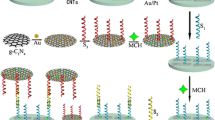
Abstract
We report on a disposable microdevice suitable for sandwich-type electrochemiluminescence (ECL) detection of DNA. The method is making use of CdTe quantum dots functionalized with hierarchical nanoporous PtFe (CdTe@PtFe) nanoparticles and with magnetic graphene nanosheets. The latter were selected as carriers for the capture DNA due to their excellent biomagnetic separation capability and electrical properties. The CdTe@PtFe nanoparticles were used to label the signal DNA which resulted in distinctly enhanced ECL owing to the large specific surface area and good electrical conductivity of the PtFe alloy. A DNA sensor was constructed on a disk-shaped indium tin oxide electrode that was fabricated via etching. Under optimal conditions, the biosensor responds linearly to DNA in the 0.02 fM to 5000 fM concentration range, with a detection limit as low as 15 aM. The electrode is regenerable. The method displays excellent specificity, extremely good sensitivity, and is highly reproducible.

CdTe quantum dots functionalized hierarchical nanoporous PtFe alloy (CdTe@PtFe) and magnetic graphene nanosheet (MGN) were applied for sensitive sandwich-type electrochemiluminescence DNA detection based on a disposable microdevice. The method displays excellent specificity, extremely good sensitivity, and is highly reproducible.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Huang J, Wu YR, Chen Y, Zhu Z, Yang XH, Yang CYJ, Wang KM, Tan WH (2011) Pyrene-excimer probes based on the hybridization chain reaction for the detection of nucleic acids in complex biological fluids. Angew Chem Int Ed 50:401–404
Dong HF, Gao WC, Yan F, Ji HX, Ju HX (2010) Fluorescence resonance energy transfer between quantum dots and graphene oxide for sensing biomolecules. Anal Chem 82:5511–5517
Zhang YY, Tang ZW, Wang J, Wu H, Maham AH, Lin YH (2010) Hairpin DNA switch for ultrasensitive spectrophotometric detection of DNA hybridization based on gold nanoparticles and enzyme signal amplification. Anal Chem 82:6440–6446
Sanborn ME, Connolly BK, Gurunathan K, Levitus MJ (2007) Fluorescence properties and photophysics of the sulfoindocyanine Cy3 linked covalently to DNA. J Phys Chem B 111:11064–11074
Cai S, Xin L, Lau CW, Lu JZ (2010) Highly sensitive non-stripping gold nanoparticles-based chemiluminescent detection of DNA hybridization coupled to magnetic beads. Analyst 135:615–620
Fojta M, Kostecka P, Trefulka MR, Havran L, Palecek E (2007) “Multicolor” electrochemical labeling of DNA hybridization probes with osmium tetroxide complexes. Anal Chem 79:1022–10029
Zhou H, Liu J, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2011) Ultrasensitive DNA detection based on Au nanoparticles and isothermal circular double-assisted electrochemiluminescence signal amplification. Chem Commun 47:8358–8360
Zou GZ, Ju HX, Ding WP, Chen HY (2005) J. Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe hollow spherical assemblies in aqueous system by immobilization in carbon paste. Electroanal Chem 579:175–180
Lin DJ, Wu J, Wang M, Yan F, Ju HX (2012) Triple signal amplification of graphene film, polybead carried gold nanoparticles as tracing tag and silver deposition for ultrasensitive electrochemical immunosensing. Anal Chem 84:3662–3668
Liu DY, Xin YY, He XW, Yin XB (2011) A sensitive, non-damaging electrochemiluminescent aptasensor via a low potential approach at DNA-modified gold electrodes. Analyst 136:479–485
Shan Y, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2009) Distance-dependent quenching and enhancing of electrochemiluminescence from a CdS: Mn nanocrystal film by Au nanoparticles for highly sensitive detection of DNA. Chem Commun 0: 905–907
Zhou H, Zhang YY, Liu J, Xu JJ, Chen HY (2013) Efficient quenching of electrochemiluminescence from K-doped graphene–CdS:Eu NCs by G-quadruplex–hemin and target recycling-assisted amplification for ultrasensitive DNA biosensing. Chem Commun 49:2246–2248
Jie GF, Wang L, Zhang SS (2011) Magnetic electrochemiluminescent Fe3O4/CdSe–CdS nanoparticle/polyelectrolyte nanocomposite for highly efficient immunosensing of a cancer biomarker. Chem Eur J 17:641–648
Giliohann D, Mirkin C (2009) Drivers of biodiagnostic development. Nature 462:461–464
Xu CX, Li Q, Liu YQ, Wang JP, Geng HR (2012) Hierarchical nanoporous PtFe alloy with multimodal size distributions and its catalytic performance toward methanol electrooxidation. Langmuir 28:1886–1892
Shen QM, Zhao XM, Zhou SW, Hou WH, Zhu JJ (2011) ZnO/CdS hierarchical nanospheres for photoelectrochemical sensing of Cu2+. J Phys Chem C 115:17958–17964
Wang SW, Zhang Y, Yu JH, Song XR, Ge SG, Yan M (2012) Application of indium tin oxide device in gold-coated magnetic iron solid support enhanced electrochemiluminescent immunosensor for determination of carcinoma embryonic antigen. Sensors Actuators B 171–172:891–898
Im K, Cho K, Kim J, Kim S (2010) Transparent heaters based on solution-processed indium tin oxide nanoparticles. Thin Solid Films 518:3960–3963
Li CF, Fu ZF, Li ZY, Wang ZX, Wei W (2011) Cross-talk-free multiplexed immunoassay using a disposable electrochemiluminescent immunosensor array coupled with a non-array detector. Biosens Bioelectron 27:141–147
Metters JP, Kadara RO, Banks CE (2011) New directions in screen printed electro-analytical sensors: an overview of recent developments. Analyst 136:1067–1076
Zen JM, Song YS, Chung HH, Hsu CT, Senthil Kumar A (2002) Oxygen sensor using copper-plated screen-printed carbon electrodes. Anal Chem 74:6126–6130
Chen YT, Jiang YY, Lin ZY, Sun JJ, Zhang L, Chen GN (2009) Fabrication of an electrically heated indium-tin-oxide electrode for electrochemiluminescent detection system. Analyst 134:731–737
He HK, Gao C (2010) Supraparamagnetic, conductive, and processable multifunctional graphene nanosheets coated with high-density Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Appl Mater Interfaces 2:3201–3210
Li D, Muller MB, Gilje S, Kaner RB, Wallace GG (2008) Processable aqueous dispersions of graphene nanosheets. Nat Nanotechnol 3:101–105
Gaponik N, Talapin DV, Rogach AL, Hoppe K, Shevchenko EV, Kornowski A, Eychmüller A, Weller H (2002) J Phys Chem B 106:7177–7185
Xu J, Hua K, Sun G, Wang C, Lv X, Wan Y (2006) Electrooxidation of methanol on carbon nanotubes supported Pt–Fe alloy electrode. Electrochem Commun 8:982–986
Mandal S, Roy D, Chaudhari RV, Sastry M (2004) Pt and Pd nanoparticles immobilized on amine-functionalized zeolite: excellent catalysts for hydrogenation and heck reactions. Chem Mater 16:3714–3724
Rolison DR (2003) Catalytic nanoarchitectures–the importance of nothing and the unimportance of periodicity. Science 299:1698–1701
Liu S, Li C, Cheng J, Zhou Y (2006) Selective photoelectrochemical detection of DNA with high-affinity metallointercalator and tin oxide nanoparticle electrode. Anal Chem 78:4722–4726
Peng H, Soeller C, Vigar N, Caprio V, Travas-Sejdic J (2007) Label-free detection of DNA hybridization based on a novel functionalized conducting polymer. Biosens Bioelectron 22:1868–1873
Patolsky F, Lichtenstein A, Willner I (2000) Electrochemical transduction of liposome-amplified DNA sensing. Angew Chem Int Ed 39:940–943
Park SJ, Taton TA, Mirkin CA (2002) Array-based electrical detection of DNA with nanoparticle probes. Science 295:15031506
Ding CF, Zhong H, Zhang SS (2008) Ultrasensitive flow injection chemiluminescence detection of DNA hybridization using nanoCuS tags. Biosens Bioelectron 23:1314–1318
Ding Z, Quinn BM, Haram SK, Pell LE, Korgel BA, Bard AJ (2002) Electrochemistry and electrogenerated chemiluminescence from silicon nanocrystal quantum dots. Science 296:1293–1297
Myung N, Bae Y, Bard AJ (2003) Effect of surface passivation on the electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe/ZnSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett 3:1053–1055
Myung N, Ding ZF, Bard AJ (2002) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence of CdSe nanocrystals. Nano Lett 2:1315–1319
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by Natural Science Research Foundation of China (21277058, 21175058, 21207048) and Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, China (ZR2011BQ019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(PDF 150 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, F., Deng, W., Zhang, Y. et al. Highly sensitive hybridization assay using the electrochemiluminescence of an ITO electrode, CdTe quantum dots functionalized with hierarchical nanoporous PtFe nanoparticles, and magnetic graphene nanosheets. Microchim Acta 181, 213–222 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1102-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1102-8