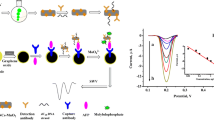
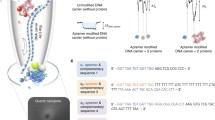
Abstract
The autosomal recessive-hyper immunoglobulin E syndromes (AR-HIES) are inherited inborn primary immunodeficiency disorders caused mainly by mutations in the dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) gene. A method is described for the selection of DNA aptamers against DOCK8 protein. The selection was performed by using a gold electrode as the solid matrix for immobilization of DOCK8. This enables voltammetric monitoring of the bound DNA after each selection cycle. After eight rounds of selection, high affinity DNA aptamers for DOCK8 were identified with dissociation constants (Kds) ranging from 3.3 to 66 nM. The aptamer which a Kd of 8.8 nM was used in an aptasensor. A gold electrode was modified by self-assembly of the thiolated aptamer, and the response to the DOCK8 protein was detected by monitoring the change in the electron transfer resistance using the ferro/ferricyanide system as a redox probe. The aptasensor works in the 100 pg.mL−1 to 100 ng.mL−1 DOCK8 concentration range, has a detection limit of 81 pg.mL−1 and good selectivity over other proteins in the serum.

Schematic representation of an electrochemical screening protocol for the selection of DNA aptamer against dedicator of cytokinesis 8 protein using electrode as solid support for target immobilization.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Freeman AF, Holland SM (2008) The hyper-IgE syndromes. Immunol Allergy Clin N Am 28(2):277–291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.iac.2008.01.005
Hashemi H, Mohebbi M, Mehravaran S, Mazloumi M, Jahanbani-Ardakani H, Abtahi S-H (2017) Hyperimmunoglobulin E syndrome: genetics, immunopathogenesis, clinical findings, and treatment modalities. J Res Med Sci: 22:53–53. https://doi.org/10.4103/jrms.JRMS_1050_16
Ozcan E, Notarangelo LD, Geha RS (2008) Primary immune deficiencies with aberrant IgE production. J Allergy Clin Immunol 122(6):1054–1062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2008.10.023
Yong PFK, Freeman AF, Engelhardt KR, Holland S, Puck JM, Grimbacher B (2012) An update on the hyper-IgE syndromes. Arthritis Res Ther 14(6):228–228. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar4069
Aydin S, Kilic S, Aytekin C, Kumar A, Porras O, Kainulainen L, Kostyuchenko L, Genel F, Kutukculer N, Karaca N, Gonzalez-Granado L, Abbott J, Al-Zahrani D, Rezaei N, Baz Z, Thiel J, Ehl S, Marodi L, S Orange J, H Albert M (2015) DOCK8 deficiency: clinical and immunological phenotype and treatment options - a review of 136 patients. J Clin Immunol 35(2):189–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10875-014-0126-0
Biggs CM, Keles S, Chatila TA (2017) DOCK8 deficiency: insights into pathophysiology, clinical features and management. Clin Immunol 181:75–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clim.2017.06.003
Engelhardt KR, McGhee S, Winkler S, Sassi A, Woellner C, Lopez-Herrera G, Chen A, Kim HS, Lloret MG, Schulze I, Ehl S, Thiel J, Pfeifer D, Veelken H, Niehues T, Siepermann K, Weinspach S, Reisli I, Keles S, Genel F, Kutuculer N, Camcıoğlu Y, Somer A, Karakoc-Aydiner E, Barlan I, Gennery A, Metin A, Degerliyurt A, Pietrogrande MC, Yeganeh M, Baz Z, Al-Tamemi S, Klein C, Puck JM, Holland SM, McCabe ERB, Grimbacher B, Chatila TA (2009) Large deletions and point mutations involving the dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) in the autosomal-recessive form of hyper-IgE syndrome. J Allergy Clin Immunol 124(6):1289–1302.e1284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2009.10.038
Jabara HH, McDonald DR, Janssen E, Massaad MJ, Ramesh N, Borzutzky A, Rauter I, Benson H, Schneider L, Baxi S, Recher M, Notarangelo LD, Wakim R, Dbaibo G, Dasouki M, Al-Herz W, Barlan I, Baris S, Kutukculer N, Ochs HD, Plebani A, Kanariou M, Lefranc G, Reisli I, Fitzgerald KA, Golenbock D, Manis J, Keles S, Ceja R, Chatila TA, Geha RS (2012) DOCK8 functions as an adaptor that links TLR-MyD88 signaling to B cell activation. Nat Immunol 13(6):612–620. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni.2305
Freeman AF, Olivier KN (2016) Hyper-IgE syndromes and the lung. Clin Chest Med 37(3):557–567. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccm.2016.04.016
Schimke LF, Sawalle-Belohradsky J, Roesler J, Wollenberg A, Rack A, Borte M, Rieber N, Cremer R, Maaß E, Dopfer R, Reichenbach J, Wahn V, Hoenig M, Jansson AF, Roesen-Wolff A, Schaub B, Seger R, Hill HR, Ochs HD, Torgerson TR, Belohradsky BH, Renner ED (2010) Diagnostic approach to the hyper-IgE syndromes: immunologic and clinical key findings to differentiate hyper-IgE syndromes from atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol 126(3):611–617.e611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.029
Zhang Q, Davis JC, Lamborn IT, Freeman AF, Jing H, Favreau AJ, Matthews HF, Davis J, Turner ML, Uzel G, Holland SM, Su HC (2009) Combined immunodeficiency associated with DOCK8 mutations. N Engl J Med 361(21):2046–2055. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa0905506
Mahdieh N, Rabbani B (2013) An overview of mutation detection methods in genetic disorders. Iran J Pediatr 23(4):375–388
Bejjani BA, Shaffer LG (2006) Application of array-based comparative genomic hybridization to clinical diagnostics. J Mol Diagn: JMD 8(5):528–533. https://doi.org/10.2353/jmoldx.2006.060029
Pai S-Y, de Boer H, Massaad MJ, Chatila TA, Keles S, Jabara HH, Janssen E, Lehmann LE, Hanna-Wakim R, Dbaibo G, McDonald DR (2014) Al-Herz W, Geha RS flow cytometry diagnosis of dedicator of cytokinesis 8 (DOCK8) deficiency. J Allergy Clin Immunol 134(1):221–223.e227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaci.2014.02.023
Eissa S, Abdulkarim H, Hawalta I, Jacob M, Dasouki M, Rahman AA, Zourob M (2018) Development of Impedimetric Immunosensors for the diagnosis of DOCK8 and STAT3 related hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome. Electroanalysis 30(9):2021–2027. https://doi.org/10.1002/elan.201800228
Eissa S, Abdulkarim H, Dasouki M, Al Mousa H, Arnout R, Al Saud B, Rahman AA, Zourob M (2018) Multiplexed detection of DOCK8, PGM3 and STAT3 proteins for the diagnosis of hyper-immunoglobulin E syndrome using gold nanoparticles-based immunosensor array platform. Biosens Bioelectron 117:613–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2018.06.058
Dunn MR, Jimenez RM, Chaput JC (2017) Analysis of aptamer discovery and technology. Nat Rev Chem 1:0076
Ilgu M, Nilsen-Hamilton M (2016) Aptamers in analytics. Analyst 141(5):1551–1568. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5an01824b
Song S, Wang L, Li J, Fan C, Zhao J (2008) Aptamer-based biosensors. TrAC Trends in Anal Chem 27(2):108–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2007.12.004
Mendonsa SD, Bowser MT (2004) In vitro evolution of functional DNA using capillary electrophoresis. J Am Chem Soc 126(1):20–21. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja037832s
Berezovski M, Drabovich A, Krylova SM, Musheev M, Okhonin V, Petrov A, Krylov SN (2005) Nonequilibrium capillary electrophoresis of equilibrium mixtures: a universal tool for development of aptamers. J Amer Chem Soc 127(9):3165–3171. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja042394q
Jing M, Bowser MT (2013) Tracking the emergence of high affinity aptamers for rhVEGF(165) during CE-SELEX using high throughput sequencing. Anal Chem 85(22):10761–10770. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac401875h
Gopinath SCB (2007) Methods developed for SELEX. Anal Bioanal Chem 387(1):171–182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-006-0826-2
Nabavinia MS, Charbgoo F, Alibolandi M, Mosaffa F, Gholoobi A, Ramezani M, Abnous K (2018) Comparison of flow cytometry and ELASA for screening of proper candidate aptamer in cell-SELEX Pool. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 184(2):444–452. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2548-7
Wang J, Gong Q, Maheshwari N, Eisenstein M, Arcila ML, Kosik KS, Soh HT (2014) Particle display: a quantitative screening method for generating high-affinity aptamers. Angew Chem Int Ed 53(19):4796–4801. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201309334
Raddatz M-SL, Dolf A, Endl E, Knolle P, Famulok M, Mayer G (2008) Enrichment of cell-targeting and population-specific aptamers by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(28):5190–5193. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200800216
Wang Q, Liu W, Xing Y, Yang X, Wang K, Jiang R, Wang P, Zhao Q (2014) Screening of DNA aptamers against myoglobin using a positive and negative selection units integrated microfluidic Chip and its biosensing application. Anal Chem 86(13):6572–6579. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac501088q
Jing M, Bowser MT (2011) Isolation of DNA aptamers using micro free flow electrophoresis. Lab Chip 11(21):3703–3709. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1lc20461k
Hybarger G, Bynum J, Williams RF, Valdes JJ, Chambers JP (2006) A microfluidic SELEX prototype. Anal Bioanal Chem 384(1):191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00216-005-0089-3
Hung L-Y, Wang C-H, Fu C-Y, Gopinathan P, Lee G-B (2016) Microfluidics in the selection of affinity reagents for the detection of cancer: paving a way towards future diagnostics. Lab Chip 16(15):2759–2774. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6lc00662k
Weng C-H, Huang C-J, Lee G-B (2012) Screening of aptamers on microfluidic Systems for Clinical Applications. Sensors (Basel, Switzerland) 12(7):9514–9529. https://doi.org/10.3390/s120709514
Eissa S, Ng A, Siaj M, Tavares AC, Zourob M (2013) Selection and identification of DNA aptamers against Okadaic acid for biosensing application. Anal Chem 85(24):11794–11801. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac402220k
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 570 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Eissa, S., Siddiqua, A., Chinnappan, R. et al. Electrochemical selection of a DNA aptamer, and an impedimetric method for determination of the dedicator of cytokinesis 8 by self-assembly of a thiolated aptamer on a gold electrode. Microchim Acta 186, 828 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3817-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3817-7