Abstract
A series of phosphorene (BP) nanocomposites was prepared to realize simultaneous electrochemical determination of clenbuterol (CLB) and ractopamine (RAC). CLB and RAC are the most commonly used β-agonists in animal-derived food. The BP nanohybrid was obtained by co-decoration with both mono(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanoparticles. It displays high stability, antifouling capability, a large electrochemical active surface and good electrochemical response. The electrochemical assisted antifouling strategy was selected by further eliminating the fouling of the electrode surface using continuous cyclic voltammetry. The electrode was employed for electrochemical sensing of CLB and RAC at typical peak voltages of 0.8 and 1.0 V (vs. SCE). Responses are linear in the 0.3–90 μM concentration range for CLB, and from 0.3 to 9.4 μM for RAC under optimal conditions. The limit of detection are 0.14 and 0.12 μM, respectively. The sensor was employed for simultaneous determination of CLB and RAC in (spiked) beef, feed and bovine serum samples with acceptable recoveries.

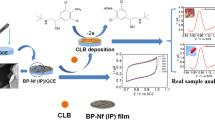
An electrochemically assisted anti-fouling method for simultaneous voltammetric nanosensing of clenbuterol (CLB) and ractopamine (RAC) in edible cattle product samples using high-stable and anti-foul phosphorene (BP) co-decorated with mono(6-mercapto-6-deoxy)-β-cyclodextrin (S-β-CD) and poly(3,4-ethylenedioxythiophene) (PEDOTNPs).






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hu LM, Luo K, Xia J, Xu GM, Wu CH, Han JJ, Lai WH (2017) Advantages of time-resolved fluorescent nanobeads compared with fluorescent submicrospheres, quantum dots, and colloidal gold as label in lateral flow assays for detection of ractopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 91:95–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.12.030
Pleadin J, Vulić A, Perši N, Vahčić N (2010) Clenbuterol residues in pig muscle after repeat administration in a growth-promoting dose. Meat Sci 86:733–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.meatsci.2010.06.013
Zhai H, Liu Z, Chen Z, Liang Z, Su Z, Wang S (2015) A sensitive electrochemical sensor with sulfonated graphene sheets/oxygen-functionalized multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified electrode for the detection of clenbuterol. Sens Atuators B 210:483–490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.12.121
Zhang D, Liu Q (2016) Biosensors and bioelectronics on smartphone for portable biochemical detection. Biosens Bioelectron 75:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.08.037
Broza YY, Haick H (2013) Nanomaterial-based sensors for detection of disease by volatile organic compounds. Nanomedicine-UK 8:785–806. https://doi.org/10.2217/nnm.13.64
Yan F, Zhang Y, Zhang S, Zhao J, Liu S, He L, Zhang Z (2015) Carboxyl-modified graphene for use in an immunoassay for the illegal feed additive clenbuterol using surface plasmon resonance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. Microchim Acta 182:855–862. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1399-y
Song Y, Luo Y, Zhu C, Li H, Du D, Lin Y (2016) Recent advances in electrochemical biosensors based on graphene two-dimensional nanomaterials. Biosens Bioelectron 76:195–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2015.07.002
Yang Y, Zhang H, Huang C, Yang D, Jia N (2017) Electrochemical non-enzyme sensor for detecting clenbuterol (CLB) based on MoS2-au-PEI-hemin layered nanocomposites. Biosens Bioelectron 89:461–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.019
Yola ML, Atar N (2019) Simultaneous determination of β-agonists on hexagonal boron nitride nanosheets/multi-walled carbon nanotubes nanocomposite modified glassy carbon electrode. Mater Sci Eng C 96:669–676. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2016.04.019
Ge Y, Camarada MB, Xu L, Qu M, Liang H, Zhao E, Wen Y (2018) A highly stable black phosphorene nanocomposite for voltammetric detection of clenbuterol. Microchim Acta 185:566. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3084-z
Lu S, Wen Y, Bai L, Liu G, Chen Y, Du H, Wang X (2015) pH-controlled voltammetric behaviors and detection of phytohormone 6-benzylaminopurine using MWCNT/GCE. J Electroanal Chem 750:89–99. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2015.05.019
Lu S, Bai L, Wen Y, Li M, Yan D, Zhang R, Chen K (2015) Water-dispersed carboxymethyl cellulose-montmorillonite-single walled carbon nanotube composite with enhanced sensing performance for simultaneous voltammetric determination of two trace phytohormones. J Solid State Electrochem 19:2023–2037. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10008-014-2695-5
Xiang Y, Camarada MB, Wen Y, Wu H, Chen J, Li M, Liao X (2018) Simple voltammetric analyses of ochratoxin a in food samples using highly-stable and antifoulinging black phosphorene nanosensor. Electrochim Acta 282:490–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2018.06.055
Hanlon D, Backes C, Doherty E, Cucinotta CS, Berner NC, Boland C, Zhang S (2015) Liquid exfoliation of solvent-stabilized few-layer black phosphorus for applications beyond electronics. Nat Commun 6:8563. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms9563
Zhang J, Ding W, Zhang Z, Xu J, Wen Y (2016) Preparation of black phosphorus-PEDOT: PSS hybrid semiconductor composites with good film-forming properties and environmental stability in water containing oxygen. RSC Adv 6:76174–76182. https://doi.org/10.1039/C6RA14762C
Abate Y, Akinwande D, Gamage S, Wang H, Snure M, Poudel N, Cronin SB (2018) Recent progress on stability and passivation of black phosphorus. Adv Mater 30:1704749. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201704749
Li Q, Zhou Q, Shi L, Chen Q, Wang J (2019) Recent advances in oxidation and degradation mechanisms of ultrathin 2D materials under ambient conditions and their passivation strategies. J Mater Chem A 7:4291–4312. https://doi.org/10.1039/C8TA10306B
Ryder CR, Wood JD, Wells SA, Yang Y, Jariwala D, Marks TJ, Hersam MC (2016) Covalent functionalization and passivation of exfoliated black phosphorus via aryl diazonium chemistry. Nat Chem 8:597. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.2505
Guo Z, Chen S, Wang Z, Yang Z, Liu F, Xu Y, Chu PK (2017) Metal-ion-modified black phosphorus with enhanced stability and transistor performance. Adv Mater 29:1703811. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201703811
Lei W, Liu G, Zhang J, Liu M (2017) Black phosphorus nanostructures: recent advances in hybridization, doping and functionalization. Chem Soc Rev 46:3492–3509. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7CS00021A
Abellán G, Lloret V, Mundloch U, Marcia M, Neiss C, Görling A, Hirsch A (2016) Noncovalent functionalization of black phosphorus. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:14557–14562. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201604784
Zhao Y, Wang H, Huang H, Xiao Q, Xu Y, Guo Z, Yu XF (2016) Surface coordination of black phosphorus for robust air and water stability. Angew Chem Int Ed 55:5003–5007. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201512038
Zhang Z, Li Y, Xu J, Wen Y (2018) Electropolymerized molecularly imprinted polypyrrole decorated with black phosphorene quantum dots onto poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene) nanorods and its voltammetric sensing of vitamin C. J Electroanal Chem 814:153–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.02.059
Li X, Niu X, Zhao W, Chen W, Yin C, Men Y, Sun W (2018) Black phosphorene and PEDOT: PSS-modified electrode for electrochemistry of hemoglobin. Electrochem Commun 86:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.elecom.2017.11.017
Niu X, Weng W, Yin C, Niu Y, Li G, Dong R, Sun W (2018) Black phosphorene modified glassy carbon electrode for the sensitive voltammetric detection of rutin. J Electroanal Chem 811:78–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2018.01.038
Wen Y, Xu J (2017) Scientific importance of water-Processable PEDOT–PSS and preparation, challenge and new application in sensors of its film electrode: a review. J Polym Sci A Polym Chem 55:1121–1150. https://doi.org/10.1002/pola.28482
Yao Y, Zhang L, Xu J, Wang X, Duan X, Wen Y (2014) Rapid and sensitive stripping voltammetric analysis of methyl parathion in vegetable samples at carboxylic acid-functionalized SWCNTs–β-cyclodextrin modified electrode. J Electroanal Chem 713:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2013.11.024
Wen Y, Xu J, Li D, Liu M, Kong F, He H (2012) A novel electrochemical biosensing platform based on poly (3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene): poly (styrenesulfonate) composites. Synth Met 162:1308–1314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.synthmet.2012.03.004
Wen Y, Xu J, He H, Lu B, Li Y, Dong B (2009) Electrochemical polymerization of 3, 4-ethylenedioxythiophene in aqueous micellar solution containing biocompatible amino acid-based surfactant. J Electroanal Chem 634:49–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2009.07.012
Kayser LV, Lipomi DJ (2019) Stretchable conductive polymers and composites based on PEDOT and PEDOT: PSS. Adv Mater 31:1806133. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201806133
Colleran JJ, Breslin CB (2012) Simultaneous electrochemical detection of the catecholamines and ascorbic acid at PEDOT/S-β-CD modified gold electrodes. J Electroanal Chem 667:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2011.12.020
Wu C, Sun D, Li Q, Wu K (2012) Electrochemical sensor for toxic ractopamine and clenbuterol based on the enhancement effect of graphene oxide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 168:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.03.084
Zhang L, Wang Q, Qi Y, Li L, Wang S, Wang X (2019) An ultrasensitive sensor based on polyoxometalate and zirconium dioxide nanocomposites hybrids material for simultaneous detection of toxic clenbuterol and ractopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 288:347–355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2019.03.033
Bai W, Huang H, Li Y, Zhang H, Liang B, Guo R, Zhang Z (2014) Direct preparation of well-dispersed graphene/gold nanorod composites and their application in electrochemical sensors for determination of ractopamine. Electrochim Acta 117:322–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2013.11.175
Xie L, Ya Y, Wei L (2017) Mesopores cellular foam-based electrochemical sensor for sensitive determination of ractopamine. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:9714–9724. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.10.34
Liu Z, Zhou Y, Wang Y, Cheng Q, Wu K (2012) Enhanced oxidation and detection of toxic ractopamine using carbon nanotube film-modified electrode. Electrochim Acta 74:139–144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2012.04.041
Deng Y, Wu J, Tu K, Xu H, Ma L, Chen J, Qian S (2017) Fabrication of an electrochemical sensor based on a graphene/au composite for the determination of clenbuterol in beef samples. Int J Electrochem Sci 12:6108–6117. https://doi.org/10.20964/2017.07.19
Lv CZ, Xun Y, Cao Z, Xie JL, Li D, Liu G, Tan SZ (2017) Sensitive determination of toxic Clenbuterol in pig meat and pig liver based on a carbon nanopolymer composite. Food Anal Methods 10:2252–2261. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12161-017-0796-3
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by National Beef Cattle Industry Technology & System (CARS-37), National Natural Science Foundation of China (51662014, 51962007, 31660492), Outstanding Young Talent Program of Jiangxi Province (20171BCB23042), Youth project of Natural Science Foundation of JiangxiProvince (20192ACBL21015, 20192BAB204020), Development and Nutrition of Feed for Beef Cattle in Guangchang County (09005392), Jiangxi Provincial Department of Education (GJJ170260).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declarethat they have no competing interests .
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Highlights
1) An electrochemically assisted anti-foul strategy was designed.
2) High-stable and anti-foul BP nanohybrid was prepared.
3) BP nanohybrid co-decorated with PEDOTNPs and S-β-CD was prepared.
4) BP nanohybrid platform for simultaneous voltammetric sensing of CLB and RAC in edible cattle product samples was fabricated.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.76 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ge, Y., Qu, M., Xu, L. et al. Phosphorene nanocomposite with high environmental stability and antifouling capability for simultaneous sensing of clenbuterol and ractopamine. Microchim Acta 186, 836 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3908-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3908-5