Abstract
A method is described for sensitive and selective fluorometric determination of morphine. It is based on the effect of morphine on quenching of the fluorescence of fluorescein by gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) via surface energy transfer. When fluorescein is added to solutions of colloidal AuNPs, its fluorescence becomes quenched due to nanometal surface energy transfer (NSET) because the absorption of AuNPs strongly overlaps the emission spectrum of fluorescein. In the presence of morphine, which contains both a tertiary nitrogen ring atom and a phenolic hydroxy group, it will coordinate to the AuNPs, and this causes recovery of fluorescence. The presence of a tertiary nitrogen ring atom and a phenolic hydroxy group (both required for the effect to occur) in morphine make the probe highly selective and sensitive for morphine. A paper strip assay also was developed by utilizing this detection scheme. The turn-on fluorescent probe was successfully applied to the determination of morphine in spiked serum and urine samples. The method has a 53 pM limit of detection. The paper strip was applied to the determination of morphine in sweat, urine and other biological fluids. It is perceived to be useful for early detection of drug abuse by adolescent.

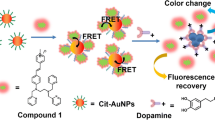
Schematic of the mechanism of fluorescence turn on detection of morphine using Au NPs (gold nanoparticles) acting asquencher of the fluorescence of fluorescein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atta NF, Galal A, Azab SM (2011) Determination of morphine at gold nanoparticles/Nafion(R) carbon paste modified sensor electrode. Analyst 136(22):4682–4691. https://doi.org/10.1039/c1an15423k
Lotfi A, Karimi S, Hassanzadeh J (2016) Molecularly imprinted polymers on multi-walled carbon nanotubes as an efficient absorbent for preconcentration of morphine and its chemiluminometric determination. RSC Adv 6(96):93445–93452. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra22074f
Cepas J, Silva M, Perez-Bendito D (1993) Automated kinetic-spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of morphine in urine. Analyst 118(7):923–927
Shcherbakova EG, Zhang B, Gozem S, Minami T, Zavalij PY, Pushina M, Isaacs LD, Anzenbacher P Jr (2017) Supramolecular sensors for opiates and their metabolites. J Am Chem Soc 139(42):14954–14960. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b06371
Holt PJ, Bruce NC, Lowe CR (1996) Bioluminescent assay for heroin and its metabolites. Anal Chem 68(11):1877–1882
Spotlights on Recent JACS Publications (2017) J Am Chem Soc 139(42):14815–14816. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.7b11051
McCord CE, McCutcheon JR (1988) Preliminary evaluation of the Abbott TDx for benzoylecgonine and opiate screening in whole blood. J Anal Toxicol 12(5):295–297
Cepas J, Silva M, Perez-Bendito D (1993) Automated kinetic-spectrofluorimetric method for the determination of morphine in urine. Analyst 118(7):923–927. https://doi.org/10.1039/an9931800923
Ma D, Hettiarachchi G, Nguyen D, Zhang B, Wittenberg JB, Zavalij PY, Briken V, Isaacs L (2012) Acyclic cucurbit[n]uril molecular containers enhance the solubility and bioactivity of poorly soluble pharmaceuticals. Nat Chem 4(6):503–510. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchem.1326
Remane D, Wissenbach DK, Peters FT (2016) Recent advances of liquid chromatography-(tandem) mass spectrometry in clinical and forensic toxicology - an update. Clin Biochem 49(13-14):1051–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2016.07.010
Chalmers JM, Edwards HG, Hargreaves MD (2012) Infrared and Raman spectroscopy in forensic science. Wiley, Chichester
Smith HS (2009) Opioid metabolism. Mayo Clin Proc 84(7):613–624. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0025-6196(11)60750-7
Ya Y, Xiaoshu W, Qing D, Lin J, Yifeng T (2015) Label-free immunosensor for morphine based on the electrochemiluminescence of luminol on indium-tin oxide coated glass functionalized with gold nanoparticles. Anal Methods 7(11):4502–4507. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5ay00764j
Toyo'oka T, Yano M, Kato M, Nakahara Y (2001) Simultaneous determination of morphine and its glucuronides in rat hair and rat plasma by reversed-phase liquid chromatography with electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Analyst 126(8):1339–1345
Eissa S, Zourob M (2017) Competitive voltammetric morphine immunosensor using a gold nanoparticle decorated graphene electrode. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2261-9
Zhang C, Han Y, Lin L, Deng N, Chen B, Liu Y (2017) Development of quantum dots-labeled antibody fluorescence immunoassays for the detection of morphine. J Agric Food Chem 65(6):1290–1295. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05305
Bonanno LM, DeLouise LA (2010) Tunable detection sensitivity of opiates in urine via a label-free porous silicon competitive inhibition Immunosensor. Anal Chem 82(2):714–722. https://doi.org/10.1021/ac902453h
Gandhi S, Banga I, Maurya PK, Eremin SA (2018) A gold nanoparticle-single-chain fragment variable antibody as an immunoprobe for rapid detection of morphine by dipstick. RSC Adv 8(3):1511–1518. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra12810j
Lin C-Y, Liu C-H, Tseng W-L (2010) Fluorescein isothiocyanate-capped gold nanoparticles for fluorescent detection of reactive oxygen species based on thiol oxidation and their application for sensing glucose in serum. Anal Methods 2(11):1810–1815. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0ay00428f
Krajczewski J, Kolataj K, Kudelski A (2017) Plasmonic nanoparticles in chemical analysis. RSC Adv 7(28):17559–17576. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra01034f
Wang X-F, Xiang L-P, Wang Y-S, Xue J-H, Zhu Y-F, Huang Y-Q, Chen S-H, Tang X (2016) A “turn-on” fluorescence assay for lead(II) based on the suppression of the surface energy transfer between acridine orange and gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(4):1333–1339. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-015-1738-7
Alegria ECBA, Ribeiro APC, Mendes M, Ferraria AM, do Rego AMB, Pombeiro AJL (2018) Effect of phenolic compounds on the synthesis of gold nanoparticles and its catalytic activity in the reduction of nitro compounds. Nanomaterials 8(5):320. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano8050320
Dharanivasan G, Rajamuthuramalingam T, Michael Immanuel Jesse D, Rajendiran N, Kathiravan K (2015) Gold nanoparticles assisted characterization of amine functionalized polystyrene multiwell plate and glass slide surfaces. Appl Nanosci 5(1):39–50. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13204-013-0290-1
Hussain SA (2009) An introduction to fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET). arXiv:0908.1815 [physics.gen-ph]. Accessed 13 Aug 2009
Didenko VV (2001) DNA probes using fluorescence resonance energy transfer (FRET): designs and applications. Biotechniques 31(5):1106–1116 1118, 1120–1101
Posokhov YO, Kyrychenko A, Ladokhin AS (2010) Steady-state and time-resolved fluorescence quenching with transition metal ions as short-distance probes for protein conformation. Anal Biochem 407(2):284–286. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ab.2010.07.035
Breshike CJ, Riskowski RA, Strouse GF (2013) Leaving Förster resonance energy transfer behind: Nanometal surface energy transfer predicts the size-enhanced energy coupling between a metal nanoparticle and an emitting dipole. J Phys Chem C 117(45):23942–23949. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp407259r
Saraswat S, Desireddy A, Zheng D, Guo L, Lu HP, Bigioni TP, Isailovic D (2011) Energy transfer from fluorescent proteins to metal nanoparticles. J Phys Chem C 115(35):17587–17593. https://doi.org/10.1021/jp2029246
Griffin J, Singh AK, Senapati D, Rhodes P, Mitchell K, Robinson B, Yu E, Ray PC (2009) Size- and distance-dependent nanoparticle surface-energy transfer (NSET) method for selective sensing of hepatitis C virus RNA. Chemistry 15(2):342–351. https://doi.org/10.1002/chem.200801812
John J, Thomas L, George NA, Kurian A, George SD (2015) Tailoring of optical properties of fluorescein using green synthesized gold nanoparticles. Phys Chem Chem Phys 17(24):15813–15821. https://doi.org/10.1039/c5cp02029h
Zu F, Yan F, Bai Z, Xu J, Wang Y, Huang Y, Zhou X (2017) The quenching of the fluorescence of carbon dots: a review on mechanisms and applications. Microchim Acta 184(7):1899–1914. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-017-2318-9
Bahram M, Madrakian T, Alizadeh S (2017) Simultaneous colorimetric determination of morphine and ibuprofen based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles using partial least square. J Pharm Anal 7(6):411–416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2017.03.001
Atta N, Galal A, Azab S (2011) Electrochemical morphine sensing using gold nanoparticles modified carbon paste electrode. Int J Electrochem Sci 6(10):5066–5081
Fonin AV, Sulatskaya AI, Kuznetsova IM, Turoverov KK (2014) Fluorescence of dyes in solutions with high absorbance. Inner filter effect correction. PLoS One 9(7):e103878. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0103878
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Head, Department of Chemistry, University of Kerala, Kariavattom Campus, Thiruvananthapuram for pursuing the platform to conduct the research. The authors also thank the Director, SICC, University of Kerala, Kariavattom campus, Thiruvananthapuram; Director, SAIF-STIC-CUSAT, Kochi; DST-SAIF, M.G. University, Kottayam. The author N.J. acknowledge support for this work by University Grants Commission, Bangalore, India through the teacher fellowship (F.No.FIP/12th plan/KLMG035, TF: 03) under faculty development programme during XIIth plan period.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 51 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nebu, J., Anjali Devi, J.S., Aparna, R.S. et al. Fluorometric determination of morphine via its effect on the quenching of fluorescein by gold nanoparticles through a surface energy transfer process. Microchim Acta 185, 532 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3050-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-3050-9