Abstract
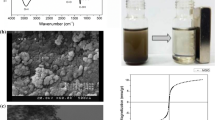
Magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) modified with organic dendrimers are shown to be a viable sorbent of the microextraction of the drug rosuvastatin (RST; also known as Crestor). The MNPs were prepared from iron(II) chloride and iron(III) chloride and then coated with silicon dioxide. The coated MNPs produced by this method have diameters ranging from 10 to 60 nm according to scanning electron microscopy. The MNPs were further modified with organic dendrimers containing methyl methacrylate and ethylene diamine. The resulting MNPs were characterized by SEM, Fourier transform infra-red and thermal gravimetry analysis. Then, the efficacy of the modified MNPs with respect to the extraction of RST was studied. The adsorption of RST by MNPs can be best described by a Langmuir isotherm. Following elution with buffer, RST was quantified by HPLC. The method was applied to the determination of RST in (spiked) human blood plasma, urine, and in tablets. RST extraction efficiencies are 54.5% in plasma, 86.6% from the drug matrix, and 94.3% in urine. The highest adsorption capacity of the RST by the MNPs adsorbent was 61 mg⋅g−1.

Co-precipitation was used to synthesize magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs). They were coated with a layer of SiO2 and then branched by organic dendrimers containing methyl methacrylate (MMA) and ethylene diamine (EDA). Rosuvastatin (RST) drug was trapped between dendrimer branches, therefore adsorption capacity of the drug was strongly increased.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown WV, Bays HE, Hassman DR, McKenney J, Chitra R, Hutchinson H, Miller E, Rosuvastatin Study Group (2002) Efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin compared with pravastatin and simvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia: a randomized, double-blind, 52-week trial. Am Heart J 144(6):1036–1043
Olsson AG, McTaggart F, Raza A (2002) Rosuvastatin: a highly effective new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor. Cardiovasc Drug Rev 20(4):303–328
Jones PH, Davidson MH, Stein EA, Bays HE, McKenney J, Miller E, Cain VA, Blasetto JW, STELLAR Study Group (2003) Comparison of the efficacy and safety of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin across doses (STELLAR trial). Am J Cardiol 92(2):152–160
Martin PD, Mitchell PD, Schneck DW (2002) Pharmacodynamic effects and pharmacokinetics of a new HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, rosuvastatin, after morning or evening administration in healthy volunteers. Br J Clin Pharmacol 54(5):472–477
Chowdhury R, Khan H, Heydon E, Shroufi A, Fahimi S, Moore C, Stricker B, Mendis S, Hofman A, Mant J, Franco OH (2013) Adherence to cardiovascular therapy: a meta-analysis of prevalence and clinical consequences. Eur Heart J 34(38):2940–2948
Cohen JD, Brinton EA, Ito MK, Jacobson TA (2012) Understanding statin use in America and gaps in patient education (USAGE): an internet-based survey of 10,138 current and former statin users. J Clin Lipidol 6(3):208–215
Bruckert E, Hayem G, Dejager S, Yau C, Bégaud B (2005) Mild to moderate muscular symptoms with high-dosage statin therapy in hyperlipidemic patients—the PRIMO study. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 19(6):403–414
Martin PD, Dane AL, Nwose OM, Schneck DW, Warwick MJ (2002) No effect of age or gender on the pharmacokinetics of Rosuvastatin: a new HMG-CoA Reductase inhibitor. J Clin Pharmacol 42(10):1116–1121
Kim J-E, Shin J-Y, Cho M-H (2012) Magnetic nanoparticles: an update of application for drug delivery and possible toxic effects. Arch Toxicol 86(5):685–700
Veiseh O, Gunn JW, Zhang M (2010) Design and fabrication of magnetic nanoparticles for targeted drug delivery and imaging. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62(3):284–304
Sun C, Lee JS, Zhang M (2008) Magnetic nanoparticles in MR imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 60(11):1252–1265
Boas U, Christensen JB, Heegaard PM (2006) Dendrimers in medicine and biotechnology: new molecular tools. Royal Society of Chemistry, London
Singh U, Dar MM, Hashmi AA (2014) Dendrimers: synthetic strategies, properties and applications. Orient J Chem 30(3):911–922
Tomalia DA, Reyna L, Svenson S (2007) Dendrimers as multi-purpose nanodevices for oncology drug delivery and diagnostic imaging. Portland Press Limited, Biochemical Society Transactions 35(1):61–67. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0350061https://doi.org/10.1042/BST0350061
LIU L, BARTH RF, ADAMS DM, SOLOWAY AH, REISFELD RA (1995) Bispecific antibodies as targeting agents for boron neutron capture therapy of brain tumors. J Hematother 4(5):477–483
Morgan MT, Nakanishi Y, Kroll DJ, Griset AP, Carnahan MA, Wathier M, Oberlies NH, Manikumar G, Wani MC, Grinstaff MW (2006) Dendrimer-encapsulated camptothecins: increased solubility, cellular uptake, and cellular retention affords enhanced anticancer activity in vitro. Cancer Res 66(24):11913–11921
Singh R, Nalwa HS (2011) Medical applications of nanoparticles in biological imaging, cell labeling, antimicrobial agents, and anticancer nanodrugs. J Biomed Nanotechnol 7(4):489–503
Abolghasemi MM, Habibiyan R, Jaymand M, Piryaei M (2018) A star-shaped polythiophene dendrimer coating for solid-phase microextraction of triazole agrochemicals. Microchim Acta 185(3):179
Lotfi Z, Mousavi HZ, Sajjadi SM (2017) A hyperbranched polyamidoamine dendrimer grafted onto magnetized graphene oxide as a sorbent for the extraction of synthetic dyes from foodstuff. Microchim Acta 184(11):4503–4512
Panahi HA et al (2013) Synthesis and characterization of poly [1-(N, N-bis-carboxymethyl) amino-3-allylglycerol-co-dimethylacrylamide] grafted to magnetic nano-particles for extraction and determination of letrozole in biological and pharmaceutical samples. Talanta 117:511–517
Ai H (2011) Layer-by-layer capsules for magnetic resonance imaging and drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(9):772–788
Kumar CS, Mohammad F (2011) Magnetic nanomaterials for hyperthermia-based therapy and controlled drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 63(9):789–808
Zhang W, Yan Z, Gao J, Tong P, Liu W, Zhang L (2015) Metal–organic framework UiO-66 modified magnetite@ silica core–shell magnetic microspheres for magnetic solid-phase extraction of domoic acid from shellfish samples. J Chromatogr A 1400:10–18
Muzzy JD, Kays AO (1984) Thermoplastic vs. thermosetting structural composites. Polym Compos 5(3):169–172
Ivanov AE, Eccles J, Panahi HA, Kumar A, Kuzimenkova MV, Nilsson L, Bergenståhl B, Long N, Phillips GJ, Mikhalovsky SV, Galaev IY, Mattiasson B (2009) Boronate-containing polymer brushes: characterization, interaction with saccharides and mammalian cancer cells. J Biomed Mater Res A 88(1):213–225
Mahdavian AR, Mirrahimi MA-S (2010) Efficient separation of heavy metal cations by anchoring polyacrylic acid on superparamagnetic magnetite nanoparticles through surface modification. Chem Eng J 159(1):264–271
Khosroshahi ME, Ghazanfari L (2012) Synthesis and functionalization of SiO 2 coated Fe 3 O 4 nanoparticles with amine groups based on self-assembly. Mater Sci Eng C 32(5):1043–1049
Andrade A et al (2009) Synthesis and characterization of magnetic nanoparticles coated with silica through a sol-gel approach. Cerâmica 55(336):420–424
Abbas M et al (2014) Fe3O4/SiO2 core/shell nanocubes: novel coating approach with tunable silica thickness and enhancement in stability and biocompatibility. J Nanomed Nanotechnol 5(6):1–8
Cao H, He J, Deng L, Gao X (2009) Fabrication of cyclodextrin-functionalized superparamagnetic Fe 3 O 4/amino-silane core–shell nanoparticles via layer-by-layer method. Appl Surf Sci 255(18):7974–7980
Liu Y (2006) Some consideration on the Langmuir isotherm equation. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 274(1):34–36
Wang L, Zhang J, Wang A (2008) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution using chitosan-g-poly (acrylic acid)/montmorillonite superadsorbent nanocomposite. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 322(1):47–53
Yagub MT, Sen TK, Afroze S, Ang HM (2014) Dye and its removal from aqueous solution by adsorption: a review. Adv Colloid Interf Sci 209:172–184
Everett D (1972) Manual of symbols and terminology for physicochemical quantities and units, appendix II: definitions, terminology and symbols in colloid and surface chemistry. Pure Appl Chem 31(4):577–638
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore-and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5(2):212–223
Freundlich H (1907) Über die adsorption in lösungen. Z Phys Chem 57(1):385–470
Tempkin M, Pyzhev V (1940) Kinetics of ammonia synthesis on promoted iron catalyst. Acta Physicochim USSR 12(1):327
Redlich O, Peterson DL (1959) A useful adsorption isotherm. J Phys Chem 63(6):1024–1024
Gao J, Zhong D, Duan X, Chen X (2007) Liquid chromatography/negative ion electrospray tandem mass spectrometry method for the quantification of rosuvastatin in human plasma: application to a pharmacokinetic study. J Chromatogr B 856(1–2):35–40
Shah Y, Iqbal Z, Ahmad L, Khan A, Khan MI, Nazir S, Nasir F (2011) Simultaneous determination of rosuvastatin and atorvastatin in human serum using RP-HPLC/UV detection: method development, validation and optimization of various experimental parameters. J Chromatogr B 879(9–10):557–563
Narapusetti A, Bethanabhatla SS, Sockalingam A, Repaka N, Saritha V (2015) Simultaneous determination of rosuvastatin and amlodipine in human plasma using tandem mass spectrometry: application to disposition kinetics. J Adv Res 6(6):931–940
Caglar S, Toker S (2012) Determination of rosuvastatin at picogram level in serum by fluorimetric derivatization with 9-anthryldiazomethane using HPLC. J Chromatogr Sci 51(1):53–58
Patel H, Rathod R, Dash RP, Nivsarkar M (2014) Simultaneous quantification of rosuvastatin and fenofibric acid by HPLC-UV in rat plasma and its application to pharmacokinetic study. J Liq Chromatogr Relat Technol 37(12):1673–1684
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 2139 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mirzapour, H., Panahi, H.A., Moniri, E. et al. Magnetic nanoparticles modified with organic dendrimers containing methyl methacrylate and ethylene diamine for the microextraction of rosuvastatin. Microchim Acta 185, 440 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2956-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2956-6