Abstract
Lateral flow assays, as a low-cost, simple, portable and disposable product of vitro diagnostic, are being widely used for point-of-care testing. However, the poor sensitivity of LFAs is the main challenge for commercialization. In order to enhance the sensitivity of LFAs, cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) have been integrated into LFAs to enhance the sensitivity of protein LFAs. A simple method is also presented to modify the properties of paper substrate by incorporating CNFs into a nitrocellulose membrane to enhance the sensitivity of nucleic acid LFAs. This method changes the pore size, porosity, surface groups and surface area of paper substrate and then increases the adsorption ability of biomolecules on paper substrate. The results indicate that the sensitivity of nucleic acid LFAs in Staphylococcus aureus testing achieves a 20-fold enhancement. Hence, we anticipate that this simple method has the potential for other paper-based devices to improve the performance.

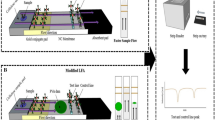
A simple method is used to modify the properties of paper substrate by incorporating cellulose nanofibers (CNFs) into nitrocellulose (NC) membrane to enhance the sensitivity of nucleic acid LFAs.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Posthuma-Trumpie AG, Korf J, van Amerongen A (2009) Lateral flow (immuno)assay: its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats. A literature survey. Anal Bioanal Chem 393:562–582
Fu E, Liang T, Houghtaling J, Ramachandran S, Ramsey SA, Lutz B, Yager P (2011) Enhanced sensitivity of lateral flow tests using a two-dimensional paper network format. Anal Chem 83(20):7941–7946. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac201950g
Oh YK, Joung HA, Han HS, Suk HJ, Kim MG (2014) A three-line lateral flow assay strip for the measurement of C-reactive protein covering a broad physiological concentration range in human sera. Biosens Bioelectron 61:285–289. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.04.032
Tang R, Yang H, Choi JR, Gong Y, Hu J, Feng S, Pingguan-Murphy B, Mei Q, Xu F (2016) Improved sensitivity of lateral flow assay using paper-based sample concentration technique. Talanta 152:269–276. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2016.02.017
Lu X, Mei T, Guo Q, Zhou W, Li X, Chen J, Zhou X, Sun N, Fang Z (2018) Improved performance of lateral flow immunoassays for alpha-fetoprotein and vanillin by using silica shell-stabilized gold nanoparticles. Mikrochimica acta 186(1):2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3107-9
Tang R, Yang H, Gong Y, Liu Z, Li X, Wen T, Qu Z, Zhang S, Mei Q, Xu F (2017) Improved analytical sensitivity of lateral flow assay using sponge for HBV nucleic acid detection. Sci Rep 7(1). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-01558-x
Tincello DG, Richmond DH (1998) Evaluation of reagent strips in detecting asymptomatic bacteriuria in early pregnancy prospective case series. BMJ 316:435–437
Marino E, Threlfall WR, Schwarze RA (2009) Early conception factor lateral flow assays for pregnancy in the mare. Theriogenology 71(6):877–883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.theriogenology.2008.06.003
Warsinke A (2009) Point-of-care testing of proteins. Anal Bioanal Chem 393(5):1393–1405. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-008-2572-0
Hu J, Wang L, Li F, Han YL, Lin M, Lu TJ, Xu F (2013) Oligonucleotide-linked gold nanoparticle aggregates for enhanced sensitivity in lateral flow assays. Lab Chip 13(22):4352–4357. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3lc50672j
Kylanpaa-Back ML, Kemppainen E, Puolakkainen P, Hedstrom J, Haapiainen R, Perhoniemi V, Kivilaakso E, Korvuo A, Stenman UH (2000) Reliable screening for acute pancreatitis with rapid urine trypsinogen-2 test strip. Brit J Surg 87(1):49–52
Moghadam BY, Connelly KT, Posner JD (2015) Two orders of magnitude improvement in detection limit of lateral flow assays using isotachophoresis. Anal Chem 87(2):1009–1017. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac504552r
Moghadam BY, Connelly KT, Posner JD (2014) Isotachophoretic preconcenetration on paper-based microfluidic devices. Anal Chem 86(12):5829–5837. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac500780w
Wong SY, Cabodi M, Rolland J, Klapperich CM (2014) Evaporative concentration on a paper-based device to concentrate Analytes in a biological fluid. Anal Chem 86(24):11981–11985. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac503751a
Chiu RY, Jue E, Yip AT, Berg AR, Wang SJ, Kivnick AR, Nguyen PT, Kamei DT (2014) Simultaneous concentration and detection of biomarkers on paper. Lab Chip 14(16):3021–3028. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00532e
Rivas L, Medina-Sanchez M, de la Escosura-Muniz A, Merkoci A (2014) Improving sensitivity of gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow assays by using wax-printed pillars as delay barriers of microfluidics. Lab Chip 14(22):4406–4414. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4lc00972j
Saisin L, Amarit R, Somboonkaew A, Gajanandana O, Himananto O, Sutapun B (2018) Significant sensitivity improvement for camera-based lateral flow immunoassay readers. Sensors 18(11). https://doi.org/10.3390/s18114026
Zhang H, Lei Z, Tian R, Wang Z (2018) Polyamidoamine starburst dendrimer-activated chromatography paper-based assay for sensitive detection of telomerase activity. Talanta 178:116–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.09.034
Ren X, Lu P, Feng R, Zhang T, Zhang Y, Wu D, Wei Q (2018) An ITO-based point-of-care colorimetric immunosensor for ochratoxin a detection. Talanta 188:593–599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2018.06.004
Wang S, Ge L, Song X, Yu J, Ge S, Huang J, Zeng F (2012) Paper-based chemiluminescence ELISA: lab-on-paper based on chitosan modified paper device and wax-screen-printing. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):212–218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2011.10.019
Yang C-H, Chen C-A, Chen C-F (2018) Surface-modified cellulose paper and its application in infectious disease diagnosis. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 265:506–513. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.092
Marín-Barroso E, Moreira CM, Messina GA, Bertolino FA, Alderete M, Soler-Illia GJAA, Raba J, Pereira SV (2018) Paper based analytical device modified with nanoporous material for the fluorescent sensing of gliadin content in different food samples. Microchem J 142:78–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.microc.2018.06.005
Barbash VA, Yaschenko OV, Shniruk OM (2017) Preparation and properties of Nanocellulose from Organosolv straw pulp. Nanoscale Res Lett 12(1):241. https://doi.org/10.1186/s11671-017-2001-4
Sulaiman S, Mokhtar MN, Naim MN, Baharuddin AS, Sulaiman A (2014) A review: potential usage of cellulose Nanofibers (CNF) for enzyme immobilization via covalent interactions. Appl Biochem Biotech 175(4):1817–1842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-014-1417-x
Quesada-Gonzalez D, Stefani C, Gonzalez I, de la Escosura-Muniz A, Domingo N, Mutje P, Merkoci A (2019) Signal enhancement on gold nanoparticle-based lateral flow tests using cellulose nanofibers. Biosens Bioelectron 141:111407. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2019.111407
Mohite BV, Patil SV (2014) Bacterial cellulose of Gluconoacetobacter hansenii as a potential bioadsorption agent for its green environment applications. J Biomat Sci-Polym E 25(18):2053–2065. https://doi.org/10.1080/09205063.2014.970063
Barros RJ, Wehtje E, Garcia FAP, Adlercreutz P (1998) Physical characterization of porous materials and correlation with the activity of immobilized enzyme in organic medium. Biocatal Biotransfor 16(1):67–85. https://doi.org/10.3109/10242429809040111
Książczak A, Radomski A, Zielenkiewicz T (2003) Nitrocellulose porosity-thermoporometry. J Therm Anal Calorim 74:559–568
Li B, Wen H-M, Wang H, Wu H, Tyagi M, Yildirim T, Zhou W, Chen B (2014) A porous metal−organic framework with dynamic pyrimidine group exhibiting record high methane storage working capacity. J Am Chem Soc 136:6207–6210 https://doi.org/10.1021/ja501810r
Hartmann M, Kostrov X (2013) Immobilization of enzymes on porous silicas--benefits and challenges. Chem Soc Rev 42(15):6277–6289. https://doi.org/10.1039/c3cs60021a
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21808132), the Natural Science Basic Research Plan of Shaanxi Province (2019JQ-517), the Project of Shaanxi Provincial Education department (18JK0096), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2018 M633525), the Opening Project of National Experimental Teaching Demonstration Center of Light Chemical Engineering (2018QGSJ02-10).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 117 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, R.H., Liu, L.N., Zhang, S.F. et al. Modification of a nitrocellulose membrane with cellulose nanofibers for enhanced sensitivity of lateral flow assays: application to the determination of Staphylococcus aureus. Microchim Acta 186, 831 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3970-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3970-z