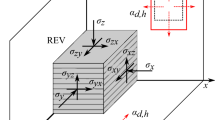
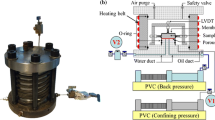
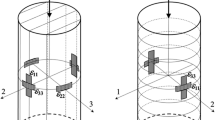
Abstract
Complex coupled thermo-hydromechanical (THM) loading paths are expected to occur in clay rocks which serve as host formations for geological radioactive waste repositories. Exothermic waste packages heat the rock, causing thermal strains and temperature induced pore pressure build-up. The drifts are designed in such a way as to limit these effects. One has to anticipate failure and fracturing of the material, should pore pressures exceed the tensile resistance of the rock. To characterise the behaviour of the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone (COx) under effective tension and to quantify the tensile failure criterion, a laboratory program is carried out in this work. THM loading paths which correspond to the expected in situ conditions are recreated in the laboratory. To this end, a special triaxial system was developed, which allows the independent control of radial and axial stresses, as well as of pore pressure and temperature of rock specimens. More importantly, the device allows one to maintain axial effective tension on a specimen. Saturated cylindrical claystone specimens were tested in undrained conditions under constrained lateral deformation and under nearly constant axial stress. The specimens were heated until the induced pore pressures created effective tensile stresses and ultimately fractured the material. The failure happened at average axial effective tensile stresses around 3.0 MPa. Fracturing under different lateral total stresses allows one to describe the failure with a Hoek–Brown or Fairhurst’s generalized Griffith criterion. Measured axial extension strains are analysed based on a transversely isotropic thermo-poroelastic constitutive model, which is able to satisfactorily reproduce the observed behaviour.
Highlights
-
Thermal pressurization of clay rock in deep radioactive waste repositories can reduce the effective stresses, which can lead to damage or failure.
-
Our novel laboratory triaxial device is able mimic in situ conditions: Constant vertical total stress, zero lateral deformation and thermal pressurization.
-
Pore pressure increase, vertical extension strains and thermal pressurization failure were recorded in a series of tests on Callovo-Oxfordian claystone specimens.
-
The effective tensile strength was reached at values around 3 MPa in tension and temperatures between 53 and 64 °C, creating sub-horizontal fractures.
-
The experimental responses can be well reproduced using a thermo-poroelasticity model.
-
Hoek–Brown and Fairhurst generalized Griffith criteria appear suitable to account for the rock's tensile resistance.











Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- h :
-
Direction parallel to bedding
- z :
-
Direction perpendicular to bedding
- \(\sigma _{i}\) :
-
Total stress in direction i
- \(\sigma '_{i}\) :
-
Terzaghi effective stress in direction i
- \(\varepsilon _i\) :
-
Strain in direction i
- \(\sigma _c\) :
-
Unconfined compressive strength
- \(\sigma _t\) :
-
Tensile strength
- \(E_i\) :
-
Young’s modulus in direction i
- \(\nu _i\) :
-
Poisson’s ratio in direction i
- \(m_i\) :
-
Hoek–Brown criterion parameter
- \(\phi\) :
-
Porosity
- \(\rho\) :
-
Wet density
- \(\rho _d\) :
-
Dry density
- w :
-
Water content
- \(S_r\) :
-
Degree of saturation
- s :
-
Suction
- \(p_f\) :
-
Pore pressure
- T :
-
Temperature
- \(\sigma\) :
-
Isotropic confining pressure
- \(\varepsilon _\mathrm{hyd}\) :
-
Volumetric hydration swelling
- \(\gamma _t\) :
-
Fracture angle with respect to bedding
- \(C_{ij}\) :
-
Elastic compliance matrix
- \(b_i\) :
-
Biot’s coefficient in direction i
- \(\alpha _{d,i}\) :
-
Drained thermal expansion coefficient in direction i
- \(G'\) :
-
Shear modulus within the isotropic plane
- G :
-
Shear modulus perpendicular to the isotropic plane
- \(\alpha _{\phi }\) :
-
Bulk thermal expansion coefficient of the pore volume
- M :
-
Biot’s modulus
- \(K_f\) :
-
Bulk modulus of the pore fluid
- \(K_{\phi }\) :
-
Bulk modulus of the pore volume
- \(\varphi\) :
-
Friction angle
- c :
-
Cohesion
- \(V_L\) :
-
Volume of the drainage system
- \(c_L\) :
-
Compressibility of the drainage system with respect to fluid pressure
- \(p_L\) :
-
Fluid pressure within the drainage system
- \(\kappa _L\) :
-
Compressibility of the drainage system with respect to radial confining pressure
- \(\sigma _\mathrm{rad}\) :
-
Radial confining pressure
- \(\alpha _L\) :
-
Bulk thermal expansion coefficient of the drainage system
- \(M_s\) :
-
Fluid mass within the specimen
- \(m_f\) :
-
Fluid mass per unit volume of the specimen
- \(V_s\) :
-
Total specimen volume
- \(M_L\) :
-
Fluid mass within the drainage system
- \(\rho _L\) :
-
Fluid density within the drainage system
- \(\rho _f\) :
-
Pore fluid density
- \(c_f\) :
-
Pore fluid compressibility
- \(\alpha _f\) :
-
Pore fluid bulk thermal expansion coefficient
References
Abuel-Naga HM, Bergado DT, Bouazza A (2007) Thermally induced volume change and excess pore water pressure of soft Bangkok clay. Eng Geol 89(1–2):144–154
Aichi M, Tokunaga T (2012) Material coefficients of multiphase thermoporoelasticity for anisotropic micro-heterogeneous porous media. Int J Solids Struct 49(23–24):3388–3396
Akazawa T (1943) New test method for evaluating internal stress due to compression of concrete (the splitting tension test) (part 1). J Jpn Civ Eng Inst 29:777–787
Andra (2005) Dossier 2005 Argile: Evaluation of the feasibility of a geological repository in an argillaceous formation. https://international.andra.fr/sites/international/files/2019-03/3-%20Dossier%202005%20Argile%20Synthesis%20-%20Evaluation%20of%20the%20feasibility%20of%20a%20geological%20repository%20in%20an%20argillaceous%20formation_0.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2022
Armand G, Dewonck S, Bosgiraud JM, Richard-Panot L (2015) Development and new research program in the Meuse Haute-Marne Underground Research Laboratory (France). In: Proceedings of the 13th ISRM International Congress of Rock Mechanics, vol 1, Montreal, Canada, pp. 1–15
Armand G, Bumbieler F, Conil N, de la Vaissière R, Bosgiraud JM, Vu MN (2017) Main outcomes from in situ thermo-hydro-mechanical experiments programme to demonstrate feasibility of radioactive high-level waste disposal in the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9(3):415–427. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2017.03.004
Auvray C, Giot R, Giraud A (2015) Caractérisation géomécanique sur échantillons - Essais de traction indirecte, Andra report. Tech. rep
Baldi G, Hueckel T, Pellegrini R (1988a) Thermal volume changes of the mineral-water system in low-porosity clay soils. Can Geotech J 25(4):807–825
Baldi G, Hight DW, Thomas GE (1988b) A reevaluation of conventional triaxial test methods. In: Advanced triaxial testing of soil and rock, ASTM STP (977), pp 219–263
Bažant ZP (1984) Size effect in blunt fracture: concrete, rock, metal. J Eng Mech 110(4):518–535. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)0733-9399(1984)110:4(518)
Belmokhtar M, Delage P, Ghabezloo S, Conil N (2017a) Thermal volume changes and creep in the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(9):2297–2309
Belmokhtar M, Delage P, Ghabezloo S, Tang AM, Menaceur H, Conil N (2017b) Poroelasticity of the Callovo-Oxfordian Claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(4):871–889
Belmokhtar M, Delage P, Ghabezloo S, Conil N (2018) Drained triaxial tests in low-permeability shales: application to the Callovo-Oxfordian Claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 51(7):1979–1993
Biot MA, Willis DG (1957) The elastic coefficients of the theory of consolidation. J Appl Mech 24:594–601
Bossart P (2011) Characteristics of the Opalinus Clay at Mont Terri Project. Wabern Switz 3:26
Brace WF (1964) Brittle fracture of rocks. In: State of stress in the Earths Crust, Rudd WR Publisher: Elsevier, New York, pp 111–174
Braun P, Ghabezloo S, Delage P, Sulem J, Conil N (2019) Determination of multiple thermo-hydro-mechanical rock properties in a single transient experiment: application to shales. Rock Mech Rock Eng 52:2023–2038
Braun P, Delage P, Ghabezloo S, Sulem J, Conil N (2020) Effect of anisotropy on the thermal volume changes of the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Géotech Lett 10(1):63–66. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgele.19.00045
Braun P, Ghabezloo S, Delage P, Sulem J, Conil N (2021a) Thermo-poro-elastic behaviour of a transversely isotropic shale: thermal expansion and pressurization. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(1):359–375. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02269-y
Braun P, Ghabezloo S, Delage P, Sulem J, Conil N (2021b) Transversely isotropic poroelastic behaviour of the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone: a set of stress-dependent parameters. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54(1):377–396. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02268-z
Bumbieler F, Plúa C, Tourchi S, Vu MN, Vaunat J, Gens A, Armand G (2021) Feasibility of constructing a full-scale radioactive high-level waste disposal cell and characterization of its thermo-hydro-mechanical behavior. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104555
Carneiro F (1943) A new method to determine the tensile strength of concrete. In: Proceedings of the 5th Meeting of the Brazilian Association for Technical Rules, vol 3, pp 126–129
Cheng AHD (1997) Material coefficients of anisotropic poroelasticity. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(2):199–205
Chiarelli AS, Shao JF, Hoteit N (2003) Modeling of elastoplastic damage behavior of a claystone. Int J Plast 19:23–45
Chiu HK, Johnston IW, Donald IB (1983) Appropriate techniques for triaxial testing of saturated soft rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 20(3):107–120. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(83)91301-3
Conil N, Talandier J, Djizanne H, de La Vaissière R, Righini-Waz C, Auvray C, Morlot C, Armand G (2018) How rock samples can be representative of in situ condition: a case study of Callovo-Oxfordian claystones. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 10(4):613–623
Conil N, Vitel M, Plua C, Vu MN, Seyedi D, Armand G (2020) In situ investigation of the thm behavior of the callovo-oxfordian claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53:2747–2769. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-020-02073-8
Coussy O (2004) Poromechanics. Wiley, New York
Coviello A, Lagioia R, Nova R (2005) On the measurement of the tensile strength of soft rocks. Rock Mech Rock Eng 38(4):251–273
Davy CA, Skoczylas F, Barnichon JD, Lebon P (2007) Permeability of macro-cracked argillite under confinement: Gas and water testing. Phys Chem Earth 32(8–14):667–680
Diederichs MS (2007) The 2003 Canadian Geotechnical Colloquium: Mechanistic interpretation and practical application of damage and spalling prediction criteria for deep tunnelling. Can Geotech J 44(9):1082–1116
Eberhardt E (2012) The Hoek-Brown failure criterion. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(6):981–988. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-012-0276-4
Escoffier S (2002) Caractérisation expérimentale du comportement hydroméchanique des argilites de Meuse/Haute-Marne. PhD thesis, Institut National Polytechnique de Lorraine
Escoffier S, Homand F, Giraud A, Hoteit N, Su K (2005) Under stress permeability determination of the Meuse/Haute-Marne mudstone. Eng Geol 81(3):329–340
Ewy RT (2015) Shale/claystone response to air and liquid exposure, and implications for handling, sampling and testing. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 80:388–401
Fairhurst C (1961) Laboratory measurement of some physical properties of rock. In: The 4th US Symposium on Rock Mechanics (USRMS). American Rock Mech Assoc 1:105–118
Fairhurst C (1964) On the validity of the ‘Brazilian’ test for brittle materials. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 1:535–546
Favero V, Ferrari A, Laloui L (2016) Thermo-mechanical volume change behaviour of Opalinus Clay. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 90(November 2015):15–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2016.09.013
Gens A, Vaunat J, Garitte B, Wileveau Y (2007) In situ behaviour of a stiff layered clay subject to thermal loading: observations and interpretation. Géotechnique 57(2):207–228
Ghabezloo S, Sulem J (2009) Stress dependent thermal pressurization of a fluid-saturated rock. Rock Mech Rock Eng 42(1):1–24
Ghabezloo S, Sulem J (2010) Effect of the volume of the drainage system on the measurement of undrained thermo-poro-elastic parameters. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(1):60–68
Griffith A (1924) The theory of rupture. In: Proceedings of the 1st International Congress of applied mechanics, Tech. Boekhandel en Drukkerij J Walter Jr, Delft, pp 55–63
Guayacán-Carrillo LM, Ghabezloo S, Sulem J, Seyedi DM, Armand G (2017) Effect of anisotropy and hydro-mechanical couplings on pore pressure evolution during tunnel excavation in low-permeability ground. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 97:1–14
Hansen FD, Vogt TJ (1987) Thermo mechanical properties of selected shales. Tech. rep., Oak Ridge National Laboratory Report ORNL/Sub/85-97343/2 (RSI-0305)
Hawkes I, Mellor M (1970) Uniaxial testing in rock mechanics laboratories. Eng Geol 4:177–285
Hoek E (1964) Fracture of Anisotropic Rock. J S Afr Inst Min Metall 64(10):501–518
Hoek E (1983) Strength of jointed rock masses. Géotechnique 33(3):187–223
Hoek E (2007) Practical rock engineering. https://www.rocscience.com/assets/resources/learning/hoek/Practical-Rock-Engineering-Full-Text.pdf. Accessed 18 Mar 2022
Hoek E, Brown E (1980) Empirical strength criterion for rock masses. J Geotech Eng Div ASCE 106(GT9):1013–1035
Hoek E, Martin C (2014) Fracture initiation and propagation in intact rock—a review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 6(4):287–300
Hoek E, Kaiser PK, Bawden WF (1995) Support of underground excavations in hard rock. A.A. Balkma, Rotterdam
IAPWS-IF97 (2008) IAPWS Industrial Formulation 1997 for the thermodynamic properties of water and steam. Springer, Berlin
ISRM (1978) Suggested methods for the quantitative description of discontinuities in rock masses. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci Geomech Abstr 15:319–368
Jobmann M, Polster M (2007) The response of opalinus clay due to heating: a combined analysis of in situ measurements, laboratory investigations and numerical calculations. Phys Chem Earth Parts A/B/C 32(8–14):929–936
Li B, Wong RC (2018) Creating tensile fractures in Colorado shale using an unconfined fast heating test. Geotech Test J 42(2):296–306
Mánica MA, Gens A, Vaunat J, Armand G, Vu MN (2021) Numerical simulation of underground excavations in an indurated clay using non-local regularisation. Part 1: formulation and base case. Géotechnique 1–21. https://doi.org/10.1680/jgeot.20.P.246, https://www.icevirtuallibrary.com/doi/10.1680/jgeot.20.P.246
Menaceur H, Delage P, Am Tang, Conil N (2015) The thermo-mechanical behaviour of the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 78:290–303
Menaceur H, Delage P, Tang AM, Conil N (2016) On the thermo-hydro-mechanical behaviour of a sheared Callovo-Oxfordian claystone sample with respect to the EDZ behaviour. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(5):1875–1888
Mohajerani M, Delage P, Sulem J, Monfared M, Tang AM, Gatmiri B (2012) A laboratory investigation of thermally induced pore pressures in the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 52:112–121
Mohajerani M, Delage P, Sulem J, Monfared M, Tang AM, Gatmiri B (2014) The thermal volume changes of the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 47(1):131–142
Mohamadi M, Wan RG (2016) Strength and post-peak response of Colorado shale at high pressure and temperature. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 84:34–46
Monfared M, Delage P, Sulem J, Mohajerani M, Tang AM, De Laure E (2011a) A new hollow cylinder triaxial cell to study the behavior of geo-materials with low permeability. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 48(4):637–649
Monfared M, Sulem J, Delage P, Mohajerani M (2011b) A laboratory investigation on thermal properties of the Opalinus claystone. Rock Mech Rock Eng 44(6):735–747
Palciauskas VV, Domenico PA (1982) Characterization of drained and undrained response of thermally loaded repository rocks. Water Resour Res 18(2):281–290
Pardoen B, Seyedi DM, Collin F (2015) Shear banding modelling in cross-anisotropic rocks. Int J Solids Struct 72:63–87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2015.07.012
Perras MA, Diederichs MS (2014) A review of the tensile strength of rock: concepts and testing. Geotech Geol Eng 32(2):525–546. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-014-9732-0
Pham QT, Vales F, Malinsky L, Minh DN, Gharbi H (2007) Effects of desaturation—resaturation on mudstone. Phys Chem Earth 32:646–655
Plúa C, Vu MN, Armand G, Rutqvist J, Birkholzer J, Xu H, Guo R, Thatcher KE, Bond AE, Wang W, Nagel T, Shao H, Kolditz O (2021a) A reliable numerical analysis for large-scale modelling of a high-level radioactive waste repository in the Callovo-Oxfordian claystone. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2020.104574
Plúa C, Vu MN, Seyedi DM, Armand G (2021b) Effects of inherent spatial variability of rock properties on the thermo-hydro-mechanical responses of a high-level radioactive waste repository. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 145(February):104682. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2021.104682
Robinet JC, Sardini P, Coelho D, Parneix JC, Prt D, Sammartino S, Boller E, Altmann S (2012) Effects of mineral distribution at mesoscopic scale on solute diffusion in a clay-rich rock: Example of the Callovo-Oxfordian mudstone (Bure, France). Water Resour Res. https://doi.org/10.1029/2011WR011352
Seyedi D, Armand G, Conil N, Vitel M, Vu MN (2017) On the thermo-hydro-mechanical pressurization in Callovo-Oxfordian claystone under thermal loading. In: Poromechanics 2017—Proceedings of the 6th Biot Conference on Poromechanics 1:754–761
Sultan N, Delage P, Cui Y (2002) Temperature effects on the volume change behaviour of boom clay. Eng Geol 64(2–3):135–145
Tourchi S, Vaunat J, Gens A, Bumbieler F, Vu MN, Armand G (2021) A full-scale in situ heating test in Callovo-Oxfordian claystone: observations, analysis and interpretation. Comput Geotech 13:3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2021.104045
Valès F, Nguyen Minh D, Gharbi H, Rejeb A (2004) Experimental study of the influence of the degree of saturation on physical and mechanical properties in Tournemire shale (France). Appl Clay Sci 26:197–207. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.12.032
Vu MN, Armand G, Plua C (2020) Thermal pressurization coefficient of anisotropic elastic porous media. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(4):2027–2031. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02021-1
Wild KM, Walter P, Amann F (2017) The response of Opalinus Clay when exposed to cyclic relative humidity variations. Solid Earth 8(2):351–360. https://doi.org/10.5194/se-8-351-2017
Wileveau Y, Cornet FH, Desroches J, Blumling P (2007) Complete in situ stress determination in an argillite sedimentary formation. Phys Chem Earth 32(8–14):866–878
Yang MT, Hsieh HY (1997) Direct tensile behavior of a transversely isotropic rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 34(5):837–849
Zhang C, Rothfuchs T (2004) Experimental study of the hydro-mechanical behaviour of the Callovo-Oxfordian argillite. Appl Clay Sci 26(1–4):325–336. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2003.12.025
Zhang F, Xie SY, Hu DW, Shao JF, Gatmiri B (2012) Effect of water content and structural anisotropy on mechanical property of claystone. Appl Clay Sci 69:79–86
Zhang CL, Conil N, Armand G (2017) Thermal effects on clay rocks for deep disposal of high-level radioactive waste. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 9(3):463–478
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Braun, P., Delage, P., Ghabezloo, S. et al. Inducing Tensile Failure of Claystone Through Thermal Pressurization in a Novel Triaxial Device. Rock Mech Rock Eng 55, 3881–3899 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02838-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-022-02838-3