Abstract
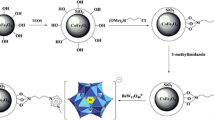
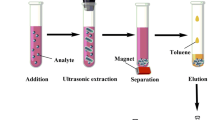
Magnetic knitting aromatic polymers (Fe3O4/KAPs) are introduced here as a new kind of sorbents. KAPs are hyper-cross-linked-polymers that were prepared via a Friedl-Crafts reaction from triphenylphosphine and benzene as building blocks. The Fe3O4/KAP composite was obtained by coprecipitation of KAP with magnetite nanoparticles. The resulting Fe3O4/KAP is shown to be a viable magnetic sorbent for various organic materials such as the phenylurea herbicides (PUHs), including metoxuron, monuron, chlortoluron, monolinuron and buturon, and also for various phthalates, polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons and chlorophenols. The Fe3O4/KAP was characterized by means of Brunauer-Emmett-Teller surface area measurements, Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy, thermogravimetry, X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy and transmission electron microscopy. Following desorption with acetonitrile, the analytes were quantified by using HPLC with UV detection. The effects of adsorbent dosage, extraction time, sample pH, ionic strength, desorption solvent and desorption time were optimized for the PUHs. Under optimal conditions, response is linear from 0.5–1.0 up to 50 ng·mL−1 for the five PUHs. Lower limits of detection range between 0.05 and 0.30 ng·mL−1. Other figures of merit include (a) high enrichment factors (60–297), (b) good recoveries (91.8–106.5%), and (c) relative standard deviations of <8.4%. The method was successfully applied to analysis of the PUHs in real samples (bottled mixed juice, milk and soymilk). The results indicate that such Fe3O4/KAPs have a wide application scope as an adsorbent for use in magnetic solid phase extraction.

A magnetic knitting aromatic polymer based nanocomposite (Fe3O4/KAP) was prepared by a one-pot method and explored as an absorbent for magnetic solid-phase extraction (MSPE) of phenylurea herbicides (PUHs) from bottled mixed juice, milk and soymilk samples before quantitation by HPLC with UV detection.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bobu M, Wilson S, Greibrokk T, Lundanes E, Siminiceanu I (2006) Comparison of advanced oxidation processes and identification of monuron photodegradation products in aqueous solution. Chemosphere 63:1718–1727. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.09.034
Carabias-Martı́nez R, Rodrı́guez-Gonzalo E, Herrero-Hernández E, Hernández-Méndez J (2004) Simultaneous determination of phenyl- and sulfonylurea herbicides in water by solid-phase extraction and liquid chromatography with UV diode array or mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta 517:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2004.05.007
Bautista A, Aaron JJ, Mahedero MC, Muñoz de la Peña A (1999) Usefulness of micellar media for the quantitative analysis of phenylurea herbicides in water by photochemically-induced fluorescence. Analusis 27:857–863. https://doi.org/10.1051/analusis:1999154
Langeron J, Sayen S, Couderchet M, Guillon E (2014) Leaching potential of phenylurea herbicides in a calcareous soil: comparison of column elution and batch studies. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 21:4906–4913. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-012-1244-y
Elcombe CR, Odum J, Foster JR, Stone S, Hasmall S, Soames AR, Kimber I, Ashby J (2002) Prediction of rodent nongenotoxic carcinogenesis: evaluation of biochemical and tissue changes in rodents following exposure to nine nongenotoxic NTP carcinogens. Environ Health Persp 110:363–375 http://ehpnet1.niehs.nih.gov/docs/2002/110p363-375elcombe/abstract.html
Melo LFC, Collins CH, Jardim ICSF (2005) High-performance liquid chromatographic determination of pesticides in tomatoes using laboratory-made NH2 and C18 solid-phase extraction materials. J Chromatogr A 1073:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2004.09.043
Mughari AR, Vázquez PP, Galera MM (2007) Analysis of phenylurea and propanil herbicides by solid-phase microextraction and liquid chromatography combined with post-column photochemically induced fluorimetry derivatization and fluorescence detection. Anal Chim Acta 593:157–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2007.04.061
Chou TY, Lin SL, Fuh MR (2009) Determination of phenylurea herbicides in aqueous samples using partitioned dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction. Talanta 80:493–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2009.07.005
Liu X, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2015) Metal-organic framework-templated synthesis of magnetic nanoporous carbon as an efficient absorbent for enrichment of phenylurea herbicides. Anal Chim Acta 870:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.02.036
McKeown NB, Budd PM (2006) Polymers of intrinsic microporosity (PIMs): organic materials for membrane separations, heterogeneous catalysis and hydrogen storage. Chem Soc Rev 35:675–683. https://doi.org/10.1039/b600349d
Zhang Y, Riduan SN (2012) Functional porous organic polymers for heterogeneous catalysis. Chem Soc Rev 41:2083–2094. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1cs15227k
Wang JT, Jiao CN, Li MH, Wang XL, Wang C, Wu QH, Wang Z (2018) Porphyrin based porous organic polymer modified with Fe3O4 nanoparticles as an efficient adsorbent for the enrichment of benzoylurea insecticides. Microchim Acta 185:36–43. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2542-3
Siriwardane RV, Shen MS, And EPF, Poston JA (2001) Adsorption of CO2 on molecular sieves and activated carbon. Energ Fuel 15:279–284. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef000241s
Meshko V, Markovska L, Mincheva M, Rodrigues AE (2001) Adsorption of basic dyes on granular activated carbon and natural zeolite. Water Res 35:3357–3366. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0043-1354(01)00056-2
Fan J, Yu C, Gao F, Lei J, Tian B, Wang L, Luo Q, Tu B, Zhou W, Zhao D (2003) Angew Chem 115:3254–3258. https://doi.org/10.1002/ange.200351027
Liu C, Yu LQ, Zhao YT, Lv YK (2018) Recent advances in metal-organic frameworks for adsorption of common aromatic pollutants. Microchim Acta 185:342–353. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2879-2
Ding SY, Wang W (2013) Covalent organic frameworks (COFs): from design to applications. Chem Soc Rev 42:548–568. https://doi.org/10.1039/c2cs35072f
Tozawa T, Jones JTA, Swamy SI, Jiang S, Adams DJ, Shakespeare S, Clowes R, Bradshaw D, Hasell T, Chong SY (2009) Porous organic cages. Nat Mater 8:973–978. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmat2545
Dawson R, Stöckel E, Holst JR, Adams DJ, Cooper AI (2011) Microporous organic polymers for carbon dioxide capture. Energy Environ Sci 4:4239. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1ee01971f
Li B, Guan Z, Wang W, Yang X, Hu J, Tan B, Li T (2012) Highly dispersed pd catalyst locked in knitting aryl network polymers for Suzuki-Miyaura coupling reactions of aryl chlorides in aqueous media. Adv Mater 24:3390–3395. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201200804
Detoni C, Gierlich CH, Rose M, Palkovits R (2014) Selective liquid phase adsorption of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural on Nanoporous hyper-cross-linked polymers. ACS Sustain Chem Eng 2:2407–2415. https://doi.org/10.1021/sc5004264
Tan L, Tan B (2017) Hypercrosslinked porous polymer materials: design, synthesis, and applications. Chem Soc Rev 46:3322–3356. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6cs00851h
Li B, Gong R, Wang W, Huang X, Zhang W, Li H, Hu C, Tan B (2011) A new strategy to microporous polymers: knitting rigid aromatic building blocks by external cross-linker. Macromolecules 44:2410–2414. https://doi.org/10.1021/ma200630s
Lu C, Liu S, Xu J, Ding Y, Ouyang G (2016) Exploitation of a microporous organic polymer as a stationary phase for capillary gas chromatography. Anal Chim Acta 902:205–211. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aca.2015.10.034
Tang P, Chen Z (2018) Capillary electrochromatography using knitted aromatic polymer as the stationary phase for the separation of small biomolecules and drugs. Talanta 178:650–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2017.10.004
Shen R, Liu H (2016) Construction of bimodal silsesquioxane-based porous materials from triphenylphosphine or triphenylphosphine oxide and their size-selective absorption for dye molecules. RSC Adv 6:37731–37739. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra02963a
Li N, Wang Z, Zhang L, Nian L, Lei L, Yang X, Zhang H, Yu A (2014) Liquid-phase extraction coupled with metal-organic frameworks-based dispersive solid phase extraction of herbicides in peanuts. Talanta 128:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2014.04.084
Dong X, Liang S, Shi Z, Sun H (2016) Development of multi-residue analysis of herbicides in cereal grain by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-mass spectrometry. Food Chem 192:432–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2015.07.025
Li N, Wu L, Nian L, Song Y, Lei L, Yang X, Wang K, Wang Z, Zhang L, Zhang H, Yu A, Zhang Z (2015) Dynamic microwave assisted extraction coupled with dispersive micro-solid-phase extraction of herbicides in soybeans. Talanta 142:43–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.talanta.2015.04.038
Li M, Wang J, Jiao C, Wang C, Wu Q, Wang Z (2016) Graphene oxide framework: An adsorbent for solid phase extraction of phenylurea herbicides from water and celery samples. J Chromatogr A 1469:17–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chroma.2016.09.056
LiuXL, Wang C, Wang ZC, Wu QH, Wang Z (2015) Nanoporous carbon derived from a metal organic framework as a new kind of adsorbent for dispersive solid phase extraction of benzoylurea insecticides. Microchim Acta 182:1903–1910. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1530-8
Acknowledgments
We greatly appreciate the financial supports from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31471643, 31571925, 31671930), the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2016204136, B2016204146, B2017204025), the Advanced Program for the Introduction of Overseas Scholars by Hebei Province (CL201713) and the Hebei “Double First Class Discipline” Construction Foundation for the Discipline of Food Science and Engineering of Hebei Agricultural University (2016SPGCA18).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 556 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gao, T., Wang, J., Hao, L. et al. A magnetic knitting aromatic polymer as a new sorbent for use in solid-phase extraction of organics. Microchim Acta 185, 554 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3085-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3085-y