Abstract
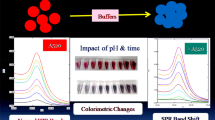
A colorimetric method is presented for the determination of the antibiotic ofloxacin (OFL) in aqueous solution. It is based on the use of an aptamer and gold nanoparticles (AuNPs). In the absence of OFL, the AuNPs are wrapped by the aptamer and maintain dispersed even at the high NaCl concentrations. The solution with colloidally dispersed AuNPs remains red and has an absorption peak at 520 nm. In the presence of OFL, it will bind to the aptamer which is then released from the AuNPs. Hence, AuNPs will aggregate in the salt solution, and color gradually turns to blue, with a new absorption peak at 650 nm. This convenient and specific colorimetric assay for OFL has a linear response in the 20 to 400 nM OFL concentration range and a 3.4 nM detection limit. The method has a large application potential for OFL detection in environmental and biological samples.

Schematic of a sensitive and simple colorimetric aptasensor for ofloxacin (OFL) detection in tap water and synthesic urine. The assay is based on the salt-induced aggregation of gold nanoparticles which results in a color change from red to purple.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballesteros O, Vílchez JL, Navalón A (2002) Determination of the antibacterial ofloxacin in human urine and serum samples by solid-phase spectrofluorimetry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 30(4):1103–1110
Gao L, Shi Y, Li W, Liu J, Cai Y (2015) Occurrence and distribution of antibiotics in urban soil in Beijing and Shanghai, China. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 22(15):11360–11371
Heberer T, Massmann G, Fanck B, Taute T, Dünnbier U (2008) Behaviour and redox sensitivity of antimicrobial residues during bank filtration. Chemosphere 73(4):451–460
Francis PS, Adcock JL (2005) Chemiluminescence methods for the determination of ofloxacin. Anal Chim Acta 541:3–12
Sun HW, He P, Lv YK, Liang SX (2007) Effective separation and simultaneous determination of seven fluoroquinolones by capillary electrophoresis with diode-array detector. J Chromatogr B 852:145–151
Timofeeva I, Timofeev S, Moskvin L, Bulatov A (2016) A dispersive liquid-liquid microextraction using a switchable polarity dispersive solvent. Automated HPLC–FLD determination of ofloxacin in chicken meat. Anal Chim Acta 949:35–42
Wu F, Xu F, Chen L, Jiang B, Sun W, Wei X (2016) Cuprous oxide/nitrogen-doped graphene nanocomposites as electrochemical sensors for ofloxacin determination. Chem Res Chin Univ 32(3):468–473
Wong A, Silva TA, Vicentini FC, Fatibello-Filho O (2016) Electrochemical sensor based on graphene oxide and ionic liquid for ofloxacin determination at nanomolar levels. Talanta 161:333–341
Jiang Z, Liu Q, Tang Y, Zhang M (2017) Electrochemical sensor based on a novel Pt−Au bimetallic nanoclusters decorated on reduced graphene oxide for sensitive detection of ofloxacin. Electroanal 29(2):602–608
Mao B, Qu F, Zhu S, You J (2016) Fluorescence turn-on strategy based on silver nanoclusters–Cu2+ system for trace detection of quinolones. Sensors Actuators B Chem 234:338–344
Chan KP, Chu KO, Lai WW–K, Choy KW, Wang CC, Lam DS–C, Pang CP (2006) Determination of ofloxacin and moxifloxacin and their penetration in human aqueous and vitreous humor by using high-performance liquid chromatography fluorescence detection. Anal Biochem 353(1):30–36
Amoli-Diva M, Pourghazi K, Hajjaran S (2016) Dispersive micro–solid phase extraction using magnetic nanoparticle modified multi-walled carbon nanotubes coupled with surfactant-enhanced spectrofluorimetry for sensitive determination of lomefloxacin and ofloxacin from biological samples. Mater Sci Eng C 60:30–36
Zhan X, Hu G, Wagberg T, Zhan S, Xu H, Zhou P (2016) Electrochemical aptasensor for tetracycline using a screen-printed carbon electrode modified with an alginate film containing reduced graphene oxide and magnetite (Fe3O4) nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(2):723–729
Ellington AD, Szostak JW (1990) In vitro selection of RNA molecules that bind specific ligands. Nature 346(6287):818–822
Tuerk C, Gold L (1990) Systematic evolution of ligands by exponential enrichment: RNA ligands to bacteriophage T4 DNA polymerase. Science 249(4968):505–510
Ni X, Xia B, Wang L, Ye J, Du G, Feng H, Zhou X, Zhang T, Wang W (2017) Fluorescent aptasensor for 17β–estradiol determination based on gold nanoparticles quenching the fluorescence of rhodamine B. Anal Biochem 523:17–23
Nikolaus N, Strehlitz B (2014) DNA-aptamers binding aminoglycoside antibiotics. Sensors 14(2):3737–3755
Charbgoo F, Soltani F, Taghdisi SM, Abnous K, Ramezani M (2016) Nanoparticles application in high sensitive aptasensor design. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 85:85–97
Priyadarshini E, Pradhan N (2017) Gold nanoparticles as efficient sensors in colorimetric detection of toxic metal ions: a review. Sensors Actuators B Chem 238:888–902
He L, Luo Y, Zhi W, Wu Y, Zhou P (2013) A colorimetric aptamer biosensor based on gold nanoparticles for the ultrasensitive and specific detection of tetracycline in milk. Aust J Chem 66(4):485–490
Du G, Zhang D, Xia B, Xu L, Wu S, Zhan S, Ni X, Zhou X, Wang L (2016) A label–free colorimetric progesterone aptasensor based on the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 183(7):2251–2258
Zhang D, Yang J, Ye J, Xu L, Xu H, Zhan S, Xia B, Wang L (2016) Colorimetric detection of bisphenol A based on unmodified aptamer and cationic polymer aggregated gold nanoparticles. Anal Biochem 499:51–56
Ramezani M, Danesh NM, Lavaee P, Abnous K, Taghdisi SM (2015) A novel colorimetric triple–helix molecular switch aptasensor for ultrasensitive detection of tetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 70:181–187
Liu J, Lu Y (2003) A colorimetric lead biosensor using DNAzyme–directed assembly of gold nanoparticles. J Am Chem Soc 125(22):6642–6643
Xiong W, Zhou L, Liu S (2016) Development of gold–doped carbon foams as a sensitive electrochemical sensor for simultaneous determination of Pb (II) and Cu (II). Chem Eng J 284:650–656
Vilela D, González MC, Escarpa A (2012) Sensing colorimetric approaches based on gold and silver nanoparticles aggregation: chemical creativity behind the assay. A review. Anal Chim Acta 751:24–43
Liu J, Lu Y (2006) Preparation of aptamer-linked gold nanoparticle purple aggregates for colorimetric sensing of analytes. Nat Protoc 1(1):246–252
Kim YS, Kim JH, Kim IA, Lee SJ, Jurng J, Gu MB (2010) A novel colorimetric aptasensor using gold nanoparticle for a highly sensitive and specific detection of oxytetracycline. Biosens Bioelectron 26(4):1644–1649
Reinemann C, von Fritsch UF, Rudolph S, Strehlitz B (2016) Generation and characterization of quinolone-specific DNA aptamers suitable for water monitoring. Biosens Bioelectron 77:1039–1047
Pilehvar S, Reinemann C, Bottari F, Vanderleyden E, Van Vlierberghe S, Blust R, Strehlitz B, De Wael K (2017) A joint action of aptamers and gold nanoparticles chemically trapped on a glassy carbon support for the electrochemical sensing of ofloxacin. Sensors Actuators B Chem 240:1024–1035
Cai Y, Cai Y, Mou S, Lu Y (2006) High performance liquid chromatography-ultraviolet photometric detection for the simultaneous determination of cephalosporins in human urine and bovine milk. Chin J Anal Chem 34(6):745–748
Wang L, Liu X, Hu X, Song S, Fan C (2006) Unmodified gold nanoparticles as a colorimetric probe for potassium DNA aptamers. Chem Commun 36:3780–3782
Wu Y, Zhan S, Xing H, He L, Xu L, Zhou P (2012) Nanoparticles assembled by aptamers and crystal violet for arsenic (III) detection in aqueous solution based on a resonance Rayleigh scattering spectral assay. Nanoscale 4(21):6841–6849
Zhao W, Brook MA, Li Y (2008) Design of gold nanoparticle-based colorimetric biosensing assays. Cheminform 39(52):2363–2371
Liu X, Tian Q, Lin T, Ke–Qian X (2012) Nanogold labeling–stepwise silver staining method for rapid detection of staphylococcus aureus. Chin J Biochem Mol Biol 7:015
Acknowledgements
This work was sponsored by Shanghai Pujiang Program (No. 16PJD026), the National Key Research and Development Program of China (2017YFD0800704), and the Natural Science Foundation of Zhejiang Province (LY18B070029).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 190 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, X., Wang, L., Shen, G. et al. Colorimetric determination of ofloxacin using unmodified aptamers and the aggregation of gold nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 185, 355 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2895-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2895-2