Abstract
The presence or absence and nature of the free patchy ends in DNA sequences has a decisive effect on the performance of colorimetric sensors based on the use of gold nanoparticles (Au NPs). The authors have designed two unmodified gene probes (probe 1: a 19-mer; probe 2: an 18-mer). They are complementary to either half of a 37-mer target derived from the conserved region of Hepatitis C Virus (HCV) RNA. Each probe has further been modified with 10-mer poly(A) and thiol-functionalized 10-mer poly(A) at the 5′ positions. Nine combinations of probe and HCV RNA were then designed to investigate the effect of free patchy ends on the stability of citrate-modified Au NPs against salt-induced aggregation which lead to color change from red to blue. The aggregation of Au NPs can be monitored by ratiometric spectroscopy at wavelengths of 520 and 700 nm. The differentiation between HCV RNA and control has also been studied by varying the concentration of probe and analyte. The particle size and zeta potentials were determined before and after aggregation. It is demonstrated that the change in surface charge density of the Au NPs governs the critical coagulation concentration of NaCl. The method presented here can be used to quantify HCV RNA in the 370 nM to 3 μM concentration range, and the detection limit is 500 nM. The results obtained with Au NPs that are chemically non-conjugated with the oligonucleotides have been found to be valuable in rationally devising the design rules for rapid and efficient colorimetric sensing of oligonucleotides.

Schematic representation of the nine combinatorial pairs of oligonucleotides that vary in the length of patchy ends and their position to unearth their effect in rapid gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric gene sensing without time-consuming and expensive thiol-conjugation step.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Veigas B, Fernandes AR, Baptista PV (2014) AuNPs for identification of molecular signatures of resistance. Front Microbiol 5:455
Gedi V, Kim Y-P (2014) Detection and characterization of cancer cells and pathogenic bacteria using aptamer-based nano-conjugates. Sens 14(10):18302–18327
Guo L, Xu Y, Ferhan AR, Chen G, Kim DH (2013) Oriented gold nanoparticle aggregation for colorimetric sensors with surprisingly high analytical figures of merit. J Am Chem Soc 135(33):12338–12345
Wei X, Chen Z, Tan L, Lou T, Zhao Y (2016) DNA-catalytically active gold nanoparticle conjugates-based colorimetric multidimensional sensor array for protein discrimination. Anal Chem 89(1):556–559
Liu Z, Zhu J, Yang C, Li X (2015) Visual detection of Listeria monocytogenes using unmodified gold nanoparticles based on a novel marker. Anal Methods 7(19):8159–8164
Storhoff JJ, Lucas AD, Garimella V, Bao YP, Muller UR (2004) Homogeneous detection of unamplified genomic DNA sequences based on colorimetric scatter of gold nanoparticle probes. Nat Biotechnol 22(7):883–887
Scott AW, Garimella V, Calabrese CM, Mirkin CA (2016) Universal Biotin–PEG-linked gold nanoparticle probes for the simultaneous detection of nucleic acids and proteins. Bioconjugate Chem 28(1):203–211
Li J, Zhu B, Yao X, Zhang Y, Zhu Z, Tu S, Jia S, Liu R, Kang H, Yang CJ (2014) Synergetic approach for simple and rapid conjugation of gold nanoparticles with oligonucleotides. ACS Appl Mater Inter 6(19):16800–16807
Samanta A, Medintz IL (2016) Nanoparticles and DNA–a powerful and growing functional combination in bionanotechnology. Nanoscale 8(17):9037–9095
Doane TL, Burda C (2012) The unique role of nanoparticles in nanomedicine: imaging, drug delivery and therapy. Chem Soc Rev 41(7):2885–2911
Mieszawska AJ, Mulder WJ, Fayad ZA, Cormode DP (2013) Multifunctional gold nanoparticles for diagnosis and therapy of disease. Mol Pharm 10(3):831–847
Bogart LK, Pourroy G, Murphy CJ, Puntes V, Pellegrino T, Rosenblum D, Peer D, Levy R (2014) Nanoparticles for imaging, sensing, and therapeutic intervention. ACS Nano 8(4):3107–3122
Saha K, Agasti SS, Kim C, Li X, Rotello VM (2012) Gold nanoparticles in chemical and biological sensing. Chem Rev 112(5):2739–2779
Tan YN, Lee KH, Su X (2011) Study of single-stranded DNA binding protein–nucleic acids interactions using unmodified gold nanoparticles and its application for detection of single nucleotide polymorphisms. Anal Chem 83(11):4251–4257
Assah E, Goh W, Zheng XT, Lim TX, Li J, Lane D, Ghadessy F, Tan YN (2018) Rapid colorimetric detection of p53 protein function using DNA-gold nanoconjugates with applications for drug discovery and cancer diagnostics. Colloids Surf B 169:214–221
Elghanian R, Storhoff JJ, Mucic RC, Letsinger RL, Mirkin CA (1997) Selective colorimetric detection of polynucleotides based on the distance-dependent optical properties of gold nanoparticles. Science 277(5329):1078–1081
Sattarahmady N, Movahedpour A, Heli H, Hatam G (2016) Gold nanoparticles-based biosensing of Leishmania major kDNA genome: visual and spectrophotometric detections. Sensors Actuat B: Chem 235:723–731
Xia F, Zuo X, Yang R, Xiao Y, Kang D, Vallee-Belisle A, Gong X, Yuen JD, Hsu BB, Heeger AJ (2010) Colorimetric detection of DNA, small molecules, proteins, and ions using unmodified gold nanoparticles and conjugated polyelectrolytes. P Natl Acad Sci 107(24):10837–10841
Liu J, Bai W, Niu S, Zhu C, Yang S, Chen A (2014) Highly sensitive colorimetric detection of 17β-estradiol using split DNA aptamers immobilized on unmodified gold nanoparticles. Sci Rep 4:7571
Wang Q, Yang X, Yang X, Wang K, Zhang H, Liu P (2015) An enzyme-free colorimetric assay using hybridization chain reaction amplification and split aptamers. Analyst 140(22):7657–7662
Liu P, Yang X, Sun S, Wang Q, Wang K, Huang J, Liu J, He L (2013) Enzyme-free colorimetric detection of DNA by using gold nanoparticles and hybridization chain reaction amplification. Anal Chem 85(16):7689–7695
Baetsen-Young AM, Vasher M, Matta LL, Colgan P, Alocilja EC, Day B (2018) Direct colorimetric detection of unamplified pathogen DNA by dextrin-capped gold nanoparticles. Biosens Bioelectron 101:29–36
Jazayeri MH, Aghaie T, Avan A, Ghaffari MRS (2018) Colorimetric detection based on gold nano particles (GNPs): An easy, fast, inexpensive, low-cost and short time method in detection of analytes (protein, DNA, and ion). Sens Bio-sens Res 20:1–8
Liu Y, Wu Z, Zhou G, He Z, Zhou X, Shen A, Hu J (2012) Simple, rapid, homogeneous oligonucleotides colorimetric detection based on non-aggregated gold nanoparticles. Chem Commun 48(26):3164–3166
Shawky SM, Guirgis BS, Azzazy HM (2014) Detection of unamplified HCV RNA in serum using a novel two metallic nanoparticle platform. Clin Chem Lab Med 52(4):565–572
Shawky SM, Bald D, Azzazy HM (2010) Direct detection of unamplified hepatitis C virus RNA using unmodified gold nanoparticles. Clin Biochem 43(13–14):1163–1168
Shawky SM, Awad AM, Allam W, Alkordi MH, El-Khamisy SF (2017) Gold aggregating gold: A novel nanoparticle biosensor approach for the direct quantification of hepatitis C virus RNA in clinical samples. Biosens Bioelectron 92:349–356
Nossier AI, Abdelzaher H, Matboli M, Eissa S (2018) Dual approach for the colorimetric determination of unamplified microRNAs by using citrate capped gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185(4):236–244
Li H, Rothberg L (2005) Detection of specific sequences in RNA using differential adsorption of single-stranded oligonucleotides on gold nanoparticles. Anal Chem 77(19):6229–6233
Li H, Rothberg L (2004) Colorimetric detection of DNA sequences based on electrostatic interactions with unmodified gold nanoparticles. P Natl Acad Sci 101(39):14036–14039
Farkhari N, Abbasian S, Moshaii A, Nikkhah M (2016) Mechanism of adsorption of single and double stranded DNA on gold and silver nanoparticles: investigating some important parameters in bio-sensing applications. Colloids Surf B 148:657–664
Kim CW, Chang K-M (2013) Hepatitis C virus: virology and life cycle. Clin Mol Hepatol 19(1):17–25
Daraee H, Pourhassanmoghadam M, Akbarzadeh A, Zarghami N, Rahmati-Yamchi M (2016) Gold nanoparticle–oligonucleotide conjugate to detect the sequence of lung cancer biomarker. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol 44(6):1417–1423
Suzuki S, Ono N, Furusawa C, Kashiwagi A, Yomo T (2007) Experimental optimization of probe length to increase the sequence specificity of high-density oligonucleotide microarrays. BMC Genomics 8(1):373–385
Dieffenbach C, Lowe T, Dveksler G (1993) General concepts for PCR primer design. PCR Meth Appl 3(3):S30–S37
Yan Z, Zhang D, Qi P, Zheng L (2017) Colorimetric detection of DNA by using target catalyzed DNA nanostructure assembly and unmodified gold nanoparticles. Microchimica Acta 184(12):4809–4815
Acknowledgements
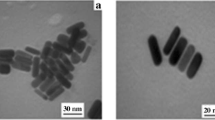
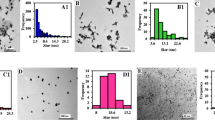
The authors would like to thank BITS, Pilani Hyderabad campus for their financial support. DLS, Zeta sizer and STEM facilities of Central Analytical Laboratory of BITS Pilani Hyderabad campus are greatly acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human or animal subjects.
Informed consent
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(PDF 1263 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammed, A.S., Nagarjuna, R., Khaja, M.N. et al. Effects of free patchy ends in ssDNA and dsDNA on gold nanoparticles in a colorimetric gene sensor for Hepatitis C virus RNA. Microchim Acta 186, 566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3685-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-019-3685-1