Abstract
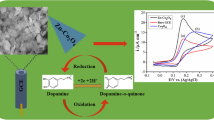
An electrochemical dopamine (DA) sensor has been fabricated by modifying a glassy carbon electrode (GCE) with ruthenium disulfide (RuS2) nanoparticles (NPs). FESEM and TEM micrographs show the NPs to have an average size of ~45 nm. XRD, Raman and EDS, in turn, confirm the successful formation of cubic phased RuS2 NPs. The modified GCE displays has attractive features of merit that include (a) an ultra-low detection limit (73.8 nM), (b) fast response time (< 4 s), (c) a low oxidation potential (0.25 V vs. Ag|AgCl), (d) excellent reproducibility and stability, (e) an electrochemical sensitivity of 18.4 μA μM−1 cm−2 and 1.8 μA.μM−1.cm−2 in the linear ranges from 0.1–10 μM of DA (R2 = 0.97) and 10–80 μM of DA (R2 = 0.99), respectively. The sensor exhibits excellent specificity over potential interferents like ascorbic acid, glucose and uric acid. The superior performance of the sensor is attributed to its high electrical conductivity, large electro-active surface, and large numbers of exposed catalytically active sites resulting from the presence of unreacted sulfur atoms.

A ruthenium disulfide modified electrochemical sensor material was obtained by single-step hydrothermal synthesis. Sensitive and highly selective detection of dopamine is demonstrated.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oh J, Lee JS, Jun J, Kim SG, Jang J (2017) Ultrasensitive and selective organic FET-type nonenzymatic dopamine sensor based on platinum nanoparticles-decorated reduced graphene oxide. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(45):39526–39533
Xu G, Jarjes ZA, Desprez V, Kilmartin PA, Travas-Sejdic J (2018) Sensitive, selective, disposable electrochemical dopamine sensor based on PEDOT-modified laser scribed graphene. Biosens Bioelectron 107:184–191
Hou Y, Sheng K, Lu Y, Ma C, Liu W, Men X et al (2018) Three-dimensional graphene oxide foams loaded with AuPd alloy: a sensitive electrochemical sensor for dopamine. Microchim Acta 185(8):397
Hsieh YS, Hong BD, Lee CL (2016) Non-enzymatic sensing of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of palladium nanocubes supported on reduced graphene oxide in a nafion matrix. Microchim Acta 183(2):905–910
Zhao P, Chen C, Ni M, Peng L, Li C, Xie Y, Fei J (2019) Electrochemical dopamine sensor based on the use of a thermosensitive polymer and an nanocomposite prepared from multiwalled carbon nanotubes and graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 186(3):134
Sáenz HSC, Hernández-Saravia LP, Selva JS, Sukeri A, Espinoza-Montero PJ, Bertotti M (2018) Electrochemical dopamine sensor using a nanoporous gold microelectrode: a proof-of-concept study for the detection of dopamine release by scanning electrochemical microscopy. Microchim Acta 185(8):367
Josephine DSR, Babu KJ, Sethuraman K (2017) Titanium dioxide anchored graphene oxide nanosheets for highly selective voltammetric sensing of dopamine. Microchim Acta 184(3):781–790
Chen D, Tian C, Li X, Li Z, Han Z, Zhai C et al (2018) Electrochemical determination of dopamine using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of nanoporous platinum-yttrium and graphene. Microchim Acta 185(2):98
Mahesh KPO, Shown I, Chen LC, Chen KH, Tai Y (2018) Flexible sensor for dopamine detection fabricated by the direct growth of α-Fe2O3 nanoparticles on carbon cloth. Appl Surf Sci 427:387–395
Sha R, Jones SS, Vishnu N, Soundiraraju B, Badhulika S (2018) A novel biomass derived carbon quantum dots for highly sensitive and selective detection of hydrazine. Electroanalysis 30(10):2228–2232
Florescu M, David M (2017) Tyrosinase-based biosensors for selective dopamine detection. Sensors 17(6):1314
Yue HY, Zhang HJ, Huang S, Gao X, Song SS, Wang Z et al (2019) A novel non-enzymatic dopamine sensors based on NiO-reduced graphene oxide hybrid nanosheets. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30(5):5000–5007
Sha R, Puttapati SK, Srikanth VV, Badhulika S (2018) Ultra-sensitive non-enzymatic ethanol sensor based on reduced graphene oxide-zinc oxide composite modified electrode. IEEE Sensors J 18(5):1844–1848
Xue H, Wang Y, Dai Y, Kim W, Jussila H, Qi M et al (2018) A MoSe2/WSe2 heterojunction-based photodetector at telecommunication wavelengths. Adv Funct Mater 28(47):1804388
Sha R, Vishnu N, Badhulika S (2019) MoS2 based ultra-low-cost, flexible, non-enzymatic and non-invasive electrochemical sensor for highly selective detection of uric acid in human urine samples. Sensors Actuators B Chem 279:53–60
Han X, Wu X, Deng Y, Liu J, Lu J, Zhong C, Hu W (2018) Ultrafine Pt nanoparticle-decorated pyrite-type CoS2 Nanosheet arrays coated on carbon cloth as a bifunctional electrode for overall water splitting. Adv Energy Mater 8(24):1800935
Sha R, Gopalakrishnan A, Sreenivasulu KV, Srikanth VV, Badhulika S (2019) Template-cum-catalysis free synthesis of α-MnO2 nanorods-hierarchical MoS2 microspheres composite for ultra-sensitive and selective determination of nitrite. J Alloys Compd 794:26–34
Krishnamoorthy K, Pazhamalai P, Kim SJ (2017) Ruthenium sulfide nanoparticles as a new pseudocapacitive material for supercapacitor. Electrochim Acta 227:85–94
Sarno M, Ponticorvo E (2019) High hydrogen production rate on RuS2@ MoS2 hybrid nanocatalyst by PEM electrolysis. Int J Hydrog Energy 44(9):4398–4405
Kubendhiran S, Sakthivel R, Chen SM, Anbazhagan R, Tsai HC (2019) A novel design and synthesis of ruthenium sulfide decorated activated graphite nanocomposite for the electrochemical determination of antipsychotic drug chlorpromazine. Compos Part B 168:282–290
Catherin N, Blanco E, Piccolo L, Laurenti D, Simonet F, Lorentz C et al (2019) Selective ring opening of decalin over bifunctional RuS2/zeolite catalysts. Catal Today 323:105–111
Park IS, Kim OH, Kim JW, Cho YH, Sung YE (2016) Carbon-supported Pt-RuS 2 nanocomposite as hydrogen oxidation reaction catalysts for fuel cells. J Appl Electrochem 46(1):77–83
Thakur N, Das Adhikary S, Kumar M, Mehta D, Padhan AK, Mandal D, Nagaiah TC (2018) Ultrasensitive and highly selective electrochemical detection of dopamine using poly (ionic liquids)–cobalt Polyoxometalate/CNT composite. ACS Omega 3(3):2966–2973
Sha R, Vishnu N, Badhulika S (2018) Bimetallic Pt-Pd nanostructures supported on MoS 2 as an ultra-high performance electrocatalyst for methanol oxidation and nonenzymatic determination of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 185(8):399
Yang T, Chen H, Jing C, Luo S, Li W, Jiao K (2017) Using poly (m-aminobenzenesulfonic acid)-reduced MoS2 nanocomposite synergistic electrocatalysis for determination of dopamine. Sensors Actuators B Chem 249:451–457
Ma L, Zhang Q, Wu C, Zhang Y, Zeng L (2019) PtNi bimetallic nanoparticles loaded MoS2 nanosheets: preparation and electrochemical sensing application for the detection of dopamine and uric acid. Anal Chim Acta 1055:17–25
Numan A, Shahid MM, Omar FS, Ramesh K, Ramesh S (2017) Facile fabrication of cobalt oxide nanograin-decorated reduced graphene oxide composite as ultrasensitive platform for dopamine detection. Sensors Actuators B Chem 238:1043–1051
Khan AF, Brownson DA, Randviir EP, Smith GC, Banks CE (2016) 2D hexagonal boron nitride (2D-hBN) explored for the electrochemical sensing of dopamine. Anal Chem 88(19):9729–9737
Mercante LA, Pavinatto A, Iwaki LE, Scagion VP, Zucolotto V, Oliveira ON Jr et al (2015) Electrospun polyamide 6/poly (allylamine hydrochloride) nanofibers functionalized with carbon nanotubes for electrochemical detection of dopamine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 7(8):4784–4790
Wang C, Du J, Wang H, Zou CE, Jiang F, Yang P, Du Y (2014) A facile electrochemical sensor based on reduced graphene oxide and Au nanoplates modified glassy carbon electrode for simultaneous detection of ascorbic acid, dopamine and uric acid. Sensors Actuators B Chem 204:302–309
Fan Y, Lu HT, Liu JH, Yang CP, Jing QS, Zhang YX et al (2011) Hydrothermal preparation and electrochemical sensing properties of TiO2–graphene nanocomposite. Colloids Surf B: Biointerfaces 83(1):78–82
Huang ZN, Zou J, Teng J, Liu Q, Yuan MM, Jiao FP et al (2019) A novel electrochemical sensor based on self-assembled platinum nanochains-multi-walled carbon nanotubes-graphene nanoparticles composite for simultaneous determination of dopamine and ascorbic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 172:167–175
Kannan PK, Moshkalev SA, Rout CS (2016) Highly sensitive and selective electrochemical dopamine sensing properties of multilayer graphene nanobelts. Nanotechnology 27(7):075504
Thanh TD, Balamurugan J, Lee SH, Kim NH, Lee JH (2016) Effective seed-assisted synthesis of gold nanoparticles anchored nitrogen-doped graphene for electrochemical detection of glucose and dopamine. Biosens Bioelectron 81:259–267
Daemi S, Ashkarran AA, Bahari A, Ghasemi S (2017) Gold nanocages decorated biocompatible amine functionalized graphene as an efficient dopamine sensor platform. J Colloid Interface Sci 494:290–299
Yuan Y, Xia J, Zhang F, Wang Z, Liu Q (2018) Nafion/polyaniline/Zeolitic Imidazolate Framework-8 nanocomposite sensor for the electrochemical determination of dopamine. J Electroanal Chem 824:147–152
Sha R, Badhulika S (2018) Few layered MoS2 grown on pencil graphite: a unique single-step approach to fabricate economical, binder-free electrode for supercapacitor applications. Nanotechnology 30(3):035402
Sha R, Badhulika S (2017) Binder free platinum nanoparticles decorated graphene-polyaniline composite film for high performance supercapacitor application. Electrochim Acta 251:505–512
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge financial assistance from Department of Science and Technology (DST), Government of India, under INSPIRE Faculty Fellowship Grant # DST/INSPIRE/04/2014/015132 and Scientific and Engineering Research Board Grant SB/WEA-03/2017.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
J. Deepika and Rinky Sha equally contributed to this work
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 105 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deepika, J., Sha, R. & Badhulika, S. A ruthenium(IV) disulfide based non-enzymatic sensor for selective and sensitive amperometric determination of dopamine. Microchim Acta 186, 480 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3622-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3622-3