Abstract
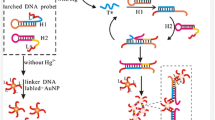
A colorimetric biosensor and visual test is described for the determination of mercury(II). It relies on the specific thymine-Hg(II)-thymine (T-Hg2+-T) interaction which induces a cyclic amplification process (caused by the enzyme exonuclease III) and the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. These results in a color change from red to violet. Under optimized conditions, this colorimetric assay (best performed at 524 nm) has a detection limit as low as 0.9 nM with a detection range over 4 orders of magnitude (from 1 nM to 10 μM).

Schematic of a colorimetric method for determination of mercury ions (Hg2+) based on the thymine-Hg2+-thymine interaction-triggered cyclic enzymatic amplification and aggregation of gold nanoparticles with the aid of exonuclease III (Exo III).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang DW, Niu CG, Wang XY, Lv XX, Zeng GM (2013) “Turn-on” fluorescent sensor for Hg2+ based on single-stranded DNA functionalized Mn:CdS/ZnS quantum dots and gold nanoparticles by time-gated mode. Anal Chem 85(2):1164–1170
Bi N, Hu MH, Xu J, Jia L (2017) Colorimetric determination of mercury (II) based on the inhibition of the aggregation of gold nanorods coated with 6-mercaptopurine. Microchim Acta 184(10):3961–3967
Liu YC, Wang XQ, Wu H (2017) Reusable DNA-functionalized-graphene for ultrasensitive mercury (II) detection and removal. Biosens Bioelectron 87:129–135
Chen YJ, Yao L, Deng Y, Pan DD, Ogabiela E, Cao JX, Adeloju SB, Chen W (2015) Rapid and ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of mercury (II) by chemically initiated aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 182(13–14):2147–2154
Office of Water (2001) Mercury update: impact on fish advisories, EPA fact sheet EPA-823-F-01-011. U.S. In: Environmental Protection Agency. D. C, Washington
Zenko Y, Masao T (1977) Indirect determination of submicrogram amounts of sulfide by flameless atomic absorption spectrometry of mercury. Microchim Acta 67(5–6):459–468
Guzmán-Mar JL, Hinojosa-Reyes L, Serra AM, Hernández-Ramírez A, Cerdà V (2011) Applicability of multisyringe chromatography coupled to cold-vapor atomic fluorescence spectrometry for mercury speciation analysis. Anal Chem Acta 708(1–2):11–18
Panichev NA, Panicheva SE (2015) Determination of total mercury in fish and sea products by direct thermal decomposition atomic absorption spectrometry. Food Chem 166:432–441
Qiu ZL, Tang DY, Shu J, Chen GN, Tang DP (2016) Enzyme-triggered formation of enzyme-tyramine concatamers on nanogold-functionalized dendrimer for impedimetric detection of Hg (II) with sensitivity enhancement. Biosens Bioelectron 75:108–115
Kumar VV, Anthony SP (2016) Highly selective colorimetric sensing of Hg2+ ions by label free AuNPs in aqueous medium across wide pH range. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 225:413–419
Wang LN, Liu FY, Sui N, Liu MH, Yu WW (2016) A colorimetric assay for Hg (II) based on the use of a magnetic aptamer and a hybridization chain reaction. Microchim Acta 183(11):2855–2860
Zhang H, Lei ZX, Fu X, Deng XC, Wang Q, Gu DY (2017) Hg2+-triggered exonuclease III-assisted dual-cycle targets recycling amplification for label-free and ultrasensitive colorimetric detection of Hg2+. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 246:896–903
He YQ, Zhang XB, Zeng K, Zhang SQ, Baloda M, Gurung AS, Liu GD (2011) Visual detection of Hg2+ in aqueous solution using gold nanoparticles and thymine-rich hairpin DNA probes. Biosens Bioelectron 26:4464–4470
Chen JH, Pan JF, Chen S (2017) A naked-eye colorimetric sensor for Hg2+ monitoring with cascade signal amplification based on target-induced conjunction of split DNAzyme fragments. Chem Commun 53:10224–10227
Lee JS, Mirkin CA (2008) Chip-based scanometric detection of mercuric ion using DNA-functionalized gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 80:6805–6808
Chen JH, Zhou SG, Wen JL (2014) Disposable strip biosensor for visual detection of Hg2+ based on Hg2+-triggered toehold binding and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Anal Chem 86:3108–3114
Liu S, Leng XQ, Wang X, Pei QQ, Cui XJ, Wang Y, Huang JD (2017) Enzyme-free colorimetric assay for mercury (II) using DNA conjugated to gold nanoparticles and strand displacement amplification. Microchim Acta 184(7):1969–1976
Hong MQ, Zeng BH, Li MY, Xu XQ, Chen GN (2018) An ultrasensitive conformation-dependent colorimetric probe for the detection of mercury(II) using exonuclease III-assisted target recycling and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(72). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2536-1
Li ZM, Zhong ZH, Liang RP, Qiu JD (2017) The colorimetric assay of DNA methyltransferase activity based on strand displacement amplification. Sensor Actuat B-Chem 238:626–632
Yang LZ, Yun W, Chen YL, Wu H, Liu XY, Fu M, Huang Y (2017) Ultrasensitive colorimetric and fluorometric detection of Hg (II) based on the use of gold nanoparticles and a catalytic hairpin assembly. Microchim Acta 184(12):4741–4747
Zarlaida F, Adlim M (2017) Gold and silver nanoparticles and indicator dyes as active agents in colorimetric spot and strip tests for mercury (II) ions: a review. Microchim Acta 184(1):45–58
Liu S, Wang Y, Xu W, Leng XQ, Wang HQ, Guo YN, Huang JD (2017) A novel sandwich-type electrochemical aptasensor based on GR-3D au and aptamer-AuNPs-HRP for sensitive detection of oxytetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 88:181–187
Tian Y, Wang Y, Xu Y, Liu Y, Li D, Fan CH (2015) A highly sensitive chemiluminescence sensor for detecting mercury (II) ions: a combination of exonuclease III-aided signal amplification and graphene oxide-assisted background reduction. Sci China Chem 58(3):514–518
Wang SQ, Yang F, Jin D, Dai Q, Tu JY, Liu YJ, Ning Y, Zhang GJ (2017) Toehold mediated one-step conformation-switchable “signal-on” electrochemical DNA sensing enhanced with homogeneous enzymatic amplification. Anal Chem 89:5349–5356
Zhang YL, Tang LN, Yang F, Sun ZY, Zhang GJ (2015) Highly sensitive DNA-based fluorometric mercury (II) bioassay based on graphene oxide and exonuclease III-assisted signal amplification. Microchim Acta 182(7–8):1535–1541
Zuo XW, Zhang HG, Zhu Q, Wang WF, Feng J, Chen XG (2016) A dual-color fluorescent biosensing platform based on WS2 nanosheet for detection of Hg2+ and Ag+. Biosens Bioelectron 85:464–470
Yan FY, Kong DP, Luo YM, Ye QH, He JJ, Guo XF, Chen L (2016) Carbon dots serve as an effective probe for the quantitative determination and for intracellular imaging of mercury (II). Microchim Acta 183(5):1611–1618
Shi DC, Yan FY, Zhou XG, Zheng TC, Shi YY, Fu WG, Chen L (2016) Preconcentration and fluorometric detection of mercury ions using magnetic core-shell chitosan microspheres modified with a rhodamine spirolactam. Microchim Acta 183(1):319–327
Kamali KZ, Pandikumar A, Jayabal S, Ramaraj R, Lim HN, Ong BH, Bien CSD, Kee YY, Huang NM (2016) Amalgamation based optical and colorimetric sensing of mercury (II) ions with silver@graphene oxide nanocomposite materials. Microchim Acta 183(1):369–377
Noor AM, Rameshkumar P, Huang NM, Wei LS (2016) Visual and spectrophotometric determination of mercury (II) using silver nanoparticles modified with graphene oxide. Microchim Acta 183(2):597–603
Shamsipur M, Safavi A, Mohammadpour Z, Ahmadi R (2016) Highly selective aggregation assay for visual detection of mercury ion based on competitive binding of sulfur-doped carbon nanodots to gold nanoparticles and mercury ions. Microchim Acta 183(7):2327–2335
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471644), the Primary Research & Development Plan of Shandong Province (2017GSF220009). University of Jinan Scientific Research Fund (Youth Project XKY1421) and Doctoral Fundation of University of Jinan (XBS1431).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 7.18 mb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, X., Wang, Y., Liu, S. et al. Colorimetric and visual mercury(II) assay based on target-induced cyclic enzymatic amplification, thymine-Hg(II)-thymine interaction, and aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 186, 105 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3193-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3193-8