Abstract
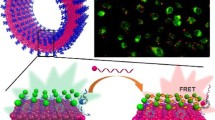
A luminescent microRNA nanoprobe based on the target-triggered Ir(III)-solvent complex release has been fabricated. The complex is initially embedded into mesoporous silica nanoparticles (MSNs), and then is capped by single-stranded (ss) DNA. In the presence of the target microRNA, the ssDNA hybridize with the microRNA forming a rigid DNA/RNA heteroduplexes and leaving the surface of MSN. Thus, the capped Ir(III) solvent complex is released and re-coordinated with histidine (His) to form a new luminescent complex. The luminescence intensity of the nascent complex (with excitation/emission maxima at 340/570 nm) is positively correlated with the concentrations of the target microRNA in the range from 0.05 to 2 nM, and the detection limit of microRNA is estimated as 0.2 pM (S/N = 3). The ability of this nanoprobe to detect microRNA in cell extract further demonstrates its potential in practical application.

Schematic of a luminescent microRNA nanoprobe based on the target-triggered release of an Ir(III)-solvent complex from mesoporous silica nanoparticles.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dong H, Lei J, Ding L, Wen Y, Ju H, Zhang X (2013) MicroRNA: function, detection, and bioanalysis. Chem Rev 113(8):6207–6233
Hao N, Li XL, Zhang HR, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2014) A highly sensitive ratiometric electrochemiluminescent biosensor for microRNA detection based on cyclic enzyme amplification and resonance energy transfer. Chem Commun 50(94):14828–14830
Yuan Z, Zhou Y, Gao S, Cheng Y, Li Z (2014) Homogeneous and sensitive detection of microRNA with ligase chain reaction and lambda exonuclease-assisted cationic conjugated polymer biosensing. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 6(9):6181–6185
Gurman SP, Carles CS, Jane B, Leigh R, Andrew H (2007) Carbodiimide-mediated cross-linking of RNA to nylon membranes improves the detection of siRNA, miRNA and piRNA by northern blot. Nucleic Acids Res 35(8):e60
Fang SP, Lee HJ, Wark AW, Corn RM (2006) Attomole microarray detection of microRNAs by nanoparticle-amplified SPR imaging measurements of surface polyadenylation reactions. J Am Chem Soc 128(43):14044–14046
Li J, Yao B, Huang H, Wang Z, Sun C, Fan Y, Chang Q, Li S, Wang X, Xi J (2009) Real-time polymerase chain reaction microRNA detection based on enzymatic stem-loop probes ligation. Anal Chem 81(13):5446–5451
Duan D, Zheng KX, Ye S, Rong C, Li J, Lu Z, Yan X, Li J (2011) Label-free high-throughput microRNA expression profiling from total RNA. Nucleic Acids Res 39(22):e154–e154
Lee JM, Jung Y (2015) Two-temperature hybridization for microarray detection of label-free microRNAs with attomole detection and superior specificity. Angew Chem 123(52):12695–12698
Xie Y, Lin X, Huang Y, Pan R, Zhu Z, Zhou L, Yang CJ (2014) Highly sensitive and selective detection of miRNA: DNase I-assisted target recycling using DNA probes protected by polydopamine nanospheres. Chem Commun 51(11):2156–2158
Rong L, He K, Chen C, Chen X, Cai C (2016) Double-Strand displacement biosensor and quencher-free fluorescence strategy for rapid detection of MicroRNA. Anal Chem 88(8):4254–4258
Hao N, Dai PP, Yu T, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2015) A dual target-recycling amplification strategy for sensitive detection of microRNAs based on duplex-specific nuclease and catalytic hairpin assembly. Chem Commun 51(70):13504–13507
Miao X, Cheng Z, Ma H, Li Z, Xue N, Wang P (2017) Label-free platform for MicroRNA detection based on the fluorescence quenching of positively charged gold nanoparticles to silver Nanoclusters. Anal Chem 90(2):1098–1103
Chen YX, Zhang WJ, Huang KJ, Zheng M, Mao YC (2017) An electrochemical microRNA sensing platform based on tungsten diselenide nanosheets and competitive RNA-RNA hybridization. Analyst 142(24):4843–4851
Cheng FF, He TT, Miao HT, Shi JJ, Jiang LP, Zhu JJ (2015) Electron transfer mediated electrochemical biosensor for MicroRNAs detection based on metal ion functionalized titanium phosphate Nanospheres at Attomole level. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(4):2979–2985
Yang D, Cheng W, Chen X, Tang Y, Miao P (2018) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of miRNA based on DNA strand displacement polymerization and Ca2+-dependent DNAzyme cleavage. Analyst 143(22):5352–5357
Zhang P, Li Z, Wang H, Zhuo Y, Yuan R, Chai Y (2017) DNA nanomachine-based regenerated sensing platform: a novel electrochemiluminescence resonance energy transfer strategy for ultra-high sensitive detection of microRNA from cancer cells. Nanoscale 9(6):2310–2316
Yue Z, Xue L, Xu Z, Chai Y, Wang H, Yuan R (2018) An ultrasensitive electrochemiluminescence biosensor for multiple detection of microRNAs based on a novel dual circuit catalyzed hairpin assembly. Chem Commun 54:10148–10151
Pu Z, Yuan R, Chai Y, Wu X (2015) An "off-on" electrochemiluminescent biosensor based on DNAzyme-assisted target recycling and rolling circle amplifications for ultrasensitive detection of microRNA. Anal Chem 87(6):3202–3207
Tu W, Cao H, Zhang L, Bao J, Liu X, Dai Z (2016) Dual signal amplification using gold nanoparticles-enhanced zinc Selenide Nanoflakes and P19 protein for ultrasensitive Photoelectrochemical biosensing of MicroRNA in cell. Anal Chem 88(21):10459–10465
Cha W, Fan R, Miao Y, Yong Z, Qin C, Shan X, Wan X, Cui T (2017) microRNAs as novel endogenous targets for regulation and therapeutic treatments. Medchemcomm 9(3):396–408
Zhou S, Sha H, Ke X, Liu B, Wang X, Du X (2015) Combination drug release of smart cyclodextrin-gated mesoporous silica nanovehicles. Chem Commun 51(33):7203–7206
Tu J, Boyle AL, Friedrich H, Bomans PH, Bussmann J, Sommerdijk NA, Jiskoot W, Kros A (2016) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles with large pores for the encapsulation and release of proteins. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(47):32211–32219
Adegoke O, Seo MW, Kato T, Kawahito S, Park EY (2016) An ultrasensitive SiO 2 -encapsulated alloyed CdZnSeS quantum dot-molecular beacon nanobiosensor for norovirus. Biosens Bioelectron 86(86):135–142
Climent E, Bernardos A, Martínezmáñez R, Maquieira A, Marcos MD, Pastornavarro N, Puchades R, Sancenón F, Soto J, Amorós P (2009) Controlled delivery systems using antibody-capped mesoporous nanocontainers. J Am Chem Soc 131(39):14075–14080
Chung PW, Kumar R, Pruski M, Lin SY (2010) Temperature responsive solution partition of organic–inorganic hybrid poly( N -isopropylacrylamide)-coated Mesoporous silica Nanospheres †. Adv Funct Mater 18(9):1390–1398
Yan H, Teh C, Sreejith S, Zhu L, Kwok A, Fang W, Ma X, Nguyen KT, Korzh V, Y Z (2012) Functional Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for Photothermal-controlled drug delivery in vivo. Angew Chem 51 (33):8373–8377
Climent E, Martínezmáñez R, Sancenón F, Marcos MD, Soto J, Maquieira A, Amorós P (2010) Controlled delivery using oligonucleotide-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Angew Chem 49(40):7281–7283
Li C, Lu W, Zhu M, Tang B (2017) Development of visible-light induced Photoelectrochemical platform based on Cyclometalated iridium(III) complex for bioanalysis. Anal Chem 89(20):11098–11106
Miao X, Wang W, Kang T, Liu J, Shiu KK, Leung CH, Ma DL (2016) Ultrasensitive electrochemical detection of miRNA-21 by using an iridium(III) complex as catalyst. Biosens Bioelectron 86:454–458
Li C, Yu M, Sun Y, Wu Y, Huang C, Li F (2011) A nonemissive iridium(III) complex that specifically lights-up the nuclei of living cells. J Am Chem Soc 133(29):11231–11239
Zhong HJ, Lu L, Leung KH, CW, Peng C, Yan SC, Ma DL, Cai Z, David Wang HM, Leung CH (2015) An iridium(iii)-based irreversible protein-protein interaction inhibitor of BRD4 as a potent anticancer agent. Chem Sci, 6 (10):5400–5408
Ma DL, Wong WL, Chung WH, Chan FY, So PK, Lai TS, Zhou ZY, Leung YC, KY W (2008) A highly selective luminescent switch-on probe for histidine/histidine-rich proteins and its application in protein staining. Angew Chem Int Ed Eng 47 (20):3735–3739
Vivero-Escoto JL, Slowing II, Trewyn BG, Victor SYL (2010) Mesoporous silica nanoparticles for intracellular controlled drug delivery. Small 6(18):1952–1967
Wang B, Wang H, Yang Z (2012) MiR-122 inhibits cell proliferation and tumorigenesis of breast cancer by targeting IGF1R. PLoS One 7(10):e47053
Zhou H, Yang C, Chen H, Li X, Li Y, Fan X (2017) A simple G-quadruplex molecular beacon-based biosensor for highly selective detection of microRNA. Biosens Bioelectron 87:552–557
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province (No. ZR2017MB064), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 21705089 and 21705087), the Project of Shandong Province Higher Educational Science and Technology Program (J17KA109), Science and Technology Program of Qingdao (No.18-6-1-83-nsh), and the Research Foundation for Distinguished Scholars of Qingdao Agricultural University (No. 663-1116010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Declaration on conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 322 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tang, X., Fan, K., Qu, B. et al. A luminescent microRNA nanoprobe based on the target-triggered release of an iridium(III)-solvent complex from mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 841 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3895-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3895-6