Abstract
The authors describe the use of gold-decorated magnetic nanoparticles (Au/MNPs) in discriminating DNA sequences with a single-base (guanine) mismatch. The Au/MNPs were characterized through dynamic light scattering, X-ray diffraction, superconducting quantum interference device, and UV/visible spectroscopy. They were then conjugated to a probe oligomer consisting of a hairpin-shaped DNA sequence carrying two signalling fluorophores: fluorescein at its 3′ end and pyrene in the loop region. When interacting with the target DNA sequences, the hybridized probe–target duplex renders the pyrene signal (at excitation/emission wavelengths of 345/375 nm) either quenched or unquenched. Quenching (or nonquenching) of the pyrene fluorescence depends on the presence of a guanine (or a nonguanine) nucleotide at the designated polymorphic site. The linear range of hybridization in these Au/MNPs is from 0.1 nM to 1.0 μM of ssDNA. Conceivably, this system may serve as a single-nucleotide polymorphism probe.

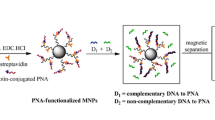
Schematic presentation of probe-conjugated Au/MNP preparation (upper panel) and working principle to discriminate DNA with or without single-base (guanine) mismatch sequences at the polymorphic sites (lower panel). Py denotes pyrene-hooked pyrrolocytidine; F denotes fluorescein.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Guo S, Wang E (2007) Synthesis and electrochemical applications of gold nanoparticles. Anal Chim Acta 598(2):181–192
Homberger M, Simon U (2010) On the application potential of gold nanoparticles in nanoelectronics and biomedicine. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences 368(1915):1405–1453
Das M, Shim KH, An SSA, Yi DK (2011) Review on gold nanoparticles and their applications. Toxicol Environ Heal Sci 3(4):193–205
Daraee H, Eatemadi A, Abbasi E, Fekri Aval S, Kouhi M, Akbarzadeh A (2016) Application of gold nanoparticles in biomedical and drug delivery. Artificial cells, nanomedicine, and biotechnology 44(1):410–422
Wu W, Wu Z, Yu T, Jiang C, Kim W-S (2015) Recent progress on magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: synthesis, surface functional strategies and biomedical applications. Sci Technol Adv Mater 16(2):023501
Lee M-H, Thomas JL, Ho M-H, Yuan C, Lin H-Y (2010) Synthesis of magnetic molecularly imprinted poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) nanoparticles and their uses in the extraction and sensing of target molecules in urine. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 2(6):1729–1736
Lee M-H, Thomas JL, Chen Y-C, Wang H-Y, Lin H-Y (2012) Hydrolysis of magnetic amylase-imprinted poly(ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) composite nanoparticles. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4(2):916–921. https://doi.org/10.1021/am201576y
Lee M-H, Thomas JL, Wang H-Y, Chang C-C, Lin C-C, Lin H-Y (2012) Extraction of resveratrol from polygonum cuspidatum with magnetic orcinol-imprinted poly (ethylene-co-vinyl alcohol) composite particles and their in vitro suppression of human osteogenic sarcoma (HOS) cell line. J Mater Chem 22(47):24644–24651
Lee M-H, Thomas JL, Chen J-Z, Jan J-S, Lin H-Y (2016) Activation of tumor suppressor p53 gene expression by magnetic thymine-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Chem Commun 52(10):2137–2140. https://doi.org/10.1039/C5CC09896C
Lee M-H, Ahluwalia A, Chen J-Z, Shih N-L, Lin H-Y (2017) Synthesis of magnetic cytosine-imprinted chitosan nanoparticles. Nanotechnology 28(8):085705
Luo J, Fan Q, Suzuki M, Suzuki IS, Engelhard MH, Lin Y, Kim N, Wang JQ, Zhong CJ (2005) Monodispersed Core−Shell Fe3O4@au nanoparticles. J Phys Chem B 109(46):21593–21601. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp0543429
Felber M, Alberto R (2015) 99m Tc radiolabelling of Fe 3 O 4–au core–shell and au–Fe 3 O 4 dumbbell-like nanoparticles. Nanoscale 7(15):6653–6660
Xu ZC, Hou YL, Sun SH (2007) Magnetic core/shell Fe3O4/au and Fe3O4/au/ag nanoparticles with tunable plasmonic properties. J Am Chem Soc 129(28):8698–8699
Xu CJ, Xie J, Ho D, Wang C, Kohler N, Walsh EG, Morgan JR, Chin YE, Sun SH (2008) Au–Fe3O4 dumbbell nanoparticles as dual-functional probes. Angew Chem Int Ed 47(1):173–176
Nguyen TT, Mammeri F, Ammar S (2018) Iron oxide and gold based magneto-Plasmonic nanostructures for medical applications: a review. Nanomaterials 8(3):149
Stafford S, Serrano Garcia R, Gun’ko YK (2018) Multimodal magnetic-Plasmonic nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Appl Sci 8(1):97
Kakwere H, Materia ME, Curcio A, Prato M, Sathya A, Nitti S, Pellegrino T (2018) Dually responsive gold–iron oxide heterodimers: merging stimuli-responsive surface properties with intrinsic inorganic material features. Nanoscale 10(8):3930–3944. https://doi.org/10.1039/C7NR06726G
Freitas M, Sá Couto M, Barroso MF, Pereira C, Delos Santos ÁN, Miranda-Ordieres AJ, Lobo-Castañón MJ, Delerue-Matos C (2016) Highly monodisperse Fe3O4@ Au superparamagnetic nanoparticles as reproducible platform for genosensing genetically modified organisms. Acs Sensors 1(8):1044–1053
Li F, Yu Z, Zhao L, Xue T (2016) Synthesis and application of homogeneous Fe3O4 core/au shell nanoparticles with strong SERS effect. RSC Adv 6(13):10352–10357
Liu X, Yang X, Xin H, Tang X, Weng L, Han Y, Geng D (2016) Ecofriendly fabrication of Au/Fe3O4-chitosan composites for catalytic reduction of methyl orange Digest. Journal of Nanomaterials & Biostructures 11(2):337–348
Kaur M, Pramanik S, Kumar M, Bhalla V (2017) Polythiophene-encapsulated bimetallic au-Fe3O4 Nano-hybrid materials: a potential tandem photocatalytic system for nondirected C (sp2)–H activation for the synthesis of Quinoline carboxylates. ACS Catal 7(3):2007–2021
Lin FH, Doong RA (2017) Catalytic Nanoreactors of au@ Fe3O4 yolk–Shell nanostructures with various au sizes for efficient Nitroarene reduction. J Phys Chem C 121(14):7844–7853
Zhou H, Lee J, Park TJ, Lee SJ, Park JY, Lee J (2012) Ultrasensitive DNA monitoring by au–Fe3O4 nanocomplex. Sensors Actuators B Chem 163(1):224–232
Du H, Disney MD, Miller BL, Krauss TD (2003) Hybridization-based unquenching of DNA hairpins on au surfaces: prototypical "molecular beacon" biosensors. J Am Chem Soc 125(14):4012–4013. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0290781
Shiddiky MJ, Shim Y-B (2007) Trace analysis of DNA: preconcentration, separation, and electrochemical detection in microchip electrophoresis using au nanoparticles. Anal Chem 79(10):3724–3733
Heim T, Preuss S, Gerstmayer B, Bosio A, Blossey R (2005) Deposition from a drop: morphologies of unspecifically bound DNA. J Phys Condens Matter 17(9):S703–S716
Okamoto A, Saito Y, Saito I (2005) Design of base-discriminating fluorescent nucleosides. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C-Photochemistry Reviews 6(2–3):108–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jphotochemrev.2005.07.002
Saito Y, Shinohara Y, Bag SS, Takeuchi Y, Matsumoto K, Saito I (2008) Design of an ultimate quencher free molecular beacon containing pyrrolocytidine-guanine base pair. Nucleic Acids Symp Ser (Oxf) 52:361–362. https://doi.org/10.1093/nass/nrn182
Lee MH, Lin HY, Chang HW, Yang CN (2018) Detection of DNA sequences with a single-base mismatch on a gold-based and pyrene-assisted platform. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 266:522–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.snb.2018.03.096
Salihov SV, Ivanenkov YA, Krechetov SP, Veselov MS, Sviridenkova NV, Savchenko AG, Klyachko NL, Golovin YI, Chufarova NV, Beloglazkina EK (2015) Recent advances in the synthesis of Fe3O4@ AU core/shell nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 394:173–178
Lepoitevin M, Lemouel M, Bechelany M, Janot J-M, Balme S (2015) Gold nanoparticles for the bare-eye based and spectrophotometric detection of proteins, polynucleotides and DNA. Microchim Acta 182(5):1223–1229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-014-1408-1
Tan C, Yu P, Hu Y, Chen J, Huang Y, Cai Y, Luo Z, Li B, Lu Q, Wang L, Liu Z, Zhang H (2015) High-yield exfoliation of ultrathin two-dimensional ternary chalcogenide Nanosheets for highly sensitive and selective fluorescence DNA sensors. J Am Chem Soc 137(32):10430–10436. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.5b06982
Zeng Y, Zhang D, Qi P, Zheng L (2017) Colorimetric detection of DNA by using target catalyzed DNA nanostructure assembly and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 184(12):4809–4815. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2463-1
Rapisarda A, Giamblanco N, Marletta G (2017) Kinetic discrimination of DNA single-base mutations by localized surface plasmon resonance. J Colloid Interface Sci 487:141–148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2016.10.026
Li BL, Zou HL, Lu L, Yang Y, Lei JL, Luo HQ, Li NB (2015) Size-dependent optical absorption of layered MoS2 and DNA oligonucleotides induced dispersion behavior for label-free detection of single-nucleotide polymorphism. Adv Funct Mater 25(23):3541–3550. https://doi.org/10.1002/adfm.201500180
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Ministry of Science and Technology, Taiwan (grant nos. MOST 106-2314-B-390-001-MY2, MOST 104-2113-M-002-019-MY2, and MOST 104-2113-M-390-003) and Armed Forces Zuoying General Hospital (grant no. ZBH 105-03) for their support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOC 908 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, MH., Leu, CC., Lin, CC. et al. Gold-decorated magnetic nanoparticles modified with hairpin-shaped DNA for fluorometric discrimination of single-base mismatch DNA. Microchim Acta 186, 80 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3192-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3192-9