Abstract
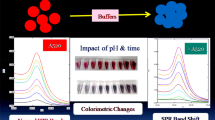
MoS2 quantum dots were hydrothermally synthesized and utilized for the formation and stabilization of a nanocomposite with silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) in a single step. This composite was characterized by transmission electron microscopy and zeta potential measurements. It is found that this nanohybrid can be stimulated by mercury(II) ion and then exhibits excellent oxidase mimicking activity. The oxidase-like activity is demonstrated by the oxidation of 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine by H2O2 that leads to the formation of a blue product. An assay was developed for determination of cysteine (Cys) at ultra-trace level because Cys inhibits the activity of the nanozyme via interaction with Hg(II). The Cys assay, best performed at a wavelength of 652 nm, works in the 1–100 μM concentration range and has a 0.82 μM detection limit. In addition, a portable Cys test kit is described that was applied to the determination of Cys in serum samples. The resulting colorations were compared with color chat wheel. The method is simple, rapid, cost-effective, and sensitive.

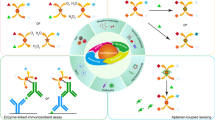
Schematic presentation of oxidase mimetic activity of the Hg@ MoS2-QDs-AgNPs and colorimetric sensing of Cys.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pan N, Li-Ying W, Wu LL et al (2017) Colorimetric determination of cysteine by exploiting its inhibitory action on the peroxidase-like activity of Au@Pt core-shell nanohybrids. Microchim Acta 184:65–72. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1981-6
He J, Wu X, Long Z, Hou X (2019) Fast and sensitive fluorescent and visual sensing of cysteine using Hg-metalated PCN-222. Microchem J 145:68–73. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.10.001
Xue Z, Xiong L, Peng H et al (2018) A selective colorimetric sensing strategy for cysteine based on an indicator-displacement mechanism. New J Chem 42:4324–4330. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NJ03887A
Wu L-L, Wang L-Y, Xie Z-J et al (2016) Colorimetric assay of l-cysteine based on peroxidase-mimicking DNA-Ag/Pt nanoclusters. Sensors Actuators B Chem 235:110–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2016.05.069
Zhang M, Yu M, Li F et al (2007) A highly selective fluorescence turn-on sensor for cysteine/Homocysteine and its application in bioimaging. J Am Chem Soc 129:10322–10323. https://doi.org/10.1021/JA073140I
Chwatko G, Kuźniak E, Kubalczyk P et al (2014) Determination of cysteine and glutathione in cucumber leaves by HPLC with UV detection. Anal Methods 6:8039–8044. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AY01574F
Menestrina F, Osorio Grisales J, Castells CB (2016) Chiral analysis of derivatized amino acids from kefir by gas chromatography. Microchem J 128:267–273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2016.05.007
Pazalja M, Kahrović E, Zahirović A (2016) ELECTROCHEMICAL SCIENCE Electrochemical sensor for determination of L-cysteine based on carbon electrodes modified with Ru(III) Schiff Base complex, carbon nanotubes and Nafion. Int J Electrochem Sci 11:10939–10952. https://doi.org/10.20964/2016.12.86
Lee PT, Thomson JE, Karina A et al (2015) Selective electrochemical determination of cysteine with a cyclotricatechylene modified carbon electrode. Analyst 140:236–242. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4AN01835D
Xue Z, Xiong L, Rao H et al (2019) A naked-eye liquid-phase colorimetric assay of simultaneous detect cysteine and lysine. Dyes Pigments 160:151–158. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.DYEPIG.2018.07.054
Wu X-Q, Xu Y, Chen Y-L et al (2014) Peroxidase-like activity of ferric ions and their application to cysteine detection. RSC Adv 4:64438–64442. https://doi.org/10.1039/C4RA11000E
Singh M, Weerathunge P, Liyanage PD et al (2017) Competitive inhibition of the enzyme-mimic activity of Gd-based Nanorods toward highly specific colorimetric sensing of l -cysteine. Langmuir 33:10006–10015. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b01926
Wei H, Wang E (2013) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42:6060–6093. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs35486e
Han KN, Choi J-S, Kwon J (2017) Gold nanozyme-based paper chip for colorimetric detection of mercury ions. Sci Rep 7:2806. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-02948-x
Zarlaida F, Adlim M (2017) Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury(II) ions: a review. Microchim Acta 184:45–58. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1967-4
Zhou Y, Dong H, Liu L et al (2014) Selective and sensitive colorimetric sensor of mercury(II) based on gold nanoparticles and 4-mercaptophenylboronic acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:106–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2014.01.060
Jazayeri MH, Aghaie T, Avan A et al (2018) Colorimetric detection based on gold nano particles (GNPs): an easy, fast, inexpensive, low-cost and short time method in detection of analytes (protein, DNA, and ion). Sens Bio-Sensing Res 20:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SBSR.2018.05.002
Chen W, Fang X, Li H et al (2016) A simple paper-based colorimetric device for rapid mercury(II) assay. Sci Rep 6:31948. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31948
Lin X-Q, Deng H-H, Wu G-W et al (2015) Platinum nanoparticles/graphene-oxide hybrid with excellent peroxidase-like activity and its application for cysteine detection. Analyst 140:5251–5256. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5AN00809C
Jiang H, Chen Z, Cao H, Huang Y (2012) Peroxidase-like activity of chitosan stabilized silver nanoparticles for visual and colorimetric detection of glucose. Analyst 137:5560–5564. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35911a
Li L, Gui L, Li W (2015) A colorimetric silver nanoparticle-based assay for Hg(II) using lysine as a particle-linking reagent. Microchim Acta 182:1977–1981. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1536-2
Rameshkumar P, Manivannan S, Ramaraj R (2013) Silver nanoparticles deposited on amine-functionalized silica spheres and their amalgamation-based spectral and colorimetric detection of Hg(II) ions. J Nanopart Res 15:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-013-1639-9
Lin Y, Ren J, Qu X (2014) Catalytically active Nanomaterials: a promising candidate for artificial enzymes. Acc Chem Res 47:1097–1105. https://doi.org/10.1021/ar400250z
He W, Wu X, Liu J et al (2010) Design of AgM bimetallic alloy nanostructures (M = au, Pd, Pt) with tunable morphology and peroxidase-like activity. Chem Mater 22:2988–2994. https://doi.org/10.1021/cm100393v
Wang Y, Yang F, Yang X (2010) Colorimetric detection of mercury(II) ion using unmodified silver nanoparticles and mercury-specific oligonucleotides. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2:339–342. https://doi.org/10.1021/am9007243
Dong H, Tang S, Hao Y et al (2016) Ent MoS2 quantum dots: ultrasonic preparation, up-conversion and Down-conversion bioimaging, and PhotodynFluorescamic therapy. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8:3107–3114. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b10459
Kufer D, Nikitskiy I, Lasanta T et al (2015) Hybrid 2D-0D MoS2-PbS quantum dot photodetectors. Adv Mater 27:176–180. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201402471
Mandal S, Gole A, Lala N et al (2001) Studies on the reversible aggregation of cysteine-capped colloidal silver particles interconnected via hydrogen bonds. Langmuir 17:6262–6268. https://doi.org/10.1021/la010536d
Katok KV, Whitby RLD, Fukuda T et al (2012) Hyperstoichiometric interaction between silver and mercury at the Nanoscale. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:2632–2635. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201106776
Mishra R, Nirala NR, Pandey RK et al (2017) Homogenous dispersion of MoS 2 Nanosheets in Polyindole matrix at air-water Interface assisted by Langmuir technique. Langmuir 33:13572–13580. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.langmuir.7b03019
Vinita NNR, Prakash R (2018) One step synthesis of AuNPs@MoS2-QDs composite as a robust peroxidase- mimetic for instant unaided eye detection of glucose in serum, saliva and tear. Sensors Actuators B Chem 263:109–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/J.SNB.2018.02.085
Gopalakrishnan D, Damien D, Shaijumon MM (2014) MoS 2 quantum dot-interspersed exfoliated MoS 2 Nanosheets. ACS Nano 8:5297–5303. https://doi.org/10.1021/nn501479e
Bai R, Wang P, Fang Y (2017) Probing microstructures of molybdenum disulfide quantum dots by resonant Raman scattering. Appl Phys Lett 110:161910. https://doi.org/10.1063/1.4981803
Gao L, Zhuang J, Nie L et al (2007) Intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Nat Nanotechnol 2:577–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nnano.2007.260
Wang G-L, Xu X-F, Cao L-H et al (2014) Mercury(ii)-stimulated oxidase mimetic activity of silver nanoparticles as a sensitive and selective mercury(ii) sensor. RSC Adv 4:5867. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3ra45226c
Lu Y, Yu J, Ye W et al (2016) Spectrophotometric determination of mercury(II) ions based on their stimulation effect on the peroxidase-like activity of molybdenum disulfide nanosheets. Microchim Acta 183:2481–2489. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1886-4
Acknowledgements
All the authors are thankful to Prof D Dash, IMS, BHU, Varanasi for his support in biological experiments and providing blood serum. Authors are also thankful to CIF, IIT (BHU) for providing instrumentation facilities. Richa Mishra is thankful to DST-INSPIRE for providing her fellowship. Dr. Narsingh R. Nirala greatly acknowledges SERB N-PDF (PDF/2016/000243).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 3978 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojha, R.P., Mishra, R., Singh, P. et al. A composite prepared from MoS2 quantum dots and silver nanoparticles and stimulated by mercury(II) is a robust oxidase mimetic for use in visual determination of cysteine. Microchim Acta 187, 74 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4041-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-4041-1