Saavedra E, Lamb J, Peck D, Sweet-Cordero A, Ebert BL, Mak RH, Ferrando AA, Downing JR, Jacks T, Horvitz HR, Golub TR (2005) MicroRNA expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature 435(7043):834–838
Rasnic R, Linial N, Linial M (2017) Enhancing identification of cancer types via lowly-expressed microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 45(9):5048–5060
Du J, Yang S, An D, Hu F, Yuan W, Zhai C, Zhu T (2009) BMP-6 inhibits microRNA-21 expression in breast cancer through repressing deltaEF1 and AP-1. Cell Res 19(4):487–496
Li X, Cheng W, Li D, Wu J, Ding X, Cheng Q, Ding S (2016) A novel surface plasmon resonance biosensor for enzyme-free and highly sensitive detection of microRNA based on multi component nucleic acid enzyme (MNAzyme)-mediated catalyzed hairpin assembly. Biosens Bioelectron 80:98–104
Kuang Y, Cao J, Xu F, Chen Y (2019) Duplex-specific nuclease-mediated amplification strategy for mass spectrometry quantification of MiRNA-200c in breast cancer stem cells. Anal Chem 91(14):8820–8826
Ouyang T, Liu Z, Han Z, Ge Q (2019) MicroRNA detection specificity: recent advances and future perspective. Anal Chem 91(5):3179–3186
Ye J, Xu M, Tian X, Cai S, Zeng S (2019) Research advances in the detection of miRNA. J Pharm Anal 9(4):217–226
Zhang C, Miao P, Sun M, Yan M, Liu H (2019) Progress in miRNA detection using graphene material-based biosensors. Small 15(38):e1901867
Wang YH, He LL, Huang KJ, Chen YX, Wang SY, Liu ZH, Li D (2019) Recent advances in nanomaterial-based electrochemical and optical sensing platforms for microRNA assays. Analyst 144(9):2849–2866
Masud MK, Umer M, Hossain MSA, Yamauchi Y, Nguyen NT, Shiddiky MJA (2019) Nanoarchitecture frameworks for electrochemical miRNA detection. Trends Biochem Sci 44(5):433–452
Deng R, Zhang K, Li J (2017) Isothermal amplification for MicroRNA detection: from the test tube to the cell. Acc Chem Res 50(4):1059–1068
Lei S, Liu Z, Xu L, Zou L, Li G, Ye B (2020) A “signal-on” electrochemical biosensor based on DNAzyme-driven bipedal DNA walkers and TdT-mediated cascade signal amplification strategy. Anal Chim Acta 1100:40–46
Wang W, Yu S, Huang S, Bi S, Han H, Zhang JR, Lu Y, Zhu JJ (2019) Bioapplications of DNA nanotechnology at the solid-liquid interface. Chem Soc Rev 48(18):4892–4920
Li D, Cheng W, Li Y, Xu Y, Li X, Yin Y, Ju H, Ding S (2016) Catalytic hairpin assembly actuated DNA nanotweezer for logic gate building and sensitive enzyme-free biosensing of MicroRNAs. Anal Chem 88(15):7500–7506
Huo M, Li S, Zhang P, Feng Y, Liu Y, Wu N, Ju H, Ding L (2019) Nanoamplicon comparator for live-cell microRNA imaging. Anal Chem 91(5):3374–3381
Bai M, Chen F, Cao X, Zhao Y, Xue J, Yu X, Fan C, Zhao Y (2020) Intracellular entropy-driven multi-bit DNA computing for tumor progression discrimination. Angew Chem Int Ed 59(32):13267–13272
Xue J, Chen F, Bai M, Cao X, Huang P, Zhao Y (2019) All-in-one synchronized DNA nanodevices facilitating multiplexed cell imaging. Anal Chem 91(7):4696–4701
Xiao M, Zou K, Li L, Wang L, Tian Y, Fan C, Pei H (2019) Stochastic DNA walkers in droplets for super-multiplexed bacterial phenotype detection. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(43):15448–15454
Xu M, Zhuang J, Jiang X, Liu X, Tang D (2019) A three-dimensional DNA walker amplified FRET sensor for detection of telomerase activity based on the MnO2 nanosheet-upconversion nanoparticle sensing platform. Chem Commun 55(66):9857–9860
Zheng J, Ji X, Du M, Tian S, He Z (2018) Rational construction of a DNA nanomachine for HIV nucleic acids ultrasensitive sensing. Nanoscale 10(36):17206–17211
Jung C, Allen PB, Ellington AD (2017) A simple, cleated DNA walker that hangs on to surfaces. ACS Nano 11(8):8047–8054
Škugor M, Valero J, Murayama K, Centola M, Asanuma H, Famulok M (2019) Orthogonally photocontrolled non-autonomous DNA walker. Angew Chem Int Ed 58(21):6948–6951
Qu X, Zhu D, Yao G, Su S, Chao J, Liu H, Zuo X, Wang L, Shi J, Wang L, Huang W, Pei H, Fan C (2017) An exonuclease III-powered, on-particle stochastic DNA walker. Angew Chem Int Ed 56(7):1855–1858
Peng H, Li XF, Zhang H, Le XC (2017) A microRNA-initiated DNAzyme motor operating in living cells. Nat Commun 8:14378
Xu Z, Chang Y, Chai Y, Wang H, Yuan R (2019) Ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for speedy detection of microRNA based on a DNA rolling machine and target recycling. Anal Chem 91(7):4883–4888
Li D, Xu Y, Fan L, Shen B, Ding X, Yuan R, Li X, Chen W (2020) Target-driven rolling walker based electrochemical biosensor for ultrasensitive detection of circulating tumor DNA using doxorubicin@tetrahedron-Au tags. Biosens Bioelectron 148:111826
Wu N, Wang K, Wang YT, Chen ML, Chen XW, Yang T, Wang JH (2020) Three-dimensional DNA nanomachine biosensor by integrating DNA walker and rolling machine cascade amplification for ultrasensitive detection of cancer-related gene. Anal Chem 92(16):11111–11118
Liu C, Hu Y, Pan Q, Yi J, Zhang J, He M, He M, Nie C, Chen T, Chu X (2020) Photocontrolled and self-powered bipedal DNA walking machine for intracellular microRNA imaging. Chem Commun 56(24):3496–3499
Wang L, Liu P, Liu Z, Zhao K, Ye S, Liang G, Zhu JJ (2020) Simple tripedal DNA walker prepared by target-triggered catalytic hairpin assembly for ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence detection of microRNA. ACS Sens 5(11):3584–3590
Yao D, Bhadra S, Xiong E, Liang H, Ellington AD, Jung C (2020) Dynamic programming of a DNA walker controlled by protons. ACS Nano 14(4):4007–4013
Wang L, Deng R, Li J (2015) Target-fueled DNA walker for highly selective miRNA detection. Chem Sci 6(12):6777–6782
Lan X, Chen Z, Dai G, Lu X, Ni W, Wang Q (2013) Bifacial DNA origami-directed discrete, three-dimensional, anisotropic plasmonic nanoarchitectures with tailored optical chirality. J Am Chem Soc 135(31):11441–11444
Orendorff CJ, Murphy CJ (2006) Quantitation of metal content in the silver-assisted growth of gold nanorods. J Phys Chem B 110(9):3990–3994
Liu B, Song C, Zhu D, Wang X, Zhao M, Yang Y, Zhang Y, Su S, Shi J, Chao J, Liu H, Zhao Y, Fan C, Wang L (2017) DNA-origami-based assembly of anisotropic plasmonic gold nanostructures. Small 13(23):1603991
Shen C, Lan X, Lu X, Meyer TA, Ni W, Ke Y, Wang Q (2016) Site-specific surface functionalization of gold nanorods using DNA origami clamps. J Am Chem Soc 138(6):1764–1767
Huang J, Zhu L, Ju H, Lei J (2019) Telomerase triggered DNA Walker with a superhairpin structure for human telomerase activity sensing. Anal Chem 91(11):6981–6985
Yang T, Fang J, Guo Y, Sheng S, Pu Q, Zhang L, Ou X, Dai L, Xie G (2019) Fluorometric determination of microRNA by using an entropy-driven three-dimensional DNA walking machine based on a catalytic hairpin assembly reaction on polystyrene microspheres. Mikrochim Acta 186(8):574
Li Q, Liang X, Mu X, Tan L, Lu J, Hu K, Zhao S, Tian J (2020) Ratiometric fluorescent 3D DNA walker and catalyzed hairpin assembly for determination of microRNA. Mikrochim Acta 187(6):365
Li D, Luo Z, An H, Yang E, Wu M, Huang Z, Duan Y (2020) Poly-adenine regulated DNA density on AuNPs to construct efficient DNA walker for microRNA-21 detection. Talanta 217:121056
Yang L, Fang J, Li J, Ou X, Zhang L, Wang Y, Weng Z, Xie G (2021) An integrated fluorescence biosensor for microRNA detection based on exponential amplification reaction-triggered three-dimensional bipedal DNA walkers. Anal Chim Acta 1143:157–165
Hu M, Mao D, Liu X, Ren L, Zhou M, Chen X, Zhu X (2019) An all-in-one homogeneous DNA walking nanomachine and its application for intracellular analysis of miRNA. Theranostics 9(20):5914–5923
Funding
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation Project of Chongqing (cstc2020jcyj-msxmX0611) and the Talent Fund of the Fengjie People’s Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary information
ESM 1
(DOCX 556 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Zeng, H., Yang, X. et al. Integrated nicking enzyme-powered numerous-legged DNA walker prepared by rolling circle amplification for fluorescence detection of microRNA. Microchim Acta 188, 214 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04875-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-021-04875-1