Abstract
A metal organic framework (MOF) of type Fe(III)-BTC (where BTC is 1,3,5-benzenetricarboxylic acid) was utilized to construct an integrated system for cascade colorimetric determination of glucose. The MOF performs a dual function in acting (a) as a peroxidase (POx) mimic, and (b) as a solid support for immobilization of glucose oxidase (GOx). The MOF was prepared by a one-pot method. Glucose is consumed while H2O2 is produced during the enzymatic oxidation by GOx. In the presence of H2O2, the POx mimic catalytically oxidizes 3,3′,5,5′-tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) to form a blue-green product. The absorbance of oxidized TMB (measured at 652 nm) increases linearly in the 5.0–100 μM glucose concentration range, and the detection limit is 2.4 μM. The GOx@Fe-BTC MOF was successfully applied to the determination of glucose in serum.

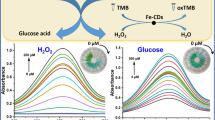
Schematic presentation of a bifunctional metal organic framework of type Fe-BTC for cascade (enzymatic and enzyme-mimicking) colorimetric determination of glucose. The Fe-BTC performs a dual function in acting as both a peroxidase mimic and support for immobilizing glucose oxidase. Using the integrated enzyme, a colorimetric method was successfully applied to one-step detection of glucose in human serum.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Navani NK, Li Y (2006) Nucleic acid aptamers and enzymes as sensors. Curr Opin Chem Biol 10:272–281
DiCosimo R, McAuliffe J, Poulose AJ, Bohlmann G (2013) Industrial use of immobilized enzymes. Chem Soc Rev 42:6437–6474
Wu J, Wang X, Wang Q, Lou Z, Li S, Zhu Y, Qin L, Wei H (2019) Nanomaterials with enzyme-like characteristics (nanozymes): next-generation artificial enzymes (II). Chem Soc Rev 48:1004–1076
Nasir M, Nawaz MH, Latif U, Yaqub M, Hayat A, Rahim A (2017) An overview on enzyme-mimicking nanomaterials for use in electrochemical and optical assays. Microchim Acta 184:323–342
Lian X, Fang Y, Joseph E, Wang Q, Li J, Banerjee S, Lollar C, Wang X, Zhou H-C (2017) Enzyme–MOF (metal–organic framework) composites. Chem Soc Rev 46:3386–3401
Mehta J, Bhardwaj N, Bhardwaj SK, Kim K-H, Deep A (2016) Recent advances in enzyme immobilization techniques: metal-organic frameworks as novel substrates. Coord Chem Rev 322:30–40
Liu X, Qi W, Wang Y, Su R, He Z (2017) A facile strategy for enzyme immobilization with highly stable hierarchically porous metal–organic frameworks. Nanoscale 9:17561–17570
Lian X, Chen Y-P, Liu T-F, Zhou H-C (2016) Coupling two enzymes into a tandem nanoreactor utilizing a hierarchically structured MOF. Chem Sci 7:6969–6973
Shieh F-K, Wang S-C, Yen C-I, Wu C-C, Dutta S, Chou L-Y, Morabito JV, Hu P, Hsu M-H, Wu KCW, Tsung C-K (2015) Imparting functionality to biocatalysts via embedding enzymes into nanoporous materials by a de novo approach: size-selective sheltering of catalase in metal–organic framework microcrystals. J Am Chem Soc 137:4276–4279
Gascón V, Castro-Miguel E, Díaz-García M, Blanco RM, Sanchez-Sanchez M (2017) In situ and post-synthesis immobilization of enzymes on nanocrystalline MOF platforms to yield active biocatalysts. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 92:2583–2593
Liang W, Ricco R, Maddigan NK, Dickinson RP, Xu H, Li Q, Sumby CJ, Bell SG, Falcaro P, Doonan CJ (2018) Control of structure topology and spatial distribution of biomacromolecules in protein@ZIF-8 biocomposites. Chem Mater 30:1069–1077
Liang K, Ricco R, Doherty CM, Styles MJ, Bell S, Kirby N, Mudie S, Haylock D, Hill AJ, Doonan CJ, Falcaro P (2015) Biomimetic mineralization of metal-organic frameworks as protective coatings for biomacromolecules. Nat Commun 6:7240
Liao F-S, Lo W-S, Hsu Y-S, Wu C-C, Wang S-C, Shieh F-K, Morabito JV, Chou L-Y, Wu KCW, Tsung C-K (2017) Shielding against unfolding by embedding enzymes in metal–organic frameworks via a de novo approach. J Am Chem Soc 139:6530–6533
Hu Y, Dai L, Liu D, Du W, Wang Y (2018) Progress & prospect of metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) for enzyme immobilization (enzyme/MOFs). Renew Sust Energ Rev 91:793–801
Wu X, Ge J, Yang C, Hou M, Liu Z (2015) Facile synthesis of multiple enzyme-containing metal–organic frameworks in a biomolecule-friendly environment. Chem Commun 51:13408–13411
Cheng H, Zhang L, He J, Guo W, Zhou Z, Zhang X, Nie S, Wei H (2016) Integrated nanozymes with nanoscale proximity for in vivo neurochemical monitoring in living brains. Anal Chem 88:5489–5497
Wang Q, Wei H, Zhang Z, Wang E, Dong S (2018) Nanozyme: an emerging alternative to natural enzyme for biosensing and immunoassay. Trends Anal Chem 105:218–224
Li S, Liu X, Chai H, Huang Y (2018) Recent advances in the construction and analytical applications of metal-organic frameworks-based nanozymes. Trends Anal Chem 105:391–403
Dong W, Liu X, Shi W, Huang Y (2016) Metal–organic framework MIL-53 (Fe): facile microwave-assisted synthesis and use as a highly active peroxidase mimetic for glucose biosensing. RSC Adv 5:17451–17457
Liu YL, Zhao XJ, Yang XX, Li YF (2013) A nanosized metal–organic framework of Fe-MIL-88NH2 as a novel peroxidase mimic used for colorimetric detection of glucose. Analyst 138:4526–4531
Ortiz-Gómez I, Salinas-Castillo A, García AG, Álvarez-Bermejo JA, de Orbe-Payá I, Rodríguez-Diéguez A, Capitán-Vallvey LF (2017) Microfluidic paper-based device for colorimetric determination of glucose based on a metal-organic framework acting as peroxidase mimetic. Microchim Acta 185:47
Yang H, Yang R, Zhang P, Qin Y, Chen T, Ye F (2017) A bimetallic (co/2Fe) metal-organic framework with oxidase and peroxidase mimicking activity for colorimetric detection of hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 184:4629–4635
Hou C, Wang Y, Ding Q, Jiang L, Li M, Zhu W, Pan D, Zhu H, Liu M (2015) Facile synthesis of enzyme-embedded magnetic metal–organic frameworks as a reusable mimic multi-enzyme system: mimetic peroxidase properties and colorimetric sensor. Nanoscale 7:18770–18779
Wang Q, Zhang X, Huang L, Zhang Z, Dong S (2017) GOx@ ZIF-8 (NiPd) nanoflower: an artificial enzyme system for tandem catalysis. Angew Chem Int Ed 56:16082–16085
Wu J, Li S, Wei H (2018) Integrated nanozymes: facile preparation and biomedical applications. Chem Commun 54:6520–6530
Zhang J-W, Zhang H-T, Du Z-Y, Wang X, Yu S-H, Jiang H-L (2014) Water-stable metal–organic frameworks with intrinsic peroxidase-like catalytic activity as a colorimetric biosensing platform. Chem Commun 50:1092–1094
Lin T, Zhong L, Guo L (2014) Seeing diabetes: visual detection of glucose based on the intrinsic peroxidase-like activity of MoS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale 6:11856–11862
Zhang F, Jin Y, Shi J, Zhong Y, Zhu W, El-Shall MS (2015) Polyoxometalates confined in the mesoporous cages of metal–organic framework MIL-100(Fe): efficient heterogeneous catalysts for esterification and acetalization reactions. Chem Eng J 269:236–244
Wu X, Yang C, Ge J, Liu Z (2015) Polydopamine tethered enzyme/metal–organic framework composites with high stability and reusability. Nanoscale 7:18883–18886
Yamashita T, Hayes P (2008) Analysis of XPS spectra of Fe2+ and Fe3+ ions in oxide materials. Appl Surf Sci 254:2441–2449
Liang W, Xu H, Carraro F, Maddigan NK, Li Q, Bell SG, Huang DM, Tarzia A, Solomon MB, Amenitsch H, Vaccari L, Sumby CJ, Falcaro P, Vaccari L (2019) Enhanced activity of enzymes encapsulated in hydrophilic metal–organic frameworks. J Am Chem Soc 141:2348–2355
Acknowledgements
The financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21765002), Guangxi Natural Science Foundation of China (2017GXNSFDA198044), State Key Laboratory for the Chemistry and Molecular Engineering of Medicinal Resources (Guangxi Normal University) (CMEMR2017-A10, CMEMR2018-C11), and the BAGUI Scholar Program is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 475 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhao, Z., Pang, J., Liu, W. et al. A bifunctional metal organic framework of type Fe(III)-BTC for cascade (enzymatic and enzyme-mimicking) colorimetric determination of glucose. Microchim Acta 186, 295 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3416-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3416-7