Abstract
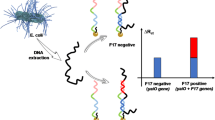
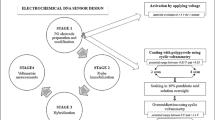
We have developed a sensitive assay for enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) by integrating DNA extraction, specific polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and DNA detection using an electrode modified with the bundle-forming pilus (bfpA) structural gene. The PCR amplified products are captured on the electrode and hybridized with biotinylated detection probes to form a sandwich hybrid containing two biotinylated detection probes. The sandwich hybridization structure significantly combined the numerous streptavidin alkaline phosphatase on the electrode by biotin-streptavidin connectors. Electrochemical readout is based on dual signal amplification by both the sandwich hybridization structure and the enzyme. The electrode can satisfactorily discriminate complementary and mismatched oligonucleotides. Under optimal conditions, synthetic target DNA can be detected in the 1 pM to 10 nM concentration range, with a detection limit of 0.3 pM. EPEC can be quantified in the 10 to 107 CFU mL−1 levels within 3.5 h. The method also is believed to present a powerful platform for the screening of pathogenic microorganisms in clinical diagnostics, food safety and environmental monitoring.

An electrochemical DNA sensor was first designed to detect a bfpA gene specifically related to the EPEC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Horner SR, Mace CR, Rothberg LJ, Miller BL (2012) A proteomic biosensor for enteropathogenic E. Coli. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1659–1663
Levine MM (1987) Escherichia coli that cause diarrhea: enterotoxigenic, enteropathogenic, enteroinvasive, enterohemorrhagic, and denteroadherent. J Infect Dis 155:377–389
Donnenberg MS, Kaper JB, Finlay BB (1997) Interactions between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and host epithelial cells. Trends Microbiol 5:109–114
Sohel I, Puente JL, Murray WJ, Varkila JV, Schoolnik GK (1993) Cloning and characterization of the bundle-forming pilin gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and its distribution in Salmonella serotypes. Mol Microbiol 7:563–575
Sur D, Bhattacharya SK (2006) Acute diarrhea diseases-an approach to management. J Indian Med Assoc 104:220–223
Li Q, Cheng W, Zhang DC, Yu TX, Yin YB, Ju HX, Ding SJ (2012) Rapid and sensitive strategy for Salmonella detection using an InvA gene- based electrochemical DNA sensor. Int J Electrochem Sci 7:844–856
Xu S (2012) Electromechanical biosensors for pathogen dectection. Microchim Acta 178:245–260
Sanvicens N, Pastells C, Pascual N, Marco MP (2009) Nanorparticle-based biosensor for detection of pathogenic bacteria. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 28:1243–1252
Roda A, Mirasoli M, Roda B, Bonvicini F, Colliva C, Reschiglian P (2012) Recent developments in rapid multiplexed bioanalytical methods for foodborne pathogenic bacteria detection. Microchim Acta 178:7–28
Bahsi ZB, Büyükaksoy A, Ölmezcan SM, Şimşek F, Aslan MH, Oral AY (2009) A novel label-free optical biosensor using synthetic oligonucleotides form E.coli O157:H7 elementary sensitivity test. Sensors 9:4890–4900
Mao XL, Yang LJ, Su XL, Li YB (2006) A nanoparticle amplification based quartz crystal microbalance DNA sensor for detection of Escherichia coli O157:H7. Biosens Bioelectron 21:1178–1185
Pathirana ST, Barbaree J, Chin BA, Hartell MG, Neely WC, Vodyanoy V (2000) Rapid and sensitive biosensor for Salmonella. Biosens Bioelectron 15:135–141
Gehring AG, Tu SI (2005) Enzyme-linked immunomagnetic electrochimdal detection of live Escherichia coli O157:H7 in apple juice. J Food Prot 68:146–149
Li SQ, Li YG, Chen HQ, Horikawa S, Shen W, Simonian A, Chin BA (2010) Direct detection of Salmonella typhimurium on fresh produce using phage-based magnetoelastic biosensors. Biosens Bioelectron 26:1313–1319
Villamizar RA, Maroto A, Rius FX, Inza I, Figueras MJ (2008) Fast detection of Salmonella infantis with carbon nanotube field effect transistors. Biosens Bioelectron 24:279–283
Liao JC, Mastali M, Li Y, Gau V, Suchard MA, Babbit J, Gornbein J, Landaw EM, Mccabe BM, Churchill ERB, Haake DA (2007) Development of an advanced electrochemical DNA biosensor for bacterial pathogen detection. J Mol Diagn 9:158–168
Salam F, Tothill IE (2009) Detection of Salmonella typhimurium using an electrochemical immunosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 24:2630–2636
Luo CH, Lei YN, Yan L, Yu TX, Li Q, Zhang DC, Ding SJ, Ju HX (2012) A rapid and sensitive aptamer-based electrochemical biosensor for direct detection of Escherichia coli O111. Electroanalysis 24:1186–1191
Li JJ, Xu M, Huang HP, Zhou JJ, Abdel-Halimb ES, Zhang JR, Zhu JJ (2011) Aptamer-quantum dots conjugates-based ultrasensitive competitive electrochemical cytosensor for the detection of tumor cell. Talanta 85:2113–2120
Du P, Li HX, Mei ZH, Liu SF (2009) Electrochemical DNA biosensor for the detection of DNA hybridization with the amplification of Au nanoparticles and CdS nanoparticles. Bioelectrochemistry 75:37–43
Ding CF, Zhao F, Zhang ML, Zhang SS (2008) Hybridization biosensor using 2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenantroline cobalt as electrochemical indicator for detection of hepatitis B virus DNA. Bioelectrochemistry 72:28–33
Wang J (2012) Electrochemical biosensing based on noble metal nanoparticles. Microchim Acta 177:245–270
Donnenberg MS, Girón JA, Nataro JP, Kaper JB (1992) A plasmid-encoded type IV fimbrial gene of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli associated with localized adhernce. Mol Microbiol 6:3427–3437
Anantha RP, Stone KD, Donnenberg MS (1998) Role of BfpF, a member of PilT family of putative nucleotide-bingd proteins, in Type IV pilus biogenesis and in interactions between enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and host cells. Infect Immun 66:122–131
Gunzburg ST, Tornieporth NG, Riley LW (1995) Identification of enteropathogenic Escherichia coli by PCR-based detection of the bundle-forming pilus gene. J Clin Microbiol 33:1375–1377
Cheng W, Ding SJ, Li Q, Yu TX, Yin YB, Ju HX, Ren GS (2012) A simple electrochemical aptasensor for ultrasensitive protein detection using cyclic target-induced primer extension. Biosens Bioelectron 36:12–17
Cheng AKH, Ge BX, Yu HZ (2007) Aptamer-based biosensors for label-free voltammetric detction of lysozyme. Anal Chem 79:5158–5164
Qian H, He L (2009) Surface-initiated activators generated by electro transfer for atom transfer radical polymerization in detection of DNA point mutation. Anal Chem 81:4536–4542
Zhang J, Chen PP, Wu XY, Chen JH, Xu LJ, Chen GN, Fu FF (2011) A signal-on electrochemiluminescence aptamer biosensor for the detection of ultratrace thrombin based on junction-probe. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2645–2650
Zhu X, Zhang YS, Yang WQ, Liu QD, Lin ZY, Qiu B, Chen GN (2011) Highly sensitive electrochemiluminescent biosensor for adenosine based on structure-switching of aptamer. Anal Chim Acta 684:121–125
Ye SJ, Li HX, Cao W (2011) Electrogenerated chemiluminescence detection of adenosine based on triplex DNA biosensor. Biosens Bioelectron 26:2215–2220
Labuda J, Ovádeková R, Galandová J (2009) DNA-based biosensor for the detection of strong damage to DNA by the quinazoline derivative as a potential anticancer agent. Microchim Acta 164:371–377
Qi XW, Gao HW, Zhang YY, Wang XZ, Chen Y, Sun W (2012) Electrochemical DNA biosensor with chitosan-Co3O4 nanorod-graphene composite for the sensitive detection of staphylococcus aureus nuc gene sequence. Bioelectrochemistry 88:42–47
Tsai TH, Thiagarajan S, Chen SM (2010) Green synthesis of silver nanoparticles using ionic liquid and application for the detection of dissolved oxygen. Electroanalysis 22:680–687
Song J, Xu JM, Zhao PS, Lu LD, Bao JC (2011) A hydrogen peroxide biosensor based on direct electron transfer from hemoglobin to an electrode modified with Nafion and activated nanocarbon. Microchim Acta 172:117–123
Li JH, Kuang DZ, Feng YL, Zhang FX, Liu MQ (2011) Voltammetric determination of bisphenol A in food package by a glassy carbon electrode modified with carboxylated. Microchim Acta 172:379–386
Sun W, Li XQ, Wang Y, Li X, Zhao CZ, Jiao K (2009) Electrochemistry of myoglobin in Nafion and multi-walled carbon nanotubes modified carbon ionic liquid electrode. Bioelectrochemistry 75:170–175
Cao W, Hu JB, Li QL, Fang WH (2009) A novel NH2/ITO ion implantation electrode:preparation characterization, and application in bioelectrochemistry. Electroanalysis 21:723–729
Sun W, Guo YQ, Li TT, Ju XM, Lou J, Ruan CX (2012) Electrochemistry of horseradish peroxidase entrapped in grapheme and dsDNA composite modified carbon ionic liquid electrode. Electrochim Acta 75:381–386
He XX, Su J, Wang YH, Wang KM, Ni XQ, Chen ZF (2011) A sensitive signal-on electrochemical assay for MTase activity using AuNPs amplification. Biosens Bioelectron 28:298–303
Botkin DJ, Galli L, Sankarapani V, Soler M, Rivas M, Torres AG (2012) Development of a multiplex PCR assay for detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli, enterohemorrhagic E. coli, and enteropathogenic E. coli strains. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 2:1–10
Persson S, Olsen KEP, Scheutz F, Krogfelt KA, Gerner-Smidt P (2007) A method for fast and simple detection of major diarrhoeagenic Escherichia coli in the routine diagnostic laboratory. Clin Microbiol Infect 13:516–524
Aranda KRS, Fabbricotti SH, Fagundes-Neto U, Scaletsky ICA (2007) Single multiplex assay to identify simultaneously enteropathogenic, enteroaggregative, enterotoxigenic, enteroinvasive and Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli strains in Brazilian children. FEMS Microbioll Lett 267:145–150
Antikainen J, Tarkka E, Haukka K, Siitonen A, Vaara M, Kirveskari J (2009) New 16-plex PCR method for rapid detection of diarrheagenic Escherichia coli directly from stool samples. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 28:899–908
Linman MJ, Sugerman K, Cheng Q (2010) Detection of low levels of Escherichia coli in fresh spinac by surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy with a TMB-based enzymatic signal enhancement method. Sensors Actuators B 145:613–619
Galikowska E, Kunikowska D, Tokarska-Pietrzak E, Dziadziuszko H, Łoś JM, Golec P, Węgrzyn G, Łoś M (2011) Specific detection of Salmonella enterica and Escherichia coli strains by using ELISA with bacteriophages as recognition agents. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 30:1067–1073
Neely E, Bell C, Finlay D, McCappin J, Wilson I, Ball HJ (2004) Development of a capture/enrichment sandwich ELISA for the rapid detection of enteropathogenic and enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O26 strains. J Appl Microbiol 97:1161–1165
Gong P, He XX, Wang KM, Tan WH, Xie WG, Wu P, Li HM (2008) Combination of functionalized nanoparticles and polymerase chain reaction-based method for SARS-CoV gene detection. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 8:293–300
Acknowledgment
This work was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21075141 and 81101638) and supported by the Special Fund Project of Chongqing Key Laboratory (CSTC).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, W., Luo, C., Zhong, L. et al. Sensitive detection of enteropathogenic E. coli using a bfpA gene-based electrochemical sensor. Microchim Acta 180, 1233–1240 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1061-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-013-1061-0