Abstract
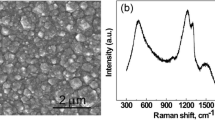
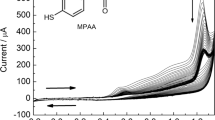
A BDD electrode modified with polyaniline (PANI) film doped with polyvinyl sulphonate (PVS), containing in-situ deposited tyrosinase (Tyr) enzyme was prepared and characterized. The PANI-PVS film was electrochemically polymerized onto the BDD surface by cyclic voltammetry (CV) at 50 mV.s−1 (versus Ag/AgCl). An increase in current density with increasing number of cycles was an indication of the polymer growth. The morphologies of the composite films were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Electrochemical characterization confirmed the successful doping of the PANI film by PVS and that the template PVS directed the electron transfer at the biosensor interface. SEM provided evidence of the influence of the synthesis medium on the morphology and surface area of the composite film. Synthesis from HCl produced homogenous, finely granular thin film with increased surface area which is thought to be responsible for the increased redox currents measured. PANI/PVS served both as an efficient mediator and biocompatible enzyme immobilisation platform for the substrate L-tyrosine at low concentrations with apparent Michaelis-Menton (\( {\hbox{K}}_{\rm{m}}^{\rm{app}} \)) 1 × 10−2 µM.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michaelson JC, McEvoy AJ, Gratzel M (1993) Electrochemical behaviour of various polyaniline morphologies in non-aqueous electrolytes. Synth Met 55–57:564
Miras MC, Barbero C, Kötz R, Haas O (1994) Voltamperommetric study of chemically made polyaniline powder with cavity microelectrode technique. J Electroanal Chem 369:399
Barbero C, Miras MC, Haas O, Kötz R (1991) Alteration of the ion exchange mechanism of an electroactive polymer by manipulation of the active site. Probe beam deflection and quartz crystal microbalance study of poly(aniline) and poly(N-methylaniline). J Electroanal Chem 310:437
Troise Frank MH, Denuault G (1994) Scanning electrochemical microscope (secm) study of the relationship between proton concentration and electronic charge as a function of ionic-strength during the oxidation of polyaniline. J Electroanal Chem 379(1–2):399–406
Pruneanu S, Csahok E, Kertész V, Inzelt G (1998) Electrochemical quartz crystal microbalance study of the influence of the solution composition on the behaviour of poly(aniline) electrodes. Electrochim Acta 16–17:2305
Focke WJ, Wneck GE, Wei Y (1987) Influence of the oxidation state, pH and counterion on conductivity of polyaniline. J Phys Chem 91:5813
Samlenski R, Haug C, Brenn R, Wild C, Locher R, Koidl P (1996) Characterisation and lattice location of nitrogen and boron in homoepitaxial CVD diamond. Diamond Relat Mater 5:947
Pleskov YV (1999) Synthetic diamond in electrochemistry. Russ Chem Rev 68:381–392
Zheng L, Xiong L, Liu C, Jin L (2006) Electrochemical synthesis of a novel sulfonated polyaniline and its electrochemical properties. Eur Polym J 42:2328
Shah AHA, Holze R (2008) Spectroelectrochemistry of two-layered composites of polyaniline and poly (o-aminophenol). Electrochim Acta 53:4642–4653
Ndangili PM, Waryo TT, Muchindu M, Baker PGL, Ngila CJ, Iwuoha EI (2009) Ferrocenium hexafluorophosphate-induced nanofibrillarity of polyaniline–polyvinyl sulfonate electropolymer and application in an amperometric enzyme biosensor. Electrochim Acta. doi:10.1016/j.electacta.2009.04.058
Granger MC, Witek M, Xu J, Wang J, Hupert M, Hanks A, Koppang MD, Butler JE, Lucazeau G, Mermoux M, Strojek JW, Swain GM (2000) Standard electrochemical behavior of high-quality, boron-doped polycrystalline diamond thin-film electrodes. Anal Chem 72(16):3793–37804
Holt KB, Bard AJ, Show Y, Swain GM (2004) Scanning electrochemical microscopy and conductive probe atomic force microscopy studies of hydrogen-terminated boron-doped diamond electrodes with different doping levels. J Phys Chem B 108(39):15117–15127
Fischer AE, Show Y, Swain GM (2004) Electrochemical performance of diamond thin-film electrodes from different commercial sources. Anal Chem 76:2553–2560
Honda K, Noda T, Yoshimura M, Nakagawa K, Fujishima A (2004) microstructural heterogeneity for electrochemical activity in polycrystalline diamond thin films observed by electrogenerated chemiluminescence imaging. J Phys Chem B 108(41):16117–16127
Troupe CE, Drummond IC, Graham C, Grice J, John P, Wilson JIB, Jubber NG, Morrison NA (1998) Diamond-based glucose sensors. Diamond Relat Mater 7:575–580
Su L, Qiu X, Guo L, Zhang F, Tung C (2004) Amperometric glucose sensor based on enzyme-modified boron-doped diamond electrode by cross-liking method. Sens Actuators B 99:499–504
Tatsuma T, Mori H, Fujishima A (2000) Electron transfer from diamond electrodes to heme peptide and peroxidise. Anal Chem 72:2919–2924
Rao TN, Yagi I, Miwa T, Tryk DA, Fujishima A (1999) Electrochemical oxidation of NADH at highly boron-doped diamond electrodes. Anal Chem 71:2506–2511
Zhou YL, Zhi JF (2006) The application of boron-doped diamond electrodes in amperometric biosensors. Electrochem Commun 8:1811
Iwuoha EI, de Villaverde DS, Garcia NP, Smyth MR, Pingarront JM (1997) Reactivities of organic phase biosensors. 2. The amperometric behaviour of horseradish peroxidise immobilised on a platinum electrode modified with an electrosynthetic polyaniline film. Biosens Bioelectron 12(8):749–761
Kazimierska E, Muchindu M, Morrin A, Iwuoha EI, Smyth MR, Killard AJ (2009) The fabrication of structurally multiordered polyaniline films and their application in electrochemical sensing and biosensing. Electroanalysis 21(3–5):595–603
Al-Ahmed A, Ndangili P, Jahed N, Baker PGL, Iwuoha EI (2009) Polyester sulphonic acid interstitial nanocomposite platform for peroxide biosensor. Sensors 9:9965
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
(DOC 130 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangombo, Z.A., Baker, P., Iwuoha, E. et al. Tyrosinase biosensor based on a boron-doped diamond electrode modified with a polyaniline-poly(vinyl sulfonate) composite film. Microchim Acta 170, 267–273 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0378-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-010-0378-1