Abstract
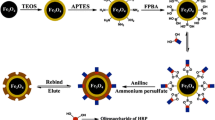
The authors introduce a new kind of surface artificial biomimetic receptor, referred to as aptameric imprinted polymer (AIP), for separation of biological macromolecules. Highly dispersed magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) were coated with silica and then functionalized with methacrylate groups via silane chemistry. The aptamer was covalently immobilized on the surface of nanoparticles via a “thiol-ene” click reaction. Once the target analyte (bovine serum albumin; BSA) has bound to the aptamer, a polymer is created by 2-dimensional copolymerization of short-length poly(ethylene glycol) and (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane. Following removal of BSA from the polymer, the AIP-MNPs presented here can selectively capture BSA with a specific absorbance (κ) as high as 65. When using this AIP, the recovery of BSA from spiked real biological samples is >97%, and the adsorption capacity is as high as 146 mg g−1. In our perception, this method has a wide scope in that it may be applied to the specific extraction of numerous other biomolecules.

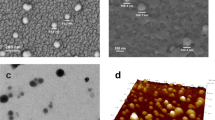
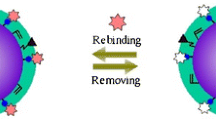
Schematic presentation of the AIP (aptamer-imprinted polymer) introduced here. The surface of silica coated magnetic nanoparticles is modified with a polymer that is covalently modified with an aptamer against bovine serum albumin (BSA).







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rezaei B, Mirahmadi-Zare S (2011) Nanoscale manipulation of prednisolone as electroactive configuration using molecularly imprinted-multiwalled carbon nanotube paste electrode. Electroanalysis 23(11):2724–2734
Whitcombe MJ, Chianella I, Larcombe L, Piletsky SA, Noble J, Porter R, Horgan A (2011) The rational development of molecularly imprinted polymer-based sensors for protein detection. Chem Soc Rev 40(3):1547–1571
Bossi A, Bonini F, Turner A, Piletsky S (2007) Molecularly imprinted polymers for the recognition of proteins: the state of the art. Biosens Bioelectron 22(6):1131–1137
Zhou X, Li W, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2007) Recent advances in the study of protein imprinting. Sep Purif Rev 36(4):257–283
Gao R, Kong X, Wang X, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2011) Preparation and characterization of uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymers functionalized with core–shell magnetic nanoparticles for the recognition and enrichment of protein. J Mater Chem 21(44):17863–17871
Gai Q-Q, Qu F, Zhang T, Zhang Y-K (2011) The preparation of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted superparamagnetic polymer with the assistance of basic functional monomer and its application for protein separation. J Chromatogr A 1218(22):3489–3495
Lin Z, Xia Z, Zheng J, Zheng D, Zhang L, Yang H, Chen G (2012) Synthesis of uniformly sized molecularly imprinted polymer-coated silica nanoparticles for selective recognition and enrichment of lysozyme. J Mater Chem 22(34):17914–17922
Li L, He X, Chen L, Zhang Y (2009) Preparation of core-shell magnetic molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles for recognition of bovine hemoglobin. Chem Asian J 4(2):286–293
Zhou W-H, Lu C-H, Guo X-C, Chen F-R, Yang H-H, Wang X-R (2010) Mussel-inspired molecularly imprinted polymer coating superparamagnetic nanoparticles for protein recognition. J Mater Chem 20(5):880–883
Lu C-H, Zhang Y, Tang S-F, Fang Z-B, Yang H-H, Chen X, Chen G-N (2012) Sensing HIV related protein using epitope imprinted hydrophilic polymer coated quartz crystal microbalance. Biosens Bioelectron 31(1):439–444
Nishino H, Huang CS, Shea KJ (2006) Selective protein capture by epitope imprinting. Angew Chem Int Ed 45(15):2392–2396
Tai D-F, Lin C-Y, Wu T-Z, Chen L-K (2005) Recognition of dengue virus protein using epitope-mediated molecularly imprinted film. Anal Chem 77(16):5140–5143
Yang Y-Q, He X-W, Wang Y-Z, Li W-Y, Zhang Y-K (2014) Epitope imprinted polymer coating CdTe quantum dots for specific recognition and direct fluorescent quantification of the target protein bovine serum albumin. Biosens Bioelectron 54:266–272
Kempe M, Glad M, Mosbach K (1995) An approach towards surface imprinting using the enzyme ribonuclease a. J Mol Recognit 8(1–2):35–39
Poma A, Guerreiro A, Whitcombe MJ, Piletska EV, Turner AP, Piletsky SA (2013) Solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymer nanoparticles with a reusable template–“plastic antibodies”. Adv Funct Mater 23(22):2821–2827
Poma A, Guerreiro A, Caygill S, Moczko E, Piletsky S (2014) Automatic reactor for solid-phase synthesis of molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (MIP NPs) in water. RSC Adv 4(8):4203–4206
Kan X, Zhao Q, Shao D, Geng Z, Wang Z, Zhu J-J (2010) Preparation and recognition properties of bovine hemoglobin magnetic molecularly imprinted polymers. J Phys Chem B 114(11):3999–4004
Gai Q-Q, Qu F, Liu Z-J, Dai R-J, Zhang Y-K (2010) Superparamagnetic lysozyme surface-imprinted polymer prepared by atom transfer radical polymerization and its application for protein separation. J Chromatogr A 1217(31):5035–5042
Mirahmadi-Zare SZ, Allafchian A, Aboutalebi F, Shojaei P, Khazaie Y, Dormiani K, Lachinani L, Nasr-Esfahani M-H (2016) Super magnetic nanoparticles NiFe2O4, coated with aluminum–nickel oxide sol-gel lattices to safe, sensitive and selective purification of his-tagged proteins. Protein Expr Purif 121:52–60
Poma A, Brahmbhatt H, Pendergraff HM, Watts JK, Turner NW (2015) Generation of novel hybrid aptamer–molecularly imprinted polymeric nanoparticles. Adv Mater 27(4):750–758
Liu X, Ren J, Su L, Gao X, Tang Y, Ma T, Zhu L, Li J (2017) Novel hybrid probe based on double recognition of aptamer-molecularly imprinted polymer grafted on upconversion nanoparticles for enrofloxacin sensing. Biosens Bioelectron 87:203–208
Brahmbhatt H, Poma A, Pendergraff H, Watts J, Turner N (2016) Improvement of DNA recognition through molecular imprinting: hybrid oligomer imprinted polymeric nanoparticles (oligoMIP NPs). Biomater Sci 4(2):281–287
Wang Z, J-c Z, H-z L, H-y C (2015) Aptamer-based organic-silica hybrid affinity monolith prepared via “thiol-ene” click reaction for extraction of thrombin. Talanta 138:52–58
Hui C, Shen C, Yang T, Bao L, Tian J, Ding H, Li C, Gao H-J (2008) Large-scale Fe 3O 4 nanoparticles soluble in water synthesized by a facile method. J Phys Chem C 112(30):11336–11339
Stöber W, Fink A, Bohn E (1968) Controlled growth of monodisperse silica spheres in the micron size range. J Colloid Interface Sci 26(1):62–69
Kryscio DR, Peppas NA (2012) Surface imprinted thin polymer film systems with selective recognition for bovine serum albumin. Anal Chim Acta 718:109–115
Kim K-M, Kim HM, Lee W-J, Lee C-W, T-i K, Lee J-K, Jeong J, Paek S-M, Oh J-M (2014) Surface treatment of silica nanoparticles for stable and charge-controlled colloidal silica. Int J Nanomedicine 9(Suppl 2):29
Ruff P, Pai RB, Storici F (2012) Real-time PCR-coupled CE-SELEX for DNA aptamer selection. ISRN Mol Biol 2012:1–9
Ye L, Cormack PA, Mosbach K (1999) Molecularly imprinted monodisperse microspheres for competitive radioassay. Anal Commun 36(2):35–38
Li X, Zhang B, Li W, Lei X, Fan X, Tian L, Zhang H, Zhang Q (2014) Preparation and characterization of bovine serum albumin surface-imprinted thermosensitive magnetic polymer microsphere and its application for protein recognition. Biosens Bioelectron 51:261–267
Xue Z, Xi-Wen H, Lang-Xing C, Wen-You L, ZHANG Y-K (2009) Optimum conditions of separation selectivity based on molecularly imprinted polymers of bovine serum albumin formed on surface of Aminosilica. Chin J Anal Chem 37(2):174–180
Ran D, Wang Y, Jia X, Nie C (2012) Bovine serum albumin recognition via thermosensitive molecular imprinted macroporous hydrogels prepared at two different temperatures. Anal Chim Acta 723:45–53
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial support from the National Elite’s Foundation (BMN) and Iran National Science Foundation (INSF).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The author(s) declare that they have no competing interests.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 367 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shoghi, E., Mirahmadi-Zare, S.Z., Ghasemi, R. et al. Nanosized aptameric cavities imprinted on the surface of magnetic nanoparticles for high-throughput protein recognition. Microchim Acta 185, 241 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2745-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-018-2745-2