Abstract
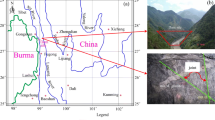
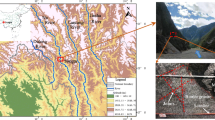
This study takes the rock masses in the dam foundation of a sluice gate of the Datengxia Hydropower Station in China as a case study to determine the geometrical and mechanical representative volume elements (RVEs) considering the special natures of rock masses (inhomogeneity and anisotropy). 3D fracture networks are generated on the basis of fracture data in the field and then used in this study for RVE determination. The representative parameters for RVE determination are selected and presented first. Through the comparison and analysis of the RVEs in different regions and directions, it is discovered that the inhomogeneity and anisotropy of the rock result in the spatial effect and directional effect in the RVE size, respectively. Therefore, the traditional method of RVE determination needs to be improved. Subsequently, on the basis of the sampling methods considering the special natures, the special natures of the geometrical and mechanical parameters are studied in detail and fully considered to improve the accuracy of the RVE results. Finally, the geometrical RVE size (10 m) and mechanical RVE size (18 m) are determined with the coefficient of variation. Moreover, the relationship between the geometrical and mechanical RVE sizes is also established.




















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- r :
-
Fracture disc diameter
- L :
-
The height of 3D space that accommodates the fractures
- θ :
-
The intersection angle between the fracture set and the outcrop surface
- α :
-
The average intersection angle between the fractures and the outcrop surface
- p n :
-
The frequency of fractures in the equal-area Schmidt projection diagram
- N α :
-
The number of fractures with an intersection angle of α in the outcrop surface
- P α :
-
The corrected fracture frequency with an intersection angle of α in 3D space
- L min :
-
The minimum side length of the model
- \({n}_{ab}\) :
-
The number of fractures with radii between a and b in the outcrop surface
- \({n}_{ab}^{\text{'}}\) :
-
The number of fractures with radii between a and b in 3D space
- RES:
-
The number of particles within the minimum side length of the model
References
Abrah B, Karami M, Faramarzi L (2011) Importance of anisotropy in dam foundation, estimated by in-situ dilatometer tests. In: Proceedings of the 12th ISRM international congress on rock mechanics, Beijing, China 1857–1860. https://doi.org/10.1201/b11646-352
Bahaaddini M (2017) Effect of boundary condition on the shear behaviour of rock joints in the direct shear test. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(5):1141–1155. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1157-z
Bahaaddini M, Sharrock G, Hebblewhite BK (2013) Numerical direct shear tests to model the shear behaviour of rock joints. Comput Geotech 51:101–115. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.02.003
Bear J (1972) Dynamics of fluids in porous media. American Elsevier, New York
Billaux D, Chiles JP, Hestir K, Long J (1989) Three-dimensional statistical modelling of a fractured rock mass-an example from the Fanay-Augères mine. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 26(3–4):281–299. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(89)91977-3
Bryant FB, Satorra A (2012) Principles and practice of scaled difference chi-square testing. Struct Equ Model 19(3):372–398. https://doi.org/10.1080/10705511.2012.687671
Cao RH, Cao P, Fan X, Xiong XG, Lin H (2016a) An experimental and numerical study on mechanical behavior of ubiquitous-joint brittle rock-like specimens under uniaxial compression. Rock Mech Rock Eng 11(49):4319–4338. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1029-6
Cao RH, Cao P, Lin H, Pu CZ, Ou K (2016b) Mechanical behavior of brittle rock-like specimens with pre-existing fissures under uniaxial loading: experimental studies and particle mechanics approach. Rock Mech Rock Eng 49(3):763–783. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-015-0779-x
Castelli M, Saetta V, Scavia C (2003) Numerical study of scale effects on the stiffness modulus of rock masses. Int J Geomech 3(2):160–169. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)1532-3641(2003)3:2(160)
Chen DH, Chen HE, Zhang W, Tan C, Ma ZF, Chen JP, Shan B (2020) Buckling failure mechanism of a rock dam foundation fractured by gentle through-going and steep structural discontinuities. Sustainability 12(13):5426. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12135426
Cheng C, Chen X, Zhang SF (2016) Multi-peak deformation behavior of jointed rock mass under uniaxial compression: insight from particle flow modeling. Eng Geol 213:25–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.08.010
Cundall PA, Potyondy DO (2004) A bonded-particle model for rock. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 41(8):1329–1364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2004.09.011
Deisman N, Ivars DM, Pierce M (2008) PFC2D Smooth joint contact model numerical experiments. In: Proceedings of GeoEdmonton’08, Edmonton, Canada 83–87
Esmaieli K, Hadjigeorgiou J, Grenon M (2010) Estimating geometrical and mechanical REV based on synthetic rock mass models at Brunswick Mine. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 47(6):915–926. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2010.05.010
Fereshtenejad S, Afshari MK, Bafghi AY, Laderian A, Safaei H, Song JJ (2016) A discrete fracture network model for geometrical modeling of cylindrically folded rock layers. Eng Geol 215:81–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2016.11.004
Guo SF, Qi SW, Zhan ZF, Ma L, Gure EG, Zhang SS (2020) Numerical study on the progressive failure of heterogeneous geomaterials under varied confining stresses. Eng Geol 269:105556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105556
Harrison J, Hudson J, Popescu M (2002) Engineering rock mechanics: Part 2. illustrative worked examples. Appl Mech Rev 55(2): B30–B31. https://doi.org/10.1115/1.1451166
Il’Chenko VL, Gannibal MA (2019) Elastic anisotropy and internal structure of rocks from the uranium ore occurrences of the Litsa Ore Area (Kola Region, Russia). Geosciences 9(7):284. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences9070284
Ivars DM, Pierce M, DeGagnè D, Darcel C (2008) Anisotropy and scale dependency in jointed rock-mass strength—A synthetic rock mass study. In: Proceedings of the 1st international FLAC/DEM symposium on numerical modeling, Minneapolis, USA 231–239.
Koyama T, Jing L (2007) Effects of model scale and particle size on micro-mechanical properties and failure processes of rocks—a particle mechanics approach. Eng Anal Bound Elem 31(5):458–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enganabound.2006.11.009
Kulatilake PHSW (1985) Estimating elastic constants and strength of discontinuous rock. J Geotech Eng 111(7):847–864. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9410(1985)111:7(847)
Kulatilake PHSW, Wu TH (1984) Estimation of mean trace length of discontinuities. Rock Mech Rock Eng 17(4):215–232. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01032335
Lee H, Jeon S (2011) An experimental and numerical study of fracture coalescence in pre-cracked specimens under uniaxial compression. Int J Solids Struct 48(6):979–999. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2010.12.001
Lee DT, Schachter BJ (1980) Two algorithms for constructing a Delaunay triangulation. Int J Parallel Prog 9(3):219–242. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00977785
Li YY, Chen JP, Shang YJ (2017) Determination of the geometrical REV based on fracture connectivity: a case study of an underground excavation at the Songta dam site. China B Eng Geol Environ 77(4):1599–1606. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-017-1063-y
Li KQ, Li DQ, Liu Y (2020) Meso-scale investigations on the effective thermal conductivity of multi-phase materials using the finite element method. Int J Heat Mass Tran 151:119383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijheatmasstransfer.2020.119383
Liu Y, Wang Q, Chen JP, Song SY, Zhan JW, Han XD (2018) Determination of geometrical REVs based on volumetric fracture intensity and statistical tests. Appl Sci 8(5):800. https://doi.org/10.3390/app8050800
Min KB, Jing L (2003) Numerical determination of the equivalent elastic compliance tensor for fractured rock masses using the distinct element method. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 40(6):795–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(03)00038-8
Mitchell DW (2009) 93.10 A heron-type area formula in terms of sines. Math Gaz 93(526):108–109. https://doi.org/10.1017/S002555720018430X
Ni PP, Wang SH, Wang CG, Zhang SM (2016) Estimation of REV size for fractured rock mass based on damage coefficient. Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(3):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-016-1122-x
Nie ZB, Chen JP, Zhang W, Tan C, Ma ZF, Wang FY, Zhang Y, Que JS (2019) A new method for three-dimensional fracture network modelling for trace data collected in a large sampling window. Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(3):1145–1161. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-01969-4
Piggott AR, Elsworth D (1989) Physical and numerical studies of a fracture system model. Water Resour Res 25(3):457–462. https://doi.org/10.1029/WR025i003p00457
Pinto A, Da CH (1993) Scale effects in rock mechanics. A. A. Balkema Publishers, Rotterdam
Shanley RJ, Mahtab MA (1976) Delineation and analysis of clusters in orientation data. Math Geol 8(1):9–23. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01039681
Song SY, Sun FY, Chen JP, Zhang W, Han XD, Zhang XD (2017) Determination of RVE size based on the 3D fracture persistence. Q J Eng Geol Hydroge 50(1):60–68. https://doi.org/10.1144/qjegh2016-127
Terzaghi RD (1965) Sources of error in joint surveys. Geotechnique 15(3):287–304. https://doi.org/10.1680/geot.1965.15.3.287
Wu Q, Kulatilake PHSW (2012) REV and its properties on fracture system and mechanical properties, and an orthotropic constitutive model for a jointed rock mass in a dam site in China. Comput Geotech 43:124–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2012.02.010
Wu FQ, Deng Y, Wu J, Li B, Sha P, Guan SG, Zhang K, He KQ, Liu HD, Qiu SH (2020) Stress-strain relationship in elastic stage of fractured rock mass. Eng Geol 268:105498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105498
Xu L, Ren Q W (2015) Shear failure mechanism of infilling rock joints and its PFC simulation. Appl Mech Mater 723:317–321. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.723.317
Xu L, Ren QW (2015) Particle flow simulation of direct shear test of rock discontinuities. Adv Mat Res 1065–1069:159–163. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.1065-1069(159-163)
Yang BD, Jiao Y, Lei ST (2006) A study on the effects of microparameters on macroproperties for specimens created by bonded particles. Eng Computation 23(6):607–631. https://doi.org/10.1108/02644400610680333
Yang SQ, Huang YH, Jing HW, Liu XR (2014) Discrete element modeling on fracture coalescence behavior of red sandstone containing two unparallel fissures under uniaxial compression. Eng Geol 178:28–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2014.06.005
Yao W, Cai YY, Yu J, Zhou JF, Liu SY, Tu BX (2019) Experimental and numerical study on mechanical and cracking behaviors of flawed granite under triaxial compression. Measurement 145:573–582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.measurement.2019.03.035
Yong R, Ye J, Li B, Du SG (2018) Determining the maximum sampling interval in rock joint roughness measurements using Fourier series. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 101:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2017.11.008
Yoon J (2007) Application of experimental design and optimization to PFC model calibration in uniaxial compression simulation. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 44(6):871–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2007.01.004
Zhang LY, Einstein HH (2000) Estimating the intensity of rock discontinuities. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 37(5):819–837. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1365-1609(00)00022-8
Zhang W, Chen JP, Liu C, Huang R, Li M, Zhang Y (2012) Determination of geometrical and structural representative volume elements at the Baihetan dam site. Rock Mech Rock Eng 45(3):409–419. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-011-0191-0
Zhang W, Chen JP, Cao ZX, Wang RY (2013a) Size effect of RQD and generalized representative volume elements: a case study on an underground excavation in Baihetan dam, Southwest China. Tunn Undergr Sp Tech 35:89–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tust.2012.12.007
Zhang W, Chen JP, Chen HE, Xu DZ, Li Y (2013b) Determination of RVE with consideration of the spatial effect. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 61(7):154–160. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2013.02.013
Zhang XP, Jiang YJ, Wang G, Wu XZ, Zhang YZ (2016) Numerical experiments on rate-dependent behaviors of granite based on particle discrete element model. Rock Soil Mech 37(9):2679–2686. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2016.09.033
Zhang W, Zhao QH, Huang RQ, Ma DH, Chen JP, Xu PH, Que JS (2017a) Determination of representative volume element considering the probability that a sample can represent the investigated rock mass at Baihetan dam site. China Rock Mech Rock Eng 50(10):2817–2825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-017-1248-5
Zhang YZ, Wang G, Jiang YJ, Wang SG, Zhao HH, Jing WJ (2017b) Acoustic emission characteristics and failure mechanism of fractured rock under different loading rates. Shock Vib 2017:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5387459
Zhang W, Fu R, Tan C, Ma ZF, Zhang Y, Song SY, Xu PH, Wang SN, Zhao YP (2020a) Two-dimensional discrepancies in fracture geometric factors and connectivity between field-collected and stochastically modeled DFNs: A case study of sluice foundation rock mass in Datengxia. China Rock Mech Rock Eng 53(5):2399–2417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-019-02029-7
Zhang W, Lan ZG, Ma ZF, Tan C, Que JS, Wang FY, Cao C (2020b) Determination of statistical discontinuity persistence for a rock mass characterized by non-persistent fractures. Int J Rock Mech Min Sci 126:104177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijrmms.2019.104177
Zhou Y, Wu SC, Jiao JJ, Zhang XP (2011) Research on mesomechanical parameters of rock and soil mass based on BP neural network. Rock Soil Mech 32(12):3821–3826. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLU.0b013e3181f49ac7
Acknowledgements
This work was financially supported by the National Key Research and Development program of China [grant number: 2019YFA0705504] and the National Nature Science Foundation of China [grant numbers: 42022053; 41877220; U1702241; 41702301].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ma, W., Chen, H., Zhang, W. et al. Study on Representative Volume Elements Considering Inhomogeneity and Anisotropy of Rock Masses Characterised by Non-persistent Fractures. Rock Mech Rock Eng 54, 4617–4637 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02546-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-021-02546-4