Abstract
An ultrasensitive and highly selective method is described for the determination of adenosine triphosphate (ATP) via surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS). Two split aptamers are used for specific recognition of ATP. They were attached to two SERS substrates. The first was placed on a nanolayer of gold nanoparticle-decorated graphene oxide (GO/Au3), and the other on gold nanoparticles (Au2). When ATP is introduced, it will interact with the split aptamers on the gold nanostructures to form a sandwich structure that brings the GO/Au3 nanolayer and the Au2 nanoparticle in close proximity. Consequently, the SERS signal, best measured at 1072 cm−1, is strongly enhanced. The sandwich structure also displays good water solubility and stability. Under optimized conditions, the SERS signal increases in the 10 pM - 10 nM ATP concentration range, and the limit of detection (LOD) is 0.85 pM. The method was applied to the determination of ATP in spiked human serum, and the LODs in serum and buffer are comparable. In our perception, the method has a wide scope in that numerous other aptamers may be used. This may result in a variety of other highly sensitive aptasensors for use in in-vitro diagnostics.

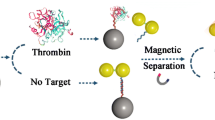
Schematic presentation of a self-assembly sandwich nanostructure as unique SERS assay platform for the sensitive detection of ATP.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ATP:
-
Adenosine Triphosphate
- PATP:
-
p-aminothiophenol
References
Palleros DR, Raid KL, Shi L, Welch WJ, Fink AL (2018) ATP-induced protein Hsp70 complex dissociation requires potassium but not ATP hydrolysis. Nature 365:664–666
Desai A, Verma S, Mitchison TJ, Walczak CE (1999) Kin I kinesins are microtubule-destabilizing enzymes. Cell 96:69–78
Gourine AV, Llaudet E, Dale N, Spyer KM (2005) ATP is a mediator of chemosensory transduction in the central nervous system. Nature 436:108–111
Jhaveri S, Rajendran M, Ellington AD (2000) In vitro selection of signaling aptamers. Nat Biotechnol 18:1293–1297
Kang Y, Hua Y, Ning D, Zhu GC, Zhua TF, Jiang NJ (2017) A novel SERS-based magnetic aptasensor for prostate specific antigen assay with high sensitivity. Biosens Bioelectron 94:286–291
Berkley S, Bertram K, Delfraissy JF, Draghia-Akli R, Fauci A, Hallenbeck C, Kagame MJ, Kim P, Mafubelu D, Makgoba MW (2010) The 2010 scientific strategic plan of the global HIV vaccine Enterprise. Nat Med 16:981–989
Wanunu M, Dadosh T, Ray V, Jin J, McReynolds L, Drndic M (2010) Rapid electronic detection of probe-specific microRNAs using thin nanopore sensors. Nat Nanotechnol 5:807–814
Qian X, Peng XH, Ansari DO, Yin GQ, Chen GZ, Shin DM, Yang L, Young AN, Wang MD, Nie S (2008) In vivo tumor targeting and spectroscopic detection with surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle tags. Nat Biotechnol 26:83–90
Zhang ZY, Chen NC, Li SH, Battig MR, Wang Y (2012) Programmable hydrogels for controlled cell catch and release using hybridized aptamers and complementary sequences. J Am Chem Soc 134:15716–15719
Zuo XL, Xiao Y, laxco KWP (2009) High specificity, high specificity, electrochemical sandwich assays based on single aptamer sequences and suitable for the direct detection of small-molecule target. J Am Chem Soc 131:6944–6945
Lim DK, Jeon KS, Hwang JH, Kim H, Kwon S, Suh YD, Nam JM (2011) Highly uniform and reproducible surface-enhanced Raman scattering from DNA-tailorable nanoparticles with 1-nm interior gap. Nat Nanotechnol 6:452–460
Joseph V, Engelbrekt C, Zhang JD, Gernert U, Ulstrup J, Kneipp J (2012) Characterizing the kinetics of nanoparticle-catalyzed reactions by surface-enhanced Raman scattering. Angew Chem Int Ed 51:7592–7596
Banholzer MJ, Millstone JE, Qin L, Mirkin C (2008) Rationally designed nanostructures for surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Chem Soc Rev 37:885–897
Xu W, Ling X, Xiao J, Dresselhaus MS, Kong J, Xu H, Liu Z (2012) Surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy on a flat graphene surface. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 109:9281–9286
Kleinman SL, Ringe E, Valley N, Wustholz KL, Phillips E, Scheidt KA, Schatz GC, Van DRP (2011) Single-molecule surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of crystal violet Isotopologues: theory and experiment. J Am Chem Soc 133:4115–4122
Brown LV, Zhao K, King N, Sobhani H, Nordlander P, Halas NJ (2013) Surface-enhanced infrared absorption using individual cross antennas tailored to chemical moieties. J Am Chem Soc 135:3688–3695
Fan Z, Kanchanapally R, Ray PC (2013) Hybrid graphene oxide based ultrasensitive SERS probe for label-free biosensing. J Phys Chem Lett 4:3813–3818
Barhoumi A, Zhang DM, Tam F, Halas NJ (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy of DNA. J Am Chem Soc 130:5523–5529
Braun G, Lee SJ, Dante M, Nguyen T, Moskovits M, Reich N (2007) A heterogeneous PNA-based SERS method for DNA detection. J Am Chem Soc 129:6378–6379
Lu G, Li H, Liusman C, Yin Z, Wu S, Zhang H (2011) Towards low-cost flexible substrates for nanoplasmonic sensing. Chem Sci 2:1817–1826
Huang J, Zhang L, Chen B, Ji N, Chen F, Zhang Y, Zhang Z (2010) Nanocomposites of size-controlled gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: formation and applications in SERS and catalysis. Nanoscale 2:2733–2738
Loh KP, Bao Q, Eda G, Chhowalla M (2010) Nanocomposites of size-controlled gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide: formation and applications in SERS and catalysis. Nat Chem 2:1015–1024
Anker JN, Hall WP, Lyandres O, Shah NC, Zhao J, Van DRP (2008) Biosensing with plasmonic nanosensors. Nat Mater 7:442–453
Fang N, Lee H, Sun C, Zhang X (2005) Sub-diffraction-limited optical imaging with a silver Superlens. Science 308:534–537
Qian XM, Zhou X, Nie SM (2008) Surface-enhanced Raman nanoparticle beacons based on bioconjugated gold nanocrystals and long range Plasmonic coupling. J Am Chem Soc 130:14934–14935
Hummers WS, Offeman RE (1958) Preparation of graphitic oxide. J Am Chem Soc 80:1339–1339
Qian XM, Li J, Nie SM (2009) Bimetallic nano-mushrooms with DNA-mediated interior nanogaps for high-efficiency SERS signal amplification. J Am Chem Soc 131:7540–7541
Qiu XJ, You XR, Chen X, Chen HL, Dhinakar A, Liu SG, Guo ZY, Wu J, Liu ZM (2017) A new interval-valued 2-tuple linguistic Bonferroni mean operator and its application to multiattribute group decision making. Int J Nanomedicine 12:4349–4360
Lal S, Grady NK, Goodrich GP, Halas NJ (2006) Profiling the near field of a Plasmonic nanoparticle with Raman-based molecular rulers. Nano Lett 6:2338–2343
Zhou CY, Wu CT, Liu YQ, Wang EK (2016) Effective construction of a AuNPs–DNA system for the implementation of various advanced logic gates. RSC Adv 6:106641–106647
Zhang X, Servos MR, Liu JW (2012) Instantaneous and quantitative functionalization of gold nanoparticles with thiolated DNA using a pH-assisted and surfactant-free route. J Am Chem Soc 134:7266–7269
Akki SU, Werth CJ (2018) Critical Review: DNA aptasensors, Are they ready for monitoring organic pollutants in natural and treated water sources? https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.8b00558
Su Y, Xu HG, Chen YH, Qi JX, Zhou X, Ge R, Lin ZK (2018) Real-time and label-free detection of bisphenol a by an ssDNA aptamer sensor combined with dual polarization interferometry. New J Chem 42:2850–2856
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFB1104700), The Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC, 21404015, 61774155, 61705227) and Jilin Science and Technology Department Project (20150204019GX).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1139 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, C., Yu, Z., Yu, W. et al. Split aptamer-based detection of adenosine triphosphate using surface enhanced Raman spectroscopy and two kinds of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 251 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3356-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3356-2