Abstract
Co3O4/carbon hybrid hollow nanospheres (hs-Co3O4/C) with an empty cavity and a thin shell, were synthesized starting from the pectin and cobalt acetate via cross-linking deposition at room temperature and post-calcination. The hierarchical structure is constructed from the interconnected nanoparticles in the residual carbon matrix, and the carbon content can be adjusted by changing the calcination temperature. The gas sensor based on hs-Co3O4/C calcined at 300 °C in air shows high response towards 50 ppm of H2S (S = 95.5) and good selectivity at a low working temperature (92 °C). The detection limit is as low as 0.1 ppm. The non-enzymatic glassy carbon electrode based sensor constructed from the same material exhibits excellent electrocatalytic activity for H2O2 with the sensitivity of 405.8 μA∙mM∙cm−2 at 0.3 V (vs. SCE) in alkaline solution. The chronoamperometric response time is < 3 s and the detection limit (at S/N = 3) is 0.30 μM. The good sensing performances are attributed to the synergetic effect of unique hollow nanostructure and appropriate amount of carbon in the hybrid material. The porous nanostructure can increase the mass transfer efficiency, and the cross-linked nanoparticles with good crystallinity also improve the conductivity of materials. The presence of carbon enhances the charge transfer ability and increases the specific surface, thereby improving the sensor performance.

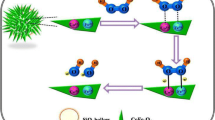
Schematic illustration of the formation of hollow Co3O4 nanospheres composited with pectin-derived carbon. The material displays excellent selectivity for H2S gas and in non-enzymatic detection of dissolved H2O2.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang X, Tian W, Zhai TY, Zhi CY, Bando Y, Golberg D (2012) Cobalt (II,III) oxide hollow structures: fabrication, properties and applications. J Mater Chem 22:23310–23326. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2jm33940d
Han L, Yang DP, Liu AH (2015) Leaf-templated synthesis of 3D hierarchical porous cobalt oxide nanostructure as direct electrochemical biosensing interface with enhanced electrocatalysis. Biosens Bioelectron 63:145–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2014.07.031
Peng L, Feng YY, Bai YJ, Qiu HJ, Wang Y (2015) Designed synthesis of hollow Co3O4 nanoparticles encapsulated in a thin carbon nanosheet array for high and reversible lithium storage. J Mater Chem A 3:8825–8831. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ta01187f
Quang PL, Nguyen DC, Hoa TT, Hoang TL, Chu MH, Dang TTL, Nguyen VH (2018) Simple post-synthesis of mesoporous p-type Co3O4 nanochains for enhanced H2S gas sensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 270:158–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.05.026
Ding LJ, Zhao MG, Fan SS, Ma Y, Liang JJ, Wang XT, Song YW, Chen SG (2016) Preparing Co3O4 urchin-like hollow microspheres self-supporting architecture for improved glucose biosensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 235:162–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.05.068
Li YY, Zhou F, Gao L, Duan GT (2018) Co3O4 nanosheet-built hollow spheres containing ultrafine neck-connected grains templated by PS@Co-LDH and their ppb-level gas-sensing performance. Sensors Actuators B Chem 261:553–565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.01.162
Jo YM, Kim TH, Lee CS, Lim K, Na CW, Faissal AH, Abdulaziz AW, Lee JH (2018) Metal-organic framework-derived hollow hierarchical Co3O4 nanocages with tunable size and morphology: ultrasensitive and highly selective detection of methylbenzenes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 10:8860–8868. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.8b00733
Wang XJ, Feng J, Bai YC, Zhang Q, Yin YD (2016) Synthesis, properties, and applications of hollow micro-/nanostructures. Chem Rev 116:10983–11060. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00731
Tan JF, Dun MH, Li L, Zhao JY, Tan WH, Lin ZD, Huang XT (2017) Synthesis of hollow and hollowed-out Co3O4 microspheres assembled by porous ultrathin nanosheets for ethanol gas sensors: responding and recovering in one second. Sensors Actuators B Chem 249:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.04.063
Zhang R, Zhang T, Zhou TT, Wang LL (2018) Rapid sensitive sensing platform based on yolk-shell hybrid hollow sphere for detection of ethanol. Sensors Actuators B Chem 256:479–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.10.064
Xiong C, Zhang TF, Kong WY, Zhang ZX, Qu H, Chen W, Wang YB, Luo LB, Zheng L (2018) ZIF-67 derived porous Co3O4 hollow nanopolyhedron functionalized solution-gated graphene transistors for simultaneous detection of glucose and uric acid in tears. Biosens Bioelectron 101:21–28. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bios.2017.10.004
Moon S, Vuong NM, Lee DS, Kim D, Lee HD, Kim DJ, Hong SK, Yoon SG (2016) Co3O4-SWCNT composites for H2S gas sensor application. Sensors Actuators B Chem 222:166–172. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2015.08.072
Zhang JJ, Liang YQ, Mao J, Yang XJ, Cui ZD, Zhu SL, Li ZY (2016) 3D microporous Co3O4-carbon hybrids biotemplated from butterfly wings as high performance VOCs gas sensor. Sensors Actuators B Chem 235:420–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2016.05.081
Ni Y, Liao Y, Zheng MB, Shao SJ (2017) In-situ growth of Co3O4 nanoparticles on mesoporous carbon nanofibers: a new nanocomposite for nonenzymatic amperometric sensing of H2O2. Microchim Acta 184:3689–3695. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2395-9
Wu MY, Hong Y, Zang XX, Dong XC (2016) ZIF-67 derived Co3O4/rGO electrodes for electrochemical detection of H2O2 with high sensitivity and selectivity. ChemistrySelect 1:5727–5732. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601259
Selvapathy P, Ramakrishna TV, Pitcha R (1989) Improved method of sampling and determination of traces of hydrogen sulphide. Microchim Acta II: 23–29
Lee DY, Huang WC, GuTJ CG (2018) Quantitative and comparative liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry analyses of hydrogen sulfide and thiolmetabolites derivaitized with 2-iodoacetanilide isotopologues. J Chromatogr A 1552:43–52
Wu ZL, Sun LP, Yang M, Huo LH, Zhao H, Grenier JC (2016) Facile synthesis and excellent electrochemical performance of reduced graphene oxide-Co3O4 yolk-shell nanocages as a catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. J Mater Chem A 4:13534–13542. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.201601259
Balouria V, Samanta S, Singh A, Debnath AK, Aman M, Bedi RK, Aswal DK, Gupta SK (2013) Chemiresistive gas sensing properties of nanocrystalline Co3O4 thin films. Sensors Actuators B Chem 176:38–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2012.08.064
Navale ST, Liu C, Gaikar PS, Patil VB, Sagar RUR, Du B, Mane RS, Stadler SFJ (2017) Solution-processed rapid synthesis strategy of Co3O4 for the sensitive and selective detection of H2S. Sensors Actuators B Chem 245:524–532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.01.195
Cui GL, Zhang PH, Chen L, Wang XL, Li JF, Shi CM, Wang DC (2017) Highly sensitive H2S sensors based on Cu2O/Co3O4 nano/microstructure heteroarrays at and below room temperature. Sci Rep 7:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep43887
Yang M, Zhang XF, Cheng XL, Xu YM, Gao S, Zhao H, Huo LH (2017) Hierarchical NiO cube / nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide composite with enhanced H2S sensing properties at low temperature. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9:26293–26303. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b04969
Liu MM, He SJ, Chen W (2014) Co3O4 nanowires supported on 3D N-doped carbon foam as an electrochemical sensing platform for efficient H2O2 detection. Nanoscale 6:11769–11776. https://doi.org/10.1039/c4nr03043e
Kogularasu S, Govindasamy M, Chen SM, Akilarasan M, Mani V (2017) 3D graphene oxide-cobalt oxide polyhedrons for highly sensitive non-enzymatic electrochemical determination of hydrogen peroxide. Sensors Actuators B Chem 253:773–783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2017.06.172
Ensafi AA, Jafari-Asl M, Rezaei B (2013) A novel enzyme-free amperometric sensor for hydrogen peroxide based on Nafion/exfoliated graphene oxide-Co3O4 nanocomposite. Talanta 103:322–329. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2012.10.063
Das RK, Golder AK (2017) Co3O4 spinel nanoparticles decorated graphite electrode: bio-mediated synthesis and electrochemical H2O2 sensing. ElectrochimActa 251:415–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.08.122
Asif SAB, Khan SB, Asiri AM (2016) Electrochemical sensor for H2O2 using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a nanocomposite consisting of graphene oxide, cobalt(III) oxide, horseradish peroxidase and nafion. Microchim Acta 183:3043–3052. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1942-0
Zhang XM, Li KZ, Li HJ, Lu JH, Fu QG, Zhang LL (2016) Hydrothermal synthesis of cobalt oxide porous nanoribbons anchored with reduced graphene oxide for hydrogen peroxide detection. J Nanopart Res 232:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11051-016-3544-5
Barkaoui S, Haddaoui M, Dhaouadi H, Raouafi N, Touati F (2015) Hydrothermal synthesis of urchin-like Co3O4 nanostructures and their electrochemical sensing performance of H2O2. J Solid State Chem 228:226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssc.2015.04.043
Hou CT, Qin X, Yin L, Hu XY (2012) Metal-organic framework templated synthesis of Co3O4 nanoparticles for direct glucose and H2O2 detection. Analyst 137:5803–5808. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2an35954e
Wu Q, Sheng QL, Zheng JB (2016) Nonenzymatic amperometric sensing of hydrogen peroxide using a glassy carbon electrode modified with a sandwich-structured nanocomposite consisting of silver nanoparticles, Co3O4 and reduced graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183:1943–1951. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-016-1829-0
Karuppiah C, Palanisamy S, Chen SM, Veeramani V, Periakaruppan P (2014) A novel enzymatic glucose biosensor and sensitive non-enzymatic hydrogen peroxide sensor based on graphene and cobalt oxide nanoparticles composite modified glassy carbon electrode. Sensors Actuators B Chem 196:450–456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2014.02.034
Mu JS, Zhang L, Zhao M, Wang Y (2013) Co3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient catalase mimic: properties, mechanism and its electrocatalytic sensing application for hydrogen peroxide. J Mol Catal A Chem 378:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcata.2013.05.016
George G, Anandhan S (2016) Tuning characteristics of Co3O4 nanofiber mats developed for electrochemical sensing of glucose and H2O2. Thin Solid Films 610:48–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tsf.2016.05.005
Kong LG, Ren ZY, Zheng NN, Du SC, Wu J, Tang JL, Fu HG (2015) Interconnected 1D Co3O4 nanowires on reduced grapheme oxide for enzymeless H2O2 detection. Nano Res 8:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12274-014-0617-6
Jia WZ, Guo M, Zheng Z, Yu T, Rodriguez EG, Wang Y, Lei Y (2009) Electrocatalytic oxidation and reduction of H2O2 on vertically aligned Co3O4 nanowalls electrode: toward H2O2 detection. J Electroanal Chem 625:27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jelechem.2008.09.020
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21771060, 61271126, and 21305033), International Science & Technology Cooperation Program of China (2016YFE0115100).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 1.42 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, L., Yang, M., Zhao, H. et al. Co3O4/carbon hollow nanospheres for resistive monitoring of gaseous hydrogen sulfide and for nonenzymatic amperometric sensing of dissolved hydrogen peroxide. Microchim Acta 186, 184 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3253-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3253-8